Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
STP Service Creation User Guide
Contents
- 1 Installation
- 2 Creating service component
- 2.1 Creating JAX-WS component
- 2.1.1 Concepts
- 2.1.2 Tasks
- 2.1.2.1 Overview
- 2.1.2.2 Choosing a JAX-WS runtime
- 2.1.2.3 Setting annotation preferences
- 2.1.2.4 Setting the SOAP version
- 2.1.2.5 Enabling JAX-WS in an existing project
- 2.1.2.6 Creating a JAX-WS Java First project
- 2.1.2.7 Creating a JAX-WS WSDL First project
- 2.1.2.8 Annotating a class
- 2.1.2.9 Annotating a method
- 2.1.2.10 Generating stub code
- 2.1.2.11 Adding JAX-WS handler
- 2.1.2.12 Using the annotation property view
- 2.1.2.13 Annotation validation
- 2.1.2.14 Editing the wsdl document
- 2.2 Creating RESTful service (TBD)
- 2.3 Creating JBI component (TBD)
- 2.4 Creating SCA component (TBD)
- 2.5 Creating simple frontend for Apache CXF
- 2.1 Creating JAX-WS component
- 3 Packaging and deploying service component
- 4 Testing and debugging your component
- 5 Example
- 5.1 Choosing a JAX-WS runtime
- 5.2 Beginning from creating an empty java project
- 5.3 Developing a java interface
- 5.4 Enabling JAX-WS
- 5.5 Annotating web method
- 5.6 Generating WSDL
- 5.7 Generating stub code
- 5.8 Adding implementation code to your web service
- 5.9 Running the stand-alone web server and test
- 5.10 Deploying and testing on Apache Tomcat
- 6 Reference
- 7 Reporting bug/Getting help
Installation
Installing from update site
This kind of installation downloads STP plugins, and plugins required from other Eclipse projects automatically.
Downloading from STP website
The latest STP 0.7.0 build can be downloaded from here
Plugins required from other Eclipse projects
*emf-sdo-xsd-SDK-2.3.0 *GEF-ALL-3.3 *JEM-SDK-1.2.3_jem *wtp-sdk-S-2.0 *GMF-sdk-2.0 *mdt-ocl-SDK-1.1 *emf-validation-SDK-1.1 *emf-query-SDK-1.1 *emf-transaction-SDK-1.1 *javax.wsdl 1.5.1
Installing to eclipse
Extract all required plugins to the STP Installation directory
Downloading runtime
Select one of the following as Pre-requisite SOA runtime:
- JAX-WS runtime: Apache CXF 2.1 SNAPSHOT, or Sun JAX-WS RI
- SCA runtime: Apache Tuscany SCA Java 1.0
- Apache Tomcat (Install only if you want to deploy the generated service to Tomcat Container)
In order to deploy JAX-WS service to Tomcat container, please copy all jars under ${apache_cxf_install}/libs and ${apache_cxf_install}/modules into ${tomcat_install}/shared/lib
Creating service component
Creating JAX-WS component
Concepts
JAX-WS
The Java API for XML Web Services (JAX-WS) specification defines a set of APIs and annotations for developing Web services. It makes extensive use of the annotations introduced in Java 5.0. These annotations make it easier to map a Java object to a service and map a WSDL contract to a Java object.
Related information
Annotations
Annotations are a way of adding metadata to Java source code that is available to the programmer at runtime.
They play a critical role in JAX-WS, where they are used to map Java to WSDL and XML Schema, and to control how the JAX-WS runtime processes and responds to web service invocations.
When you create a JAX-WS Java First project, you need to add JAX-WS annotations to your starting point code, in order to have Eclipse automatically generate the required WSDL and stub code for your web service.
You can add annotations to types, methods, and parameters. Each method that is public within the Java class must include a @WebRequest annotation, while each types requires a @WebService annotation.
You can add annotations to your Java code using the JAX-WS menu and further refine your annotations in the Annotation Properties view.
When you create a WSDL First project, annotated code is generated for you automatically.
