|
|
| (58 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
| | ==== Install Method under Eclipse 3.4 ==== | | ==== Install Method under Eclipse 3.4 ==== |
| | --> | | --> |
| − |
| |
| − | = Using modeling editors =
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == UML modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Getting Started ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Papyrus Perspective ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The Papyrus perspective contains :
| |
| − |
| |
| − | *Model Explorer view
| |
| − | *Outline view
| |
| − | *Multi diagram editor view
| |
| − | *Properties view
| |
| − | *Toolbar
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus Perspective.png|600px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Model Explorer View =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The model explorer is used to navigate to the all model's elements and the diagrams.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ModelExplorer.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This action link the model explorer with the active diagram selection. This action works bidirectionally.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME Sync.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This action allow to add new semantic element.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME NewChild.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This action allow to add new diagram in current selection.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME NewDiagram.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | All actions are available on diagram item.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME DiagramMenu.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The model explorer used Common Navigator Framework and provide facilities to customize view.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME CustomizeView.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | To customize the content of treeViewer:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME CustomizeView Content.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | To filter the content of treeViewer:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME CustomizeView Filters.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Outline View =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The Outline offers a thumbnail of the graphical representation and the list of semantic elements used in current diagram.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus OutLine.png]][[Image:Papyrus OutLine All.png]][[Image:Papyrus OutLine Tree.png]] <!--
| |
| − | ===== Multi Editor View =====
| |
| − | ===== Properties View =====
| |
| − | -->
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Tutorials on UML modeling with Papyrus ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Model/Diagram creation wizard ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Create a new Model. =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus CreateNewModel.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <br> Choose the model file name and the first diagram to create.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus CreateNewModel-2.png|400px]] [[Image:Papyrus CreateNewModel-3.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Create a diagram from an existing uml file =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | From your uml file, select the "Initialize Papyrus diagram" to access the creation wizard of Papyrus. Your Papyrus diagram will be linked with your existing model.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:CreateDiagramFromModel.PNG]] <!--
| |
| − | == UML Diagrams ==
| |
| − | === Class Diagram ===
| |
| − | === Sequence Diagram ===
| |
| − | === Activity Diagram ===
| |
| − | === Use Case Diagram ===
| |
| − | -->
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===<span id="_ucc00fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Papyrus stereotype display</span>===
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====<span id="_uceC8fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Display applied stereotype name</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_uceC8fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Display applied stereotype name</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_ucf4IPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZluEPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Apply a stereotype]], [[#_uZm8MPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Drop from the model explorer]], [[#_uZoKUPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Display the name of the stereotype ]], [[#_uZpYcPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Display each applied stereotype name differently]], [[#_uZkf8PwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Display stereotype name]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_ucgfMfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">The diagram contains a shape. When you applied a stereotype on the element, the applied stereotype name is displayed on the shape below the name of the element.
| |
| − | When an element is dropped form the model explorer to the diagram, the applied stereotype named is displayed on the shape.
| |
| − | This is the same behavior for links. </span><br>
| |
| − | =====<span id="_uchtUfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">How to</span>=====
| |
| − | <span id="_uci7cfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Inside papyrus, it is possible to display the name of applied stereotype.
| |
| − | To do that:
| |
| − | 1. Apply the profile that contains the stereotype on your model.
