|
|
| (121 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
| | ==== Install Method under Eclipse 3.4 ==== | | ==== Install Method under Eclipse 3.4 ==== |
| | --> | | --> |
| − |
| |
| − | = Using UML modeling editors =
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == UML modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Getting Started ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Papyrus Perspective ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The Papyrus perspective contains :
| |
| − |
| |
| − | *Model Explorer view
| |
| − | *Outline view
| |
| − | *Multi diagram editor view
| |
| − | *Properties view
| |
| − | *Toolbar
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus Perspective.png|600px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Model Explorer View =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The model explorer is used to navigate to the all model's elements and the diagrams.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ModelExplorer.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This action link the model explorer with the active diagram selection. This action works bidirectionally.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME Sync.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This action allow to add new semantic element.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME NewChild.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This action allow to add new diagram in current selection.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME NewDiagram.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | All actions are available on diagram item.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME DiagramMenu.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The model explorer used Common Navigator Framework and provide facilities to customize view.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME CustomizeView.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | To customize the content of treeViewer:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME CustomizeView Content.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | To filter the content of treeViewer:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus ME CustomizeView Filters.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Outline View =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The Outline offers a thumbnail of the graphical representation and the list of semantic elements used in current diagram.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus OutLine.png]][[Image:Papyrus OutLine All.png]][[Image:Papyrus OutLine Tree.png]] <!--
| |
| − | ===== Multi Editor View =====
| |
| − | ===== Properties View =====
| |
| − | -->
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Tutorials on UML modeling with Papyrus ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Model/Diagram creation wizard ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Create a new Model. =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus CreateNewModel.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <br> Choose the model file name and the first diagram to create.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:Papyrus CreateNewModel-2.png|400px]] [[Image:Papyrus CreateNewModel-3.png|400px]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Create a diagram from an existing uml file =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | From your uml file, select the "Initialize Papyrus diagram" to access the creation wizard of Papyrus. Your Papyrus diagram will be linked with your existing model.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:CreateDiagramFromModel.PNG]] <!--
| |
| − | == UML Diagrams ==
| |
| − | === Class Diagram ===
| |
| − | === Sequence Diagram ===
| |
| − | === Activity Diagram ===
| |
| − | === Use Case Diagram ===
| |
| − | -->
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Apply a static profile =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | *1 - Select a package element (ie a Model or a Package).
| |
| − | *2 - Select the tab "Profile" on the "Properties" view
| |
| − | *3 - Click on the plug-in icon
| |
| − | *4 - Select your static profile
| |
| − | *5 - Choose profiles to apply
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:PapyrusApplyStaticProfil.PNG]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Load an additionnal resource =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====== Show additional resources in your model explorer view ======
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Ensure that the filter for the additional resources is not checked on your model explorer view : [[Image:PapyrusFilterAdditionalResources.PNG]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====== Add an additional resource ======
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Right click on an element of your model and select the menu "Load resource..."
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:PapyrusLoadResources.PNG]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | ====Table Documentation====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | See http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_User_Guide/Table_Documentation
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Papyrus Zoo of UML Models ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Composite Structure Diagram ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:CompositeSupport.PNG]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The project is available here [http://wiki.eclipse.org/images/1/10/CompositeSupport.zip]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Constraints in Papyrus ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Create and edit constraints ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Creation and edition comprises includes multiple use case, namely creation of a constraint and its context and setting a specification.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[image:Constraint_CreationUseCase.png]]<br/>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Define a constraint and its context =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Papyrus supports the creation of UML constraints. To create a constraint, and associated context, do one of the following:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * Within any Papyrus diagram select the constraint tool from the palette and then press the mouse button at the position where you want to create the constraint on the diagram canvas. The constraint should then be connected to another element on the diagram, via a ContextLink relationship, by clicking on the target element in the diagram (in two-click mode). If you are in one-click-mode (connection tool preference), press the mouse button on the constraint and keep it pressed until the context object is selected. This ContextLink relationship defines the context for which the constraint will be evaluated.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:Constraint_CreateViaDiagram.png]] [[Image:Constraint_ContextViaDiagram.png]]<br>
| |
| − | The constraint and context-link tools in the palette
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * Within the Model Explorer via right clicking a model element and then selecting New Child -> Create a new Constraint. The context is automatically set to the parent of the constraint. The context can be changed via the Properties View if required.<br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:Constraint_CreateViaME.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Create a constraint via the model explorer
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:Constraint_ContextViaPropertyView.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Set the context via the property view
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Define constraint specification =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Each constraint has a specification containing a condition. Whereas it may be an arbitrary value specification, such as a StringExpression or LiteralInteger, it is in most cases useful to define an opaque expression consisting of a pair of language and body (a list of these pairs). The constraint body may be written in at least OCL, JAVA, or natural language. In order to make constraints evaluable by Papyrus the constraint must be written in either OCL or JAVA. To define a constraint's specification, first select a constraint on either a diagram or in the Model Explorer, then do the following:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * On the diagram open the default editor for constraints using the keyboard shortcut F2 or with a second click on an already selected constraint. The editor assume the language is OCL but this can be changed later via the Properties View. The constraint text is defined directly in the editor. The default editor can be controlled via the preferences.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * On the diagram select a specific editor via the context menu, as shown in the following screenshot.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:Constraint_ChooseEditor.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Explicitly choose the editor for the constraint
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Use the property view to create a new or open an existing specification, as shown in the following figure.