Related information
JAX-WS Annotations specification
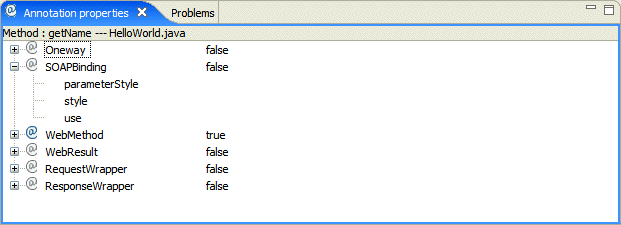
Annotation Properties view
The Annotation Properties view allows you to edit the JAX-WS annotations in your Java code.
To open the Annotation Properties view, select Window > Show View > Other ... > SOA Tools > Annotation Properties.
As you move through the types, methods, and parameters in your Java code in either the Editor view or the Package Explorer, the Annotation Properties view changes to display the annotations that are possible for a particular element.
To add an annotation, select true in the Value column.
Click the + icon next to the annotation to display the attributes associated with it.
Supported annotations
The following annotations are supported in the Eclipse STP Annotation Properties editor:
JSR 181
javax.jws.WebService
javax.jws.WebMethod
javax.jws.Oneway
javax.jws.WebParam
javax.jws.WebResult
javax.jws.HandlerChain
javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding
javax.jws.soap.SOAPMessageHandlers
JAX-WS 2.0
javax.xml.ws.ServiceMode
javax.xml.ws.WebFault
javax.xml.ws.RequestWrapper
javax.xml.ws.ResponseWrapper
javax.xml.ws.WebServiceClient
javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint
javax.xml.ws.WebServiceProvider
javax.xml.ws.BindingType
javax.xml.ws.WebServiceRef
javax.xml.ws.WebServiceRefs
SCA 0.95
org.osoa.sca.annotations.AnnotationSupport
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Callback
org.osoa.sca.annotations.ComponentName
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Constructor
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Context
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Destroy
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Init
org.osoa.sca.annotations.OneWay
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Property
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Reference
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Remotable
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Scope
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Service
org.osoa.sca.annotations.Session
org.osoa.sca.annotations.SessionID
Apache Tuscany 1.0
org.apache.tuscany.api.annotation.DataType
org.apache.tuscany.api.annotation.DataContext
org.apache.tuscany.api.annotation.LogLevel
org.apache.tuscany.api.annotation.Monitor
Handler
Handlers are interceptors that can be easily plugged into the Java API for XML-Based Web Services (JAX-WS) 2.0 runtime environment to do additional processing of inbound and outbound messages. JAX-WS defines two types of handlers: protocol handlers and logical handlers. Protocol handlers are specific to a protocol such as SOAP. They can access or change any part of the message, including protocol-specific parts such as the message header. Logical handlers are protocol-agnostic. They cannot change any protocol-specific parts of a message. Logical handlers act only on the payload of the message.
So far, STP support logical handler and one kind of protocol handler(SOAP Handler).
Tasks
Overview
Creating and deploying a JAX-WS service using Eclipse STP involves the following steps:
2.Do one of the following:
- Create a Java First project, add annotations to the code, and then generate stub code.
- Create a WSDL First project. Annotated stub code is generated for you automatically.
3.Update the generated stub code as required and rebuild your project.
4.Generate a deployment archive.
Choosing a JAX-WS runtime
Before you can create a JAX-WS Web service in STP, you need to point Eclipse at a JAX-WS runtime installed on your machine.
STP supports the following JAX-WS runtimes:
- Apache Incubator CXF, which also ships as the IONA FUSE Services Framework product
- JAX-WS Reference Implementation (JAX-WS RI)
To choose a runtime:
1.Select Window > Preferences from the menu bar.
2.Select SOA Tools > Installed Runtimes.
3.In the Installed Server Runtime Environments preferences panel, click Add.
4.In the New Server runtime wizard, do one of the following:
- Expand the Apache folder and select Apache CXF 2.0
- Expand the Sun folder and select Sun JAX-WS RI 2.1.2
5.Click Next...