| |
| − | 2. Apply the wanted stereotype on the element.</span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:ApplyProfile.png|Apply a profile]]
| |
| − | <br>''Apply a profile''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:applyStereotype.png|Apply the stereotype]]
| |
| − | <br>''Apply the stereotype''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:AppliedStereotype.png|Resulted applied stereotype]]
| |
| − | <br>''Resulted applied stereotype''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_ucnM4fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Display stereotype properties</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_ucnM4fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Display stereotype properties</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_ucpCEPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZdLMfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Stereotype application properties dipslay]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_ucqQMPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">It is possible to display properties of stereotypes as "comment", as "compartment", as "brace"</span><br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_ucq3QfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">As "brace"</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_ucq3QfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">As "brace"</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_ucsFYfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZiqwPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Display Requirement as a "brace"]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_uctTgfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Properties of applied stereotype can be displayed as "brace". This is label that is set below the name, and contains a sequence of properties name with their values.</span><br>
| |
| − | =====<span id="_ucuhofwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">How to</span>=====
| |
| − | <span id="_ucvvwPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">To do that:
| |
| − | 1. Select your Element
| |
| − | 2. Select the Appearance Tab in the property view
| |
| − | 3. Select "In braces" for the line of your applied stereotype</span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:DisplayInBrace.png|Sequence of actions to display in brace]]
| |
| − | <br>''Sequence of actions to display in brace''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:ResultDisplayInBrace.png|Properties of stereotypes displayed in brace]]
| |
| − | <br>''Properties of stereotypes displayed in brace''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_ucyzEfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">As "compartment"</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_ucyzEfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">As "compartment"</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_uc0BMfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZg1kPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Display Requirement as a "compartment"]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_uc1PUfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Properties of applied stereotype can be displayed as a compartment. This compartment contains all labels that are properties of the applied stereotype.</span><br>
| |
| − | =====<span id="_uc12YfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">How to</span>=====
| |
| − | <span id="_uc3EgfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">To do that:
| |
| − | 1. Select your Element
| |
| − | 2. Select the Appearance Tab in the property view
| |
| − | 3. Select "In Compartment" for the line of your applied stereotype</span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:DisplayInCompartment.png|Sequence of actions to display in compartment]]
| |
| − | <br>''Sequence of actions to display in compartment''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:ResultDisplayInCompartment.png|Properties of stereotypes displayed in compartment]]
| |
| − | <br>''Properties of stereotypes displayed in compartment''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_uc6u4PwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">As "Comment"</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_uc6u4PwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">As "Comment"</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_uc79APwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZfAYfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Display Requirement as a "comment"]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_uc8kEfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Properties of applied stereotype can be displayed as a comment. This comment representation that contains all labels that are properties of the applied stereotype.</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_uc9yMfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">To do that:
| |
| − | 1. Select your Element
| |
| − | 2. Select the Appearance Tab in the property view
| |
| − | 3. Select "In Comment" for the line of your applied stereotype</span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:DisplayInComment.png|Sequence of actions to display in comment]]
| |
| − | <br>''Sequence of actions to display in comment''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:ResultDisplayInComment.png|Properties of stereotype displayed in comment]]
| |
| − | <br>''Properties of stereotype displayed in comment''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_udA1gfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Choose properties to display</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_udA1gfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Choose properties to display</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_udCqsPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZtC0PwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Use CSS file]], [[#_uZuQ8fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Use property view]], [[#_uZr0sPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Choice on Stereotype properties to display]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udD40fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">The list of properties of stereotypes can be chosen by the user by using the property view or by writing a css.
| |
| − | This choice runs for the 3 representations of applied stereotypes: brace, compartment, comment.</span><br>
| |
| − | =====<span id="_udEf4fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">How to</span>=====
| |
| − | <span id="_udFuAfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">By using the property view, it is possible to select the list of property of stereotype.
| |
| − | To do that:
| |
| − | 1. Select your element.
| |
| − | 2. Check that the applied stereotype has been displayed as brace, compartment or comment
| |
| − | 3. Select lines that correspond to wanted properties of stereotype.</span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:ChooseProperties_PV.png|Select properties by using the property view]]
| |
| − | <br>''Select properties by using the property view''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udIKQfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">By using CSS file:
| |
| − | <code>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | Compartment[type=StereotypeCompartment]{
| |
| − | visible:true;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | Compartment[type=StereotypeCompartment]>[property="derived"]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | Compartment[type=StereotypeCompartment]>[property="derivedFrom"]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | </code>
| |
| − | The compartment is displayed and the property derived and derivedFrom are not displayed
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | </span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:ChooseProperties_CSS.png|Result by using the selection by CSS]]
| |
| − | <br>''Result by using the selection by CSS''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udKmgfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">The following CSS rules are implemented by default for all the Diagrams:
| |
| − | <code>
| |
| − | Shape[type=StereotypeComment]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | StereotypeComment Compartment[type=StereotypeBrace]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Compartment[type=StereotypeCompartment]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Compartment[type=StereotypeBrace]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Label[type=StereotypeLabel]{
| |
| − | depth:"none";
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Here is some example of CSS to display the Stereotype:
| |
| − | /* To modify the depth */
| |
| − | Label[type=StereotypeLabel]{
| |
| − | depth:"-1";
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | /* To make the properties visible into compartment */
| |
| − | Compartment[type=StereotypeCompartment]{
| |
| − | visible:true;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | /* Hide the property "allocatedTo" into the compartment */
| |
| − | Compartment[type=StereotypeCompartment]>[property="allocatedTo"]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | /* Hide all the properties into the Compartment of the stereotype Block */
| |
| − | Compartment[stereotype="SysML::Blocks::Block"]{
| |
| − | visible:false;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − |
| |
| − | /* Display the Comment shape */
| |
| − | StereotypeComment{
| |
| − | visible:true;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | /* Display the properties in Brace into the Comment*/
| |
| − | StereotypeComment Compartment[type=StereotypeBrace]{
| |
| − | visible:true;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | </code>
| |
| − | </span><br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_udL0ofwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Choose QN depth</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_udL0ofwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Choose QN depth</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_udNCwfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZqmkPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Qualified name depth]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udOQ4PwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">The stereotype name can be displayed by choosing the depth. I consists on choosing the size of the qualified name of the stereotype.