| |
| − | In the sequel, we assume that the specification is an opaque expression.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:Constraint_SpecViaPropertyView.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Open the specification via the property view
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | You can add the language, as in the following figure:<br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:Constraint_OpaqueExpressionAddLang.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Specify a language.
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:Constraint_OpaqueExpressionEdit.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Write the body of the opaque expression
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This method is a bit more complicated, but gives the user full control over the opaque specification. In particular,
| |
| − | it is possible to enter more than one language, body pair (even if this is rarely needed).
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Validate OCL Constraints of a Profile ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Papyrus supports an additional profile for defining Domain Specific Modeling Languages (DSML) that refines how constraints are validated.
| |
| − | The additional profile enables a more precise specification of validation properties, for example:
| |
| − | •Mode: Defines if the validation of the constraint is done in “batch” or “live” mode
| |
| − | •Severity: Defines the severity of the constraint violation. It can be one of INFORMATION, WARNING or ERROR. The latter is the default severity (if none is specified). The CANCEL severity should be used with caution, as it causes the validation operation to be interrupted, possibly resulting in the loss of valuable diagnostic information from other constraints.
| |
| − | •Message: Defines the message that will be displayed if the constraint is violated
| |
| − | •Description: Provides a description of the constraint •Enabled by default: Defined if this constraint should be enabled by default or not
| |
| − |
| |
| − | CAVEAT: The information added via the profile using the DSML profile is not currently taken into account during OCL validation. The support will be added soon.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Advanced users can also define:
| |
| − | • Id: The constraint id
| |
| − | • Status code: The plug-in unique status code, useful for logging.
| |
| − | •The target of validation, the element to be validated
| |
| − |
| |
| − | How to apply the DSML validation profile:
| |
| − | 1.Select the profile root and apply the profile
| |
| − |
| |
| − | 2.Select the profile tab in the property view
| |
| − |
| |
| − | 3.Click on the registered profile button
| |
| − |
| |
| − | 4.Select the "DSML Validation" profile
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:DSML-profileApplication.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Open the specification via the property view
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | 5.Select the constraint
| |
| − |
| |
| − | 6.Select the profile tab of the property view
| |
| − | 7.Click on the apply profile button
| |
| − | 8.Select the ValidationRule stereotype
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <center>
| |
| − | [[Image:DSML-stereotypeApplication.png]]<br>
| |
| − | Open the specification via the property view
| |
| − | </center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | You can then edit the stereotype attribute to define information about the behavior of the validation.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== Generation from Constraints =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Constraints expressed in OCL can be validated directly in the tool. This is not the case for Java constraints which must be placed in a suitable plugin. However, Papyrus supports the generation of this plugin.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Generate constraints directly into the definition
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Constraints written in OCL within the profile can be generated into the definition of the profile and read during the validation of the model.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | How to
| |
| − |
| |
| − | When you save the profile, Papyrus asks to you if want to define the profile.
