Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
CDO
|
|
|
|
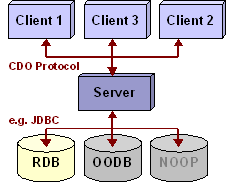
CDO is both a development-time model repository and a run-time persistence framework. Being highly optimized it supports object graphs of arbitrary size. CDO offers transactions with save points, explicit locking, change notification, queries, temporality, branching, merging, offline and fail-over modes, ... The storage back-end is pluggable and migrations between direct JDBC, Hibernate, Objectivity/DB, MongoDB or DB4O are seamless for CDO applications. You may also want to visit our homepage. |
Model Integration Features
- EMF integration at model level (as opposed to the edit level)
- Supported model types:
- Generated models (just switch two .genmodel properties)
- Dynamic models (just load .ecore file and commit to repository)
- Legacy models (for compiled models without access to .genmodel)
- Ecore meta meta model and descendants
User Interface Features
- Eclipse view for working with CDO sessions, transactions, views and resources
- Package Manager dialog per session
- Eclipse editor for working with resources and objects
- CDO Explorer
Client Side Features
- Multiple sessions to multiple repositories on multiple servers
- Multiple transactions per session
- Multiple read-only views per session
- Multiple audit views per session (an audit is a view that shows a consistent, historical version of a repository)
- Multiple resources per view (a view is always associated with its own EMF ResourceSet)
- Inter-resource proxy resolution
- Multiple root objects per resource
- Object state shared among all views of a session
- Object graph internally unconnected (unused parts of the graph can easily be reclaimed by the garbage collector)
- Only new and modified objects committed in a transaction
- Transactions can span multiple resources
- Demand loading of objects (resources are populated as they are navigated)
- Partial loading of collections (chunk size can be configured per session)
- Adaptable pre-fetching of objects (different intelligent usage analyzers are available)
- Asynchronous object invalidation (optional)
- Clean API to work with sessions, views, transactions and objects
- CDOResources are EObjects as well
- Objects carry meta information like id, state, version and life span
- Support for OSGi environments (headless, Eclipse RCP, ...)
- Support for standalone applications (non-OSGi)
Network Protocol Features
- Net4j based binary application protocol
- Pluggable transport layer (shipped with NIO socket transport, polling HTTP and JVM embedded transport)
- Pluggable fail over support
- Pluggable authentication (shipped with challenge/response negotiation)
- Multiple acceptors per server
Server Side Features
- Pluggable storage adapters
- See DB Store Features
- See Hibernate Store Features
- See Store Feature Matrix
- Objectivity support coming soon
- Native memory storage adapter
- Multiple repositories per server
- Multiple models (packages) per repository
- Multiple resources (instance documents) per repository
- Expressive XML configuration file
- Configurable storage adapter per repository (see below)
- Configurable caching per repository
- Clean API to work with repositories, sessions, views, transactions and revisions
- Support for OSGi environments (usually headless)
- Support for standalone applications (non-OSGi)