| |
| − | full = all the qualified name
| |
| − | 0= only the name of stereotype
| |
| − | -1= the name of its parent + the name of the stereotype
| |
| − | -2=the name of its great-parent+ the name of its parent + the name of the stereotype</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udO38fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Using Css:
| |
| − | Label[type=StereotypeLabel]{
| |
| − | depth:"-1";
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | By using the property view:
| |
| − | 1. Select the element.
| |
| − | 2. Select the appearance Tab
| |
| − | 3. Select the name depth and choose the size</span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:depth.png|Select the depth the applied stereotype name]]
| |
| − | <br>''Select the depth the applied stereotype name''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_udRUMfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Remove display of stereotype properties</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_udRUMfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Remove display of stereotype properties</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_udSiUfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZvfEPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Remove display of applied stereotype ]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udTwcfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">The display of stereotype can be removed by selection or by unapply stereotype or profile container</span><br>
| |
| − | ====<span id="_udU-kPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Update the display of applied stereotype properties</span>====
| |
| − | ======<span id="_udU-kPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">Update the display of applied stereotype properties</span>======
| |
| − | <span id="_udVlofwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg"> - traces to [[#_uZwtMPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg|Update display]]</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udWzwfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">When the value associated to the property of stereotype has been modified, the display must be modified.</span><br>
| |
| − | <span id="_udYB4fwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">It is possible to edit value of stereotype property by double click on the property in the diagram.
| |
| − | Important: the property must be writable and Real are not yet editable. </span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:PropertyEdition.png|Property of applied stereotype edition]]
| |
| − | <br>''Property of applied stereotype edition''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | =====<span id="_udaeIfwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">How to</span>=====
| |
| − | <span id="_udbsQPwOEeWkK6hum4lQXg">It is possible to edit property of applied stereotype by using the property view:
| |
| − | 1. Select your element
| |
| − | 2. Select the Profile tab
| |
| − | 3. Expand the stereotype
| |
| − | 4. Select the property
| |
| − | 5. Edit at right the property of the stereotype</span><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[Image:PropertyEdition_PV.png|Property edition for applied stereotypes in the property view]]
| |
| − | <br>''Property edition for applied stereotypes in the property view''<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Load an additionnal resource =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====== Show additional resources in your model explorer view ======
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Ensure that the filter for the additional resources is not checked on your model explorer view : [[Image:PapyrusFilterAdditionalResources.PNG]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====Table ====
| |
| − | In order to edit your elements by using table representation, you can see [[Papyrus_User_Guide/Table_Documentation|Documentation about table]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Constraints in Papyrus ===
| |