6.In the New ... Runtime panel, click Browse to select the directory where your JAX-WS runtime is installed.
7.Choose an alternative JRE, if required.
8.Click Finish.
Setting annotation preferences
When creating a JAX-WS web service in Eclipse, you need to add annotations to your Java code. These annotations are used to automatically generate the necessary WSDL and stub code for your service.
You can choose to:
- Have Eclipse generate annotations with default values without running the Annotations wizard
- Run the Annotations wizard and choose from the full range of JAX-WS annotations
To configure how annotations are generated:
1.Select Window > Preferences from the menu bar.
2.Select SOA Tools > JAX-WS.
3.In the Annotation Wizards section of the JAX-WS panel, choose to either overwrite or use default annotation values.
Setting the SOAP version
When generating WSDL in a JAX-WS project, you can use either SOAP 1.1 or SOAP 1.2.
To choose the version of SOAP that you want:
1.Select Window > Preferences from the menu bar.
2.In the Preferences window, select SOA Tools > JAX-WS.
3.Select either Apache CXF or JAX-WS RI, depending on which runtime you are using.
4.In the WSDL Generation Options section, select either SOAP 1.1 or SOAP 1.2.
Enabling JAX-WS in an existing project
Enabling JAX-WS adds the required builders, natures and classpath entries to a project.
To enable JAX-WS in an existing Java or Web project:
1.Select the project in the Package Explorer.
2.Choose JAX-WS > Enable JAX-WS from the menu bar.
Once you have a JAX-WS project you need to add annotations to your classes and methods.
Creating a JAX-WS Java First project
To create a JAX-WS Java First project:
1.Select File > New > Project .
2.In the New Project wizard, select SOA Tools > JAX-WS Java First Project.
3.Enter the project name in the General Details panel and click Next.
4.Select the runtime that you want to use and click Finish.
5.If prompted, click Yes to switch to the JAX-WS perspective.
An empty Eclipse project containing the JAX-WS project nature is added to your workspace. From here you can create a Java interface class and add JAX-WS annotations to it.
Related tasks
Creating a JAX-WS WSDL First project
To create a JAX-WS WSDL First project:
1.Select File > New > Project.
2.In the New Project wizard, select SOA Tools > JAX-WS WSDL First Project.
3.Enter the project name in the General Details panel and click Next.
4.Select the runtime that you want to use and click Next.
5.In the WSDL Location section, either click Browse to select a WSDL file from your file system. Alternatively, select URL, enter a URL to an external WSDL file, and click Connect to import the WSDL into the wizard.
6.Do one of the following:
- Clear the Generate Code Automatically check box and click Finish. Proceed to the final step.
- Select the Generate Code Automatically check box and click Next.
7.Select the type of artifact you want to generate - service implementation, server mainline, or client - and click Next.
8.If prompted, click Yes to switch to the JAX-WS perspective.
Annotating a class
To add a @WebService annotation to a class:
1.In the Package Explorer, expand the package and then the Java file where the class is located.
2.Select the class.
3.Select JAX-WS > Create Web Service from the menu bar.
- If you selected the Generate default annotations ... option in JAX-WS Preferences, the @Webservice annotation will be added to the code with default values
- If you selected Use wizards to overwrite defaults in JAX-WS Preferences, the Create Web Service wizard displays. Complete the fields in the wizard and click Finish.
Once you save the annotated Java class, a WSDL file is automatically generated and added to a wsdl directory in your project. Your project will also be JAX-WS enabled.
Annotating a method
To add annotations to a method:
1.In the Package Explorer, expand the package, Java file, and class where the method is located.
2.Select the method.
3.Select JAX-WS > Create Web Method from the menu bar.
- If you selected the Generate default annotations ... option in JAX-WS Preferences, the @Webmethod, @ResponseWrapper, and @RequestWrapper annotations are added to the code with default values
- If you selected Use wizards to overwrite defaults in JAX-WS Preferences, the Create Web Method wizard displays. The wizard enables you to edit the default values for the the @Webmethod, @ResponseWrapper, and @RequestWrapper annotations, and to add a @WebResult annotation if you wish. Step through in the wizard and click Finish.