| |
| − | Click on yes and then assure that the "Save OCL constraint into the definition" button is active (which is the case by default)
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == SysML Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Tutorials on SysML modeling with Papyrus ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Papyrus Zoo of SysML Models ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == MARTE Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Tutorials on MARTE modeling with Papyrus ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Papyrus Zoo of MARTE Models ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == fUML and Alf Modeling ==
| |
| − | [[Papyrus/UserGuide/fUML_ALF|Using fUML and Alf to produce executable models]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | = Developing custom DSL based editor with Papyrus =
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == UML Profile Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Profile Constraints|Define Profile Constraints]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == MetaModel Modeling ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Additional Editor Integration (this section is for the Backone) ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Diagram Editors Customizations ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Specific Diagram Editors Creation ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Diagram Editor Palette Customization ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Here you can find the documentation describing palette customization: [http://git.eclipse.org/c/papyrus/org.eclipse.papyrus.git/tree/doc/DevelopperDocuments/How-To/PapyrusDevelopperTutorial_OnPaletteCustomization_v1.0_d2010-05-10.odt Doc ]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This document can also be found in Papyrus help section => User Guide => Palette customization
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Property Editor Customization ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Model Explorer Customization ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Diagram Appearance Customization with CSS Stylesheets ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [http://wiki.eclipse.org/MDT/Papyrus/UserGuide/CSS CSS Stylesheets in Papyrus]
| |
| | | | |
| | = Additional Utilities of Papyrus = | | = Additional Utilities of Papyrus = |
| − |
| |
| − | == Collaborative Work Support ==
| |
| | | | |
| | == Layer Support == | | == Layer Support == |
| − | See [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Layers|Layers Guide]]
| + | if you want to use layer, see [https://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus/Oxygen_Work_Description/NewFeature/Layers Layers Guide] |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Automatic Layout Support ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Code Generation Support ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === JAVA Code Generation ===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === C/C++ Code Generation ===
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | see [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Codegen_description Papyrus C++ code generation] | + | == Model Execution == |
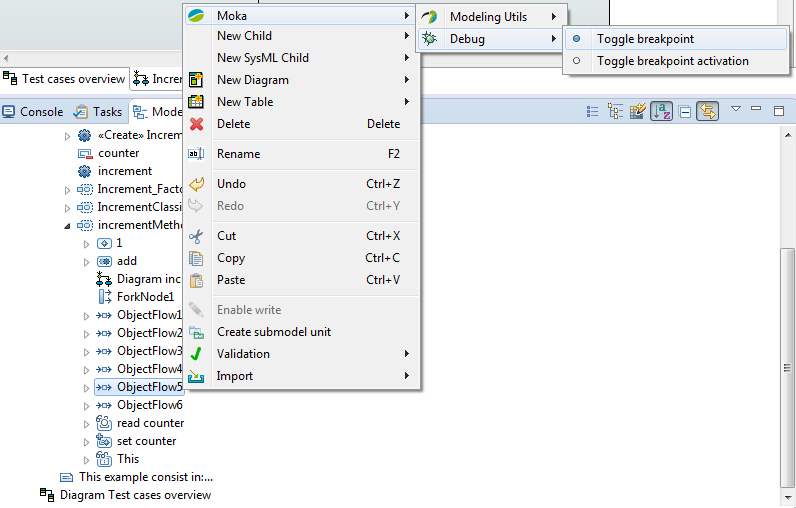
| | + | If you want to execute your model as the following picture, see [[Papyrus/UserGuide/ModelExecution|Execute your fUML models with MOKA]] |
| | | | |
| − | === ADA Code Generation ===
| + | [[File:5 - ToggleBreakpointModelExplorer.png]] |
| | | | |
| − | == Documentation Support ==
| |
| | | | |
| − | === Documentation Modelling === | + | == Papyrus for Requirements == |
| | | | |
| − | === Documentation Generation ===
| + | Papyrus for Requirements helps you to specify and analyze requirements in the context of systems modeling. It aims to cover the Specification, Management, Analysis and Validation-Verification activities of Requirements Engineering. Papyrus for Requirements depends on the components Papyrus for SysML and Papyrus for Metrics. |
| | | | |
| − | [[Category:Papyrus]] | + | Please visit the [[Installation steps of Papyrus for Requirements]] |
Papyrus for Requirements helps you to specify and analyze requirements in the context of systems modeling. It aims to cover the Specification, Management, Analysis and Validation-Verification activities of Requirements Engineering. Papyrus for Requirements depends on the components Papyrus for SysML and Papyrus for Metrics.