| − | In order to edit your constraint your can see [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Papyrus Constraints|Create and edit constraints]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | To validate constraint on your model, you can see [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Profile Constraints|Define Profile Constraints]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Working with Profiles ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Externalized Profile Applications ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Externalized Profile Applications|Managing profile applications separately from the applying models]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == SysML Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Tutorials on SysML modeling with Papyrus ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Papyrus Zoo of SysML Models ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == MARTE Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Tutorials on MARTE modeling with Papyrus ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Papyrus Zoo of MARTE Models ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == fUML and Alf Modeling ==
| |
| − | [[Papyrus/UserGuide/fUML_ALF|Using fUML and Alf to produce executable models]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | = Developing custom DSL based editor with Papyrus =
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == UML Profile Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Profile Constraints|Define Profile Constraints]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == MetaModel Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Additional Editor Integration (this section is for the Backone) ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Diagram Editors Customizations ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Specific Diagram Editors Creation ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Diagram Editor Palette Customization ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Here you can find the documentation describing palette customization: [http://git.eclipse.org/c/papyrus/org.eclipse.papyrus.git/tree/doc/DevelopperDocuments/How-To/PapyrusDevelopperTutorial_OnPaletteCustomization_v1.0_d2010-05-10.odt Doc ]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This document can also be found in Papyrus help section => User Guide => Palette customization
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Property Editor Customization ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Model Explorer Customization ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Diagram Appearance Customization with CSS Stylesheets ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [http://wiki.eclipse.org/MDT/Papyrus/UserGuide/CSS CSS Stylesheets in Papyrus]
| |
| | | | |
| | = Additional Utilities of Papyrus = | | = Additional Utilities of Papyrus = |
| − |
| |
| − | == Collaborative Work Support ==
| |
| | | | |
| | == Layer Support == | | == Layer Support == |
| − | See [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Layers|Layers Guide]]
| + | if you want to use layer, see [https://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus/Oxygen_Work_Description/NewFeature/Layers Layers Guide] |
| | | | |
| | == Model Execution == | | == Model Execution == |
| − | [[Papyrus/UserGuide/ModelExecution|Execute your fUML models with MOKA]]
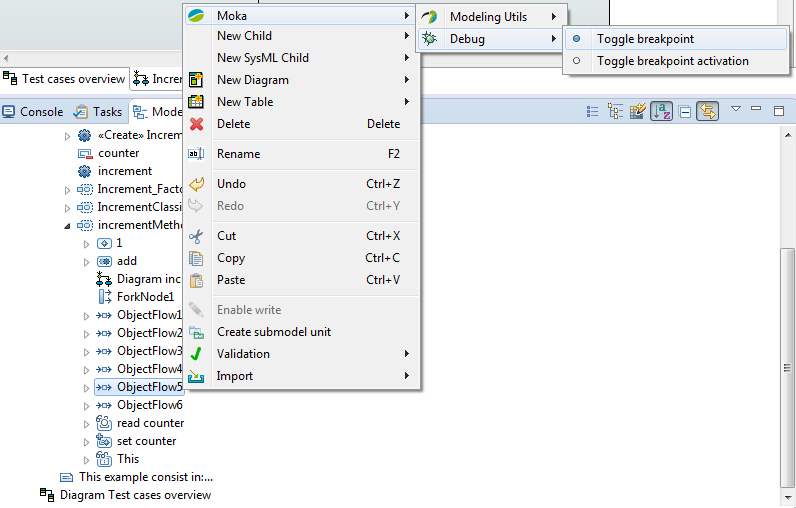
| + | If you want to execute your model as the following picture, see [[Papyrus/UserGuide/ModelExecution|Execute your fUML models with MOKA]] |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Automatic Layout Support ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Code Generation Support ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Existing Code Generation Facilities ===
| + | |
| − | Currently, Papyrus supports code generation for the following programming languages:
| + | |
| − | * [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Java_Code_Generation Java code generation]
| + | |
| − | * [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus/Codegen/Cpp_description C++ code generation]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Upcoming Code Generation Facilities ===
| + | |
| − | Papyrus is going to support code generation for the following programming languages, which are in the experimental phase now, soon:
| + | |
| − | * ADA code generation
| + | |
| − | * C code generation
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Adding a New Code Generator ===
| + | |
| − | Apart from the aforementioned programming language, it is also possible to develop and integrate other code generators to Papyrus.
| + | |
| − | To learn about how to add a new code generator to Papyrus, refer to the following [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus/Codegen/Adding_a_New_Code_Generator wikipage].
