Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
MoDisco/HeliosReview
< To: MDT
| MoDisco |
| Website |
| Download |
| Community |
| Mailing List • Forums |
| Bugzilla |
| Open |
| Help Wanted |
| Bug Day |
| Contribute |
| Browse Source • Project Set File |
This page provides the required docuware for the MoDisco v0.8.0 Release Review, as part of the upcoming Helios Simultaneous Release.
Contents
Overview
MoDisco stands for Model Discovery.
It provides a generic and extensible MDE framework to support different reverse engineering scenarios such as modernization, quality assurance, retro-documentation, architecture improvement, etc.
Thus, the focus of MoDisco is on Model Driven Reverse Engineering.
It is an Eclipse Model Development Tools (MDT) project, inside the Eclipse Modeling Project (EMP).
IMPORTANT: MoDisco was formerly part of the Generative Modeling Technologies (GMT) project, also inside EMP, and has successfully undergone a Move Review on the 27th of April 2010: the corresponding docuware can be found from the Eclipse past reviews page
Features
New in this release
For the first time, MoDisco is part of an Eclipse Simultaneous Release. The different features provided by MoDisco v0.8.0, as part of Helios, are of two categories.
Infrastructure
- The EMF reference implementation of Knowledge Discovery Metamodel (KDM, an OMG/ADM standard), corresponding discoverers and a transformation to UML2;
- The EMF reference implementation of Software Metrics Metamodel (SMM, an OMG/ADM standard);
- The customizable Model Browser for more efficiently navigating large and complex models discovered from legacy systems;
- The Discovery Manager for fastest integration of new or existing discoverers;
- The Discovery Workflow for more easily building discovery chains (including discoverers and transformations);
- The Query Manager for allowing language-independent querying on models of legacy systems;
- The Facet Manager for dynamically extending the metamodels used at different steps of the processes;
- The Metrics Visualization Builder for automatically generating HTML, SVG or Excel representations of metrics stored in a model.
Technologies
- Java
- The EMF implementation of a metamodel for the full Java language;
- The corresponding specific Model Browser customization;
- The complete discoverer for automatically creating Java models from Java source code;
- The complete generator for automatically creating Java source code from Java models;
- The transformation from Java models to KDM models.
- XML
- The EMF implementation of a metamodel for XML (W3C definition);
- The corresponding specific Model Browser customization;
- The complete discoverer for automatically creating XML models from XML documents/files.
Accordance with project plan themes and priorities
- Stabilize the architecture of the framework infrastructure
- Integrate other Eclipse technologies (done for ATL, Acceleo, CDO)
- Provide an intensive support for the Java legacy technology
- Extend the support to other legacy technologies (done for XML)
- Develop the MoDisco team and community (done through Eclipse events, conferences, books)
See http://www.eclipse.org/projects/project-plan.php?projectid=modeling.mdt.modisco
Non-Code Aspects
The complete MoDisco documentation is available from the MoDisco Wiki page:
- General documentation on the various components;
- Version specific information;
- Additional information on available use cases, as well as incubation and deprecated components.
The Help plugins are automatically generated from the content of the Wiki.
The MoDisco website provides a direct access to all the related resources.
APIs
As this is the first time MoDisco is part of an Eclipse Simultaneous Release, there are no API related issues.
Architecture
The MoDisco architecture is detailed from http://wiki.eclipse.org/MoDisco/Architecture.
Testing & Packaging
MoDisco uses the Modeling Project Releng system to build and promote versions.
Each new build is tested at least with Eclipse 3.6 (Helios).
Core plugins are provided with dedicated test plugins checking their valid behavior.
MoDisco is integrated into the Helios Release Train since December 2009.
It is also part of the Amalgamation Modeling Package for Helios.
Tool Usability
MoDisco is used for building Model Driven Reverse Engineering solutions to different scenarios such as:
- Legacy Modernization
- Quality Assurance
- Retro-documentation
- Architecture Improvement
- Etc
End-of-Life
No components from the MoDisco previous release builds (0.7.1) have been deprecated.
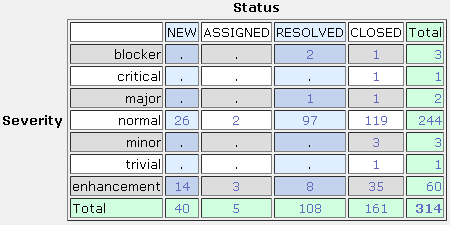
Bugzilla
- Bugzilla (v0.8.0 only, snapshot taken on the 27th of May 2010):
Standards
The MoDisco project is working in close collaboration with the OMG Architecture Driven Modernization (ADM) Task Force, which results in the EMF implementation of the Knowledge Discovery Metamodel (KDM) and Software Metrics Metamodel (SMM) specifications.
UI Usability
MDT MoDisco is conforming to the user interface guidelines.
Schedule
MDT MoDisco is a "+3" project in the simultaneous release
M4 01/19/2010 M5 02/05/2010 M6 03/19/2010 API freeze M7 05/05/2010 Feature Freeze RC1 05/19/2010 RC2 05/26/2010 RC3 06/02/2010 RC4 06/09/2010 RC5 06/16/2010 Helios 06/23/2010
Communities
- Strong collaboration with the OMG Architecture Driven Modernization (ADM) Task Force
- MoDisco book chapter in Information Systems Transformation: Architecture-Driven Modernization Case Studies by The Morgan Kaufmann/OMG Press (pages 365-400)
- Presentation at upcoming 2nd Biannual Symposium On Eclipse Open Source Software & OMG Open Specification on June, 22 2010
- Several presentations and demos at EclipseCon (2009 & 2010) and Eclipse Summit Europe (2009)
- Dedicated MoDisco newsgroup
Committer Changes
No committer change.
IP Issues
The Eclipse IP Process has been strictly followed and all plugins contain the appropriate about.html and license files.
The MoDisco IP Log is available from http://www.eclipse.org/projects/ip_log.php?projectid=modeling.mdt.modisco
- Some third-party libraries are used (cf. corresponding validated CQs)
All MoDisco content is released under EPL.
Project Plan
The current project plan is available from http://www.eclipse.org/projects/project-plan.php?projectid=modeling.mdt.modisco.
Next MoDisco version (v0.9.0) is planned to include:
- Consolidated core components (various enhancements on the Model Browser, Customization & Query mechanisms, Discovery Manager & Workflow);
- More extensive support for the Java technology;
- Dedicated support to several J2EE frameworks (Hibernate, Struts, etc).