Generating stub code
You can use Eclipse STP to generate stub code for your Web service.
Note: You can only use one generation type per project.
To generate code:
1.Right-click the root of your project.
2.Select JAX-WS Tools > Generate Code from the context menu.
3.In the CXF Java2ws Generator Parameter Page,
- Select WSDL version, SOAP 1.1 or SOAP 1.2,
- Select any combination of WSDL, Server or Client.
4.Click Finish.
Adding JAX-WS handler
To add a JAX-WS handler to web service:
1.In the Package Explorer, expand the package and then the Java file where the class is located.
2.Select the class.
3.Select JAX-WS > Create JAX-WS Handler from the menu bar.
4.Specify name.
5.Select Handler Type, Logical Handler or SOAP Handler
6.Specify the path for handler chain in two ways:
- by clicking Create button
- by adding this handler to an existing handler chain file.
7.Click Finish.
Using the annotation property view
Annotation validation
Editing the wsdl document
Double click a wsdl file from the navigator tree, you will open wsdl editor. Switch to Design Tab, you can right click to add operation or message part or Fault to wsdl file, or edit name/message part by double-clicking. In outline view, you can navigate the wsdl document tree and add/delete elements.
Creating RESTful service (TBD)
Creating JBI component (TBD)
Creating SCA component (TBD)
Creating simple frontend for Apache CXF
Packaging and deploying service component
Generating a deployment package
To create a deployment package for a Web service:
1.Right-click the WSDL file.
2.Select Build Package from the context menu.
A .war file is generated under the following path in your project folder:
Deployment/wsdl/WsdlFilename/Tomcat container deployer
Deploying component
Deploying a JAX-WS service
Once you have created a deployment package, you can deploy it to an application server or container. Eclipse STP currently supports deployment to Apache Tomcat.
To deploy a service to Tomcat:
1.Under your project folder, go to the folder Deployment/wsdl/WsdlFilename/Tomcat container deployer
2.Right-click the .war file and select Deploy.
3.In the Select Target Server dialog, expand the Tomcat folder and select your Tomcat server.
Undeploying component
Undeploying a JAX-WS service
To undeploy a service to Tomcat:
1.Under your project folder, go to the folder Deployment/wsdl/WsdlFilename/Tomcat container deployer
2.Right-click the .war file and select Undeploy.
3.In the Select Target Server dialog, expand the Tomcat folder and select your Tomcat server.
Testing and debugging your component
Creating a test client
Using REST test client (TBD)
Debugging your application
Example
Choosing a JAX-WS runtime
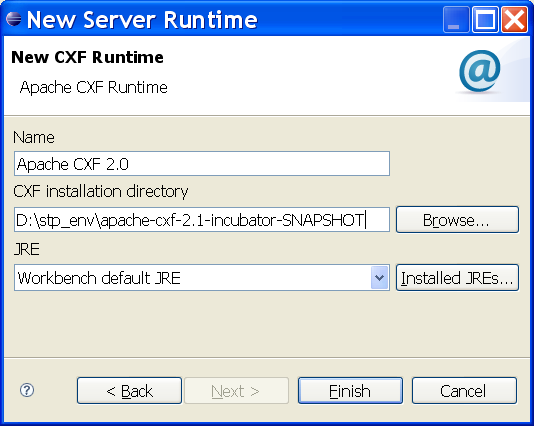
Refer to here, and choose Apache CXF 2.0 as runtime
The configure for Apache CXF 2.0 is as following figure.
Figure - Config Apache CXF 2.0 runtime
Beginning from creating an empty java project
Create an empty java project, named QuickStartProject
Developing a java interface
Create a java interface, Hello.java with package com.iona as following:
Listing - Creating simple java interface
package com.iona;
public interface Hello {
public String sayHi();
}
Enabling JAX-WS
To enable JAX-WS:
1.Select the root of QuickStartProject in the Package Explorer.