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Reverse Engineering ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Java Reverse Engineering ===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | see [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Java_reverse_engineering Java reverse engineering]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Documentation Support ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Documentation Modelling ===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Documentation Generation ===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Deploy your applications ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | see [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_Qompass Qompass for Papyrus]
| + | |
| − | == Fragment a Model ==
| + | |
| − | See [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Submodel|Submodel Guide]]
| + | |
| − | [[Category:Papyrus]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | = General Feature =
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Editors ==
| + | |
| − | === Palette ===
| + | |
| − | The palette is available with any diagrams. But its content depends on the diagrams type.
| + | |
| − | The standard palette ( the top container of the palette in red in the here-after capture) contents a standard selection tool (the white arrow), a zoom in and zoom out tool, and marquee selection tools.<br/>
| + | |
| − | [[File:Palette1.JPG]] <br/>
| + | |
| − | The standard palette is available for every diagram.
| + | |
| − | ==== Properties ====
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | See [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_User_Guide/Palette/Properties Properties]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==== Standard Selection tool ====
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | See [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_User_Guide/Palette/Standard_Selection_Tool Standard selection Tool]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==== Zoom Tools ====
| + | |
| − | See [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_User_Guide/Palette/Zoom_Tools Zoom Tools]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==== Marquee Selection Tools====
| + | |
| − | See [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_User_Guide/Palette/Marquee_Selection_Documentation Marquee Selection Tool]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Toolbars ===
| + | |
| − | Papyrus has its own set of Toolbars. A Toolbar regroups a set of tools belonging to the same kind of activity.
| + | |
| − | The different Toolbars can be shown or hide depending on the perspectives. <br/>
| + | |
| − | The toolbars visibility can be customized from the menu Windows/Customize Perspectives. <br/>
| + | |
| − | [[File:Customize_Perspective.JPG|frame|center|Alignment Perpective]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==== Alignment ====
| + | |
| − | See [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_User_Guide/Toolbars/Alignment Alignment]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ====Text alignment ====
| + | |
| − | See [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_User_Guide/Toolbars/TextAlignment Text alignment]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | --[[User:Celine.Janssens.all4tec.net|Céline Janssens [ALL4TEC]]] ([[User talk:Celine.Janssens.all4tec.net|talk]]) 12:06, 28 August 2014 (EDT)
| + | |
| − | [[Category:Papyrus]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | =Embedded Editors=
| + | |
| − | Papyrus provides embedded editors to edit UML Elements. Of course these editors allows to edit the name of the elements, but they allow to edit much more than this.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==UML ValueSpecification editor==
| + | |
| − | This editor allows to edit UMLValueSpecification. ValueSpecifications are used to define the default value of a Property or to define the multiplicity of a MultiplicityElement (lower and upper values).
| + | |
| − | Papyrus provides an Xtext Editor for UML ValueSpecification. This editor provides completion (CTRL+SPACE) to help the user to define the value to set crossing easily the model.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | You can use this editors in Papyrus table or in papyrus Property View for example.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The developer documentation for this editors is available [[Papyrus_Developer_Guide/Papyrus_Embedded_Editors_Documentation/Value_Specification_Xtext_editor#Parser_definition|here]].
| + | |
| − | ===Usage===
| + | |
| − | The default grammar of the XText parser for the Value Specification is the following:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | <code><nowiki>(visibility)? (name'=')? value</nowiki></code>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The values accepted for the differents attributes are the following:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:20%" | Attribute
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:10%" | Required
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:60%" | Values accepted
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | '''visibility'''
| + | |
| − | | align="center" | No
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | * <code>+</code> (public)
| + | |
| − | * <code>#</code> (protected)
| + | |
| − | * <code>~</code> (package)
| + | |
| − | * <code>-</code> (private)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | '''name'''
| + | |
| − | | align="center" | No
| + | |
| − | | String representing an ID (i.e. XText grammar: <code>'^'?('a'..'z'|'A'..'Z'|'_') ('a'..'z'|'A'..'Z'|'_'|'0'..'9')*</code>)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | '''value'''
| + | |
| − | | align="center" | Yes
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | * <code>true</code> or <code>false</code> (<code>LiteralBoolean</code>)
| + | |
| − | * positive integer (<code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code>)
| + | |
| − | * negative integer (<code>LiteralInteger</code>)
| + | |
| − | * double (<code>LiteralReal</code>)
| + | |
| − | * <code>null</code> (<code>LiteralNull</code>)
| + | |
| − | * String with quote (<code>LiteralSting</code>). The quote (') is essential for 2 reasons:
| + | |
| − | ** The XText parser cannot define the difference between the name representing an <code>InstanceSpecification</code> and a simple string value
| + | |
| − | ** A Non-valid value won't be defined as an <code>OpaqueExpression</code> without quote but always as a <code>LiteralString</code> value
| + | |
| − | * Instance Specification name (<code>InstanceValue</code>)
| + | |
| − | * <code><Undefined></code> or empty (<code>null</code>)
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | If the text filled is not compatible with the grammar of XText parser, an <code>OpaqueExpression</code> will be created.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The XText parser for Value Specification is not restrictive with the text filled, i.e. the different features setted on an existing Value Specification will be kept if possible.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | For example: If an existing Value Specification is a <code>LiteralBoolean</code> named 'testBoolean' with the visibility 'public' and the value setted to <code>true</code>, the text <code>+testBoolean=false</code> and <code>false</code> have the same result: the value of <code>LiteralBoolean</code> existing will pass to <code>false</code> (the name and the visilibity don't change).
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The XText parser reacts differently instead of the type of the Value Specification's container:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ====Example: Without defined type on Value Specification's container====
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | If the type of Value Specification's container is not defined, the default behaviour will be applied.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Here, some examples:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:15%" rowspan="2" | Text filled
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:20%" rowspan="2" | Namely
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:65%" rowspan="1" colspan="4" | Created ValueSpecification
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:15%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Type
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:8%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Visibility
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:15%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Name
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:27%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Value
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | rowspan="2" | +testInstanceValue=InstanceSpec1
| + | |
| − | | 'InstanceSpec1' is an <code>InstanceSpecification</code> existing in the model
| + | |
| − | | <code>InstanceValue</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | testInstanceValue
| + | |
| − | | 'instance' attribute of <code>InstanceValue</code> is a reference to the existing <code>InstanceSpecification</code> named 'InstanceSpec1'
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | No <code>InstanceSpecification</code> exist in the model
| + | |
| − | | <code>OpaqueExpression</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | +testInstanceValue=InstanceSpec1
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | +testBoolean=true
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralBoolean</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | testBoolean
| + | |
| − | | <code>true</code>
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | #testUnlimitedNatural=5
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code>
| + | |
| − | | protected
| + | |
| − | | testUnlimitedNatural
| + | |
| − | | 5
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | ~testInteger=-8
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code>
| + | |
| − | | package
| + | |
| − | | testInteger
| + | |
| − | | -8
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | -testReal=12.34
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralReal</code>
| + | |
| − | | private
| + | |
| − | | testReal
| + | |
| − | | 12.34
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | ~testNull=null
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralNull</code>
| + | |
| − | | package
| + | |
| − | | testNull
| + | |
| − | | <code>null</code>
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | -testString="foo"
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralString</code>
| + | |
| − | | private
| + | |
| − | | testString
| + | |
| − | | foo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | ##testString="foo"
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | | <code>OpaqueExpression</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | ##testString="foo"
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ====Example: With defined type on Value Specification's container====
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | If the type of Value Specification's container is setted, the same text filled will be have different behaviour depending to the type. In fact, the value filled must be consistent to the type, otherwise an <code>OpaqueExpression</code> will be created.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The different types corresponding to <code>LiteralSpecification</code> are the following:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:50%" | LiteralSpecification
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:50%" | Types corresponding
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralBoolean</code>
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | * JavaPrimitiveTypes::boolean
| + | |
| − | * EcorePrimitiveTypes::EBoolean
| + | |
| − | * EcorePrimitiveTypes::EBooleanObject
| + | |
| − | * PrimitiveTypes::Boolean
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::Boolean
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::BooleanObject
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code>
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | * PrimitiveTypes::UnlimitedNatural
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code>
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | * JavaPrimitiveTypes::int
| + | |
| − | * EcorePrimitiveTypes::EInt
| + | |
| − | * EcorePrimitiveTypes::EIntegerObject
| + | |
| − | * PrimitiveTypes::Integer
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::Int
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::Integer
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::IntObject
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralReal</code>
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | * JavaPrimitiveTypes::double
| + | |
| − | * EcorePrimitiveTypes::EDouble
| + | |
| − | * EcorePrimitiveTypes::EDoubleObject
| + | |
| − | * PrimitiveTypes::Real
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::Double
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::DoubleObject
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralString</code>
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | * EcorePrimitiveTypes::EString
| + | |
| − | * PrimitiveTypes::String
| + | |
| − | * XMLPrimitiveTypes::String
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Here, some examples:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:15%" rowspan="2" | Text filled