2.Right click, and choose JAX-WS Tools > Enable JAX-WS.
3.Choose Java First Programming Mode, click OK.
4.Choose Apache CXF 2.0 runtime, click Next.
5.Click Browse to choose src\com.iona\Hello.java as Java Source File
6.Click Finish
Then the following stuffs will be added automatically.
1. Add Apache CXF 2.0 Library to project classpath
2. Add several natures into .project:
Listing - Auto-added stp natures
org.eclipse.stp.sc.jaxws.javaFirstNature org.eclipse.stp.sc.cxf.natures.cxfNature org.eclipse.stp.sc.jaxws.nature
3. Insert @WebService annotation into java interface
Listing - Annotating the Java interface as a Web service
package com.iona; import javax.jws.WebService; @WebService(name="Hello", targetNamespace="http://iona.com/") public interface Hello { public String sayHi(); }
Annotating web method
To annotate web method:
1.Right click Hello.java, and choose JAX-WS Tools > Create Web Method
2.Choose Available Methods sayHi()
3.Click Finish
Listing - Annotations created using create Web method
package com.iona; import javax.jws.WebService; import javax.xml.ws.RequestWrapper; import javax.xml.ws.ResponseWrapper; import javax.jws.WebMethod; @WebService(name="Hello", targetNamespace="http://iona.com/") public interface Hello { @WebMethod(operationName="sayHi", exclude=false) @ResponseWrapper(className="com.iona.SayHiResponse", localName="sayHiResponse", targetNamespace="http://iona.com/") @RequestWrapper(className="com.iona.SayHi", localName="sayHi", targetNamespace="http://iona.com/") public String sayHi(); }
Generating WSDL
To generate your stub code:
1.Right-click on the root of QuickStartProject.
2.Select JAX-WS Tools > Generate WSDL from the context menu.
Double click wsdl\QuickStartProject.wsdl in Package Explorer view, you will see the following auto-generated WSDL:
Listing - Auto-generated WSDL
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <wsdl:definitions name="HelloService" targetNamespace="http://iona.com/" xmlns:tns="http://iona.com/" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"> <wsdl:types> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:tns="http://iona.com/" attributeFormDefault="unqualified" elementFormDefault="unqualified" targetNamespace="http://iona.com/"> <xsd:element name="sayHi" type="tns:sayHi"/> <xsd:complexType name="sayHi"> <xsd:sequence/> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:element name="sayHiResponse" type="tns:sayHiResponse"/> <xsd:complexType name="sayHiResponse"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element minOccurs="0" name="return" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema> </wsdl:types> <wsdl:message name="sayHi"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="tns:sayHi"> </wsdl:part> </wsdl:message> <wsdl:message name="sayHiResponse"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="tns:sayHiResponse"> </wsdl:part> </wsdl:message> <wsdl:portType name="Hello"> <wsdl:operation name="sayHi"> <wsdl:input name="sayHi" message="tns:sayHi"> </wsdl:input> <wsdl:output name="sayHiResponse" message="tns:sayHiResponse"> </wsdl:output> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:portType> <wsdl:binding name="HelloServiceSoapBinding" type="tns:Hello"> <soap:binding style="document" transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"/> <wsdl:operation name="sayHi"> <soap:operation soapAction="" style="document"/> <wsdl:input name="sayHi"> <soap:body use="literal"/> </wsdl:input> <wsdl:output name="sayHiResponse"> <soap:body use="literal"/> </wsdl:output> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:binding> <wsdl:service name="HelloService"> <wsdl:port name="HelloPort" binding="tns:HelloServiceSoapBinding"> <soap:address location="http://localhost:9090/hello"/> </wsdl:port> </wsdl:service> </wsdl:definitions>
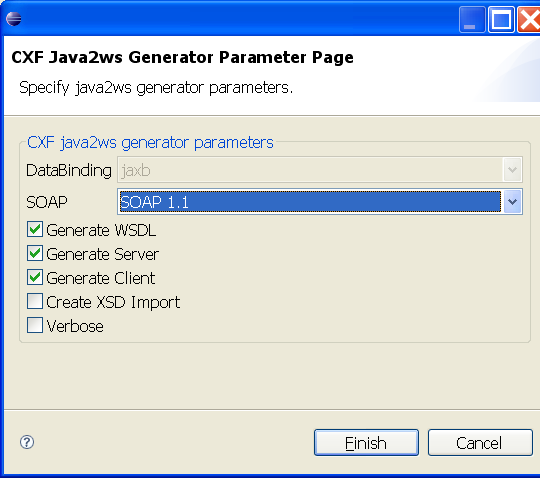
Generating stub code
To generate your stub code:
1.Right-click on the root of QuickStartProject.