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:20%" rowspan="2" | Value Specification's container type
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:65%" rowspan="1" colspan="4" | Created ValueSpecification
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:15%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Type
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:8%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Visibility
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:15%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Name
| + | |
| − | ! style="width:27%" rowspan="1" colspan="1" | Value
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | rowspan="2" | +testBoolean=true
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Boolean
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralBoolean</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | testBoolean
| + | |
| − | | <code>true</code>
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Integer
| + | |
| − | | <code>OpaqueExpression</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | +testBoolean=true
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | rowspan="4" | -testUnlimitedNatural=8
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::UnlimitedNatural
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code>
| + | |
| − | | private
| + | |
| − | | testUnlimitedNatural
| + | |
| − | | 8
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Integer
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code>
| + | |
| − | | private
| + | |
| − | | testUnlimitedNatural
| + | |
| − | | 8
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Real
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralReal</code>
| + | |
| − | | private
| + | |
| − | | testUnlimitedNatural
| + | |
| − | | 8.0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Boolean
| + | |
| − | | <code>OpaqueExpression</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | -testUnlimitedNatural=8
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | rowspan="4" | #testInteger=-6
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::UnlimitedNatural
| + | |
| − | | <code>OpaqueExpression</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | #testInteger=6
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Integer
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code>
| + | |
| − | | protected
| + | |
| − | | testInteger
| + | |
| − | | 6
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Real
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralReal</code>
| + | |
| − | | protected
| + | |
| − | | testInteger
| + | |
| − | | 6.0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Boolean
| + | |
| − | | <code>OpaqueExpression</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | #testInteger=6
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | rowspan="3" | -testReal=4.5
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Integer
| + | |
| − | | <code>OpaqueExpression</code>
| + | |
| − | | public
| + | |
| − | | -testReal=4.5
| + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | PrimitiveTypes::Real
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralReal</code>
| + | |
| − | | private
| + | |
| − | | testReal
| + | |
| − | | 4.5
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==Textual Editor For Named Element==
| + | |
| − | Since Papyrus 1.1.0 (Eclipse Mars), Papyrus provides a new texutal editor to edit references to UML NamedElement. This editor works only for references which are not in containment. This editor has not been developed using XText. It use a custom string parser and provide a completion (CTRL+SPACE) to help the user to find the named elements to reference in the model.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | You can use this editor in Property View or in Papyrus table for example.
| + | |
| − | Developer documentation is available [[Papyrus_Developer_Guide/Papyrus_Embedded_Editors_Documentation/Textual_Editor_For_NamedElement|here]].
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===Usage===
| + | |
| − | * This editors allows to find named element typing its name.
| + | |
| − | * In case of several elements to found, the separator to use is the comma </code>'</code>
| + | |
| − | * If the name of the element contains a comma, you should prefix and suffix its name by a quote <code>'</code>.
| + | |
| − | * The value will not be set if the element can't be found is the model
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===Example===
| + | |
| − | If you have 3 Classes in your model, named <code>Class1</code>, <code>Class2</code> and <code>Clas,s3</code>.
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| + | |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | typed text
| + | |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | completion proposal
| + | |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | explanation
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | empty string
| + | |
| − | | <Undefined>, ...
| + | |
| − | | we look for nothing, so we provide the <code><Undefined></code> value and <code>...</code> to ask to the user to write more text
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | Clas
| + | |
| − | | <Undefined>,Class1,Class2,Clas,s3
| + | |
| − | | 3 classes matches the string, <code><Undefined></code> is always proposed
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | Class
| + | |
| − | | <Undefined>,Class1,Class2
| + | |
| − | | 3 classes matches the string, <Undefined>is always proposed
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | 'Clas
| + | |
| − | | <Undefined>, Clas,s3
| + | |
| − | | the string starts with a quote and Clas,s3 contains a comma, so we propose <code>Clas,s3</code>; <code><Undefined></code> is always proposed
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | Clas,
| + | |
| − | | <Undefined>,...
| + | |
| − | | interpreted as a list of value, the first value is </code>Clas</code>, and we have no information for the second one, for the completion it is an empty string
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | =Property View=
| + | |
| − | ==Appearence Tab==
| + | |
| − | ===Shape Customization===
| + | |
| − | To be defined
| + | |
| − | ===Stereotype Display ===
| + | |
| − | See [https://wiki.eclipse.org/MDT/Papyrus/UserGuide/PropertyView/StereotypeDisplay Stereotype Display via Property View]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==Multiplicity Editor==
| + | |
| − | ===Description===
| + | |
| − | The multiplicity editor contains two modes of edition:
| + | |
| − | * The '''simple''' mode which allows to edit the lower and the upper values from a unique editor
| + | |
| − | * The '''advanced''' mode which allows to edit the lower and the upper values from two editors of ValueSpecification.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===Usage===
| + | |
| − | ====Simple mode====
| + | |
| − | The simple mode is represented as the following:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[File:simpleMode.png]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | This editor must be filled by the following pattern:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| + | |
| − | ! Value filled
| + | |
| − | ! Lower value
| + | |
| − | ! Upper value
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | 1
| + | |
| − | | <code>null</code> (default value is '''1''')
| + | |
| − | | <code>null</code> (default value is '''1''')
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | x..y
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code> with value '''x'''
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> with value '''y'''
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | x..*
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code> with value '''x'''
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> with value '''-1''' (interpreted as <code>*</code>)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | x
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code> with value '''x'''
| + | |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> with value '''x'''
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The values set as lower and upper are always positive (except the <code>*</code> for the upper which is valued as '''-1''').
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | This editor is usable only when the lower ValueSpecification is a <code>LiteralInteger</code> or <code>null</code> and when the upper ValueSpecification is a <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> or <code>null</code>.
| + | |
| − | On the other hand, this editor will be displayed like the following:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[File:simpleModeDisabled.png]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ====Advanced mode====
| + | |
| − | =====Simple ValueSpecification editor=====
| + | |
| − | The advanced mode with simple ValueSpecificatiton editors is represented as the following:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[File:advancedMode.png]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The lower and the upper ValueSpecification can be created/edited/deleted by the buttons:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[File:buttonsEdit.png]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | =====XText ValueSpecification editor=====
| + | |
| − | The advanced mode with XText ValueSpecification editors is represented as the following:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[File:advancedModeXText.png]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | This editor use the XText ValueSpecification editors (explain [[Papyrus_User_Guide#UML_ValueSpecification_editor|here]]) with some specificities depending on lower or upper value edition.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The specificity of the '''lower''' ValueSpecification edition is when the value filled is an integer, this one will be handled as <code>LiteralInteger</code> instead of <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> or <code>LiteralInteger</code> (the <code>*</code> value will create an <code>OpaqueExpression</code>).
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The specificity of the '''upper''' ValueSpecification edition is when the value filled is an integer or <code>*</code>:
| + | |
| − | * if the integer is '''positive or -1''', a <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> will be created
| + | |
| − | * if the integer is '''negative''', an <code>OpaqueExpression</code> will be created instead of <code>LiteralInteger</code>
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ====Switch modes====
| + | [[File:5 - ToggleBreakpointModelExplorer.png]] |
| − | This is possible to switch between the two modes by two ways:
| + | |
| − | * The button in the multiplicity editor:
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:buttonSwitch.png]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | * The '''multiplicity editor''' preferences in the '''property views''' preferences:
| + | == Papyrus for Requirements == |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:preferencesMultiplicityEditor.png]]
| + | Papyrus for Requirements helps you to specify and analyze requirements in the context of systems modeling. It aims to cover the Specification, Management, Analysis and Validation-Verification activities of Requirements Engineering. Papyrus for Requirements depends on the components Papyrus for SysML and Papyrus for Metrics. |
| | | | |
| − | Regarless of the way used to switch modes, the mode used is saved in the preferences and will be used for each multiplicity in Papyrus.
| + | Please visit the [[Installation steps of Papyrus for Requirements]] |
Papyrus for Requirements helps you to specify and analyze requirements in the context of systems modeling. It aims to cover the Specification, Management, Analysis and Validation-Verification activities of Requirements Engineering. Papyrus for Requirements depends on the components Papyrus for SysML and Papyrus for Metrics.