2.Select JAX-WS Tools > Generate Code from the context menu.
3.In the CXF Java2ws Generator Parameter Page, select a combination of Generate WSDL, Generate Server or Generate Client, and soap 1.1.
4.Click Finish
Figure - choose parameters for code generating
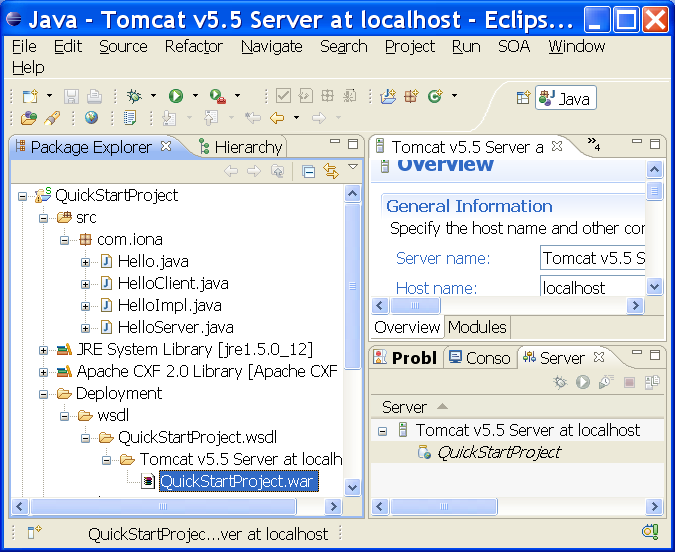
You should now see several new files created in the Navigator view, as shown in Figure Results of generating code
Figure - Results of generating code
Adding implementation code to your web service
Modify HelloImpl.java
Listing - Modified implementation
try {
java.lang.String _return = "STP";
return _return;
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
Modify HelloClient.java
Listing - Modified client
QName serviceName = new QName("http://iona.com/", "HelloService");
QName portName = new QName("http://iona.com/", "HelloPort");
Service service = Service.create(serviceName);
service.addPort(portName, SOAPBinding.SOAP11HTTP_BINDING,
"http://localhost:9090/hello");
com.iona.Hello client = service.getPort(portName, com.iona.Hello.class);
System.out.println("Invoking sayHi...");
String ret = client.sayHi();
System.out.println("Result: " + ret);
Running the stand-alone web server and test
Running the stand-alone web server
The development framework comes with a stand-alone Web server, which allows you to perform testing of your Web service within the Eclipse framework.
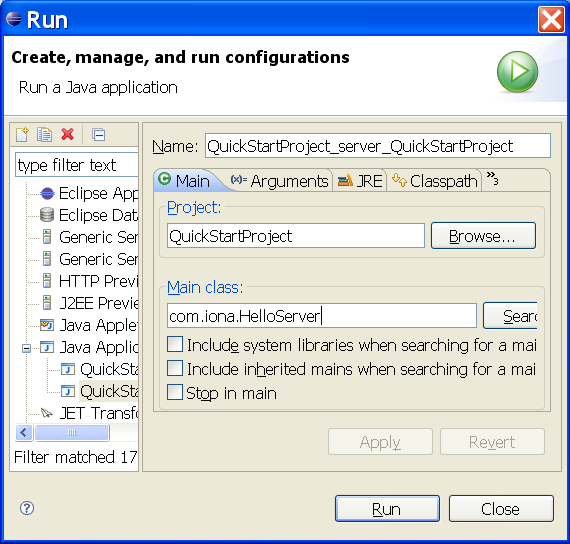
Note that the STP plug-in has created a couple preconfigured run configurations. To run the server:
1. Click Run > Open Run Dialog
2. Select Java Application > QuickStartProject_server_QuickStartProject
3. Click Run
Figure - Running the server
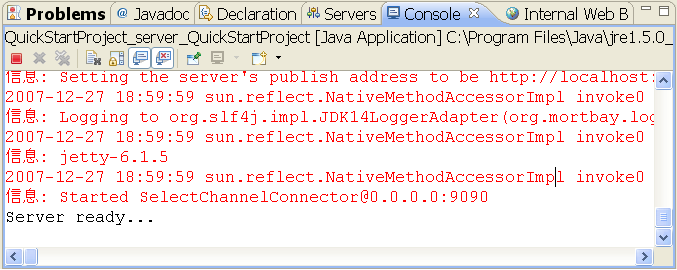
The server should then run and let you know it's ready.
Figure - Server ready
Running the stand-alone client
To run the client:
1. Click Run > Open Run Dialog
2. Select Java Application > QuickStartProject_client_QuickStartProject
3. Click Run
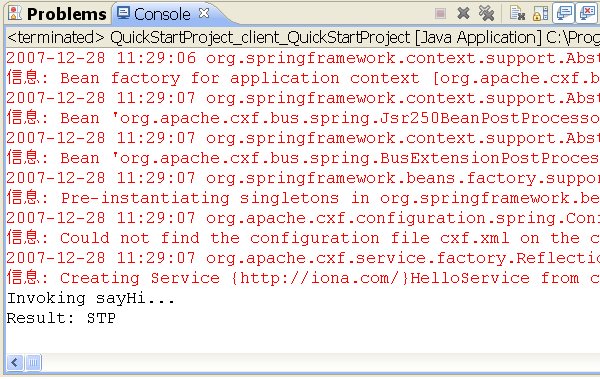
Figure - Results of executing the client
Test web service using REST
Now point your browser to http://localhost:9090/hello?wsdl and you should see the WSDL.
Point to http://localhost:9090/hello/sayHi, you should see SOAP message response as below. And STP is the invoking result.
Listing - SOAP message response
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Body> <ns1:sayHiResponse xmlns:ns1="http://iona.com/"> <return>STP</return> </ns1:sayHiResponse> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Deploying and testing on Apache Tomcat
Configing Tomcat server
1.Select Window > Show View > Other.
2.Navigate to Server > Servers.
3.In Servers view, right click, then select New > Server.
4.Select Apache > Tomcat v5.5 Server, then click Next.
5.Specify Tomcat installation directory by clicking Browse, then click Next.
6.Click Finish
Modifying server property
1.Double click Tomcat v5.5 server at localhost in Servers view
2.In Server Locations Section, choose option "Use Tomcat installation"
3.Save Tomcat Server property editor
Figure - Use Tomcat installation option
File:Use tomcat installation.PNG
Deploying service component
1.Right-click the wsdl file and select Deploy.
2.In the Select Target Server dialog, expand the Tomcat folder and select your Tomcat server.
Running Tomcat
To run Tomcat:
1.In Server view, right click Tomcat v5.5 Server at localhost
2.Select Start
Running test
Running test as standalone server.
Reference
Eclipse Help
Select Help > Help Contents, on the left panel, select SOA Tools Platform Developer Guide tree node.
Cheat Sheets
Select Help > Cheat Sheets...
FAQ
FAQ is here
Reporting bug/Getting help
Where to report STP bug
Where to get help
Maillist
There are two maillists:
stp-user maillist for stp users.
stp-dev maillist for stp developers.
For detail information on how to subscribe, please refer to stp-user, stp-dev
Newsgroup
STP newsgroup is used by end users to ask questions.
server: news.eclipse.org
For detail information on how to register, please refer to here