Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Jetty/Contributor/DevelopingWithGit"
m |
m |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Choose your access technique and follow along ... | Choose your access technique and follow along ... | ||
| − | # | + | #Make sure you have git-svn installed. You can do that by checking if there is help for you:<br/><pre>git svn --help</pre> |
| − | # | + | #Use git-svn to clone the subversion tree to your local disk. This pulls the jetty tree from Subversion, from the HEAD revision, via git-svn, to your local disk as a directory called "jetty". <br/><br/>The command line is a bit long, so here is a helper bash script to make this task a bit easier: |
#!/bin/bash | #!/bin/bash | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
--trunk $JETTYSVNROOT/trunk \ | --trunk $JETTYSVNROOT/trunk \ | ||
$JETTYSVNROOT | $JETTYSVNROOT | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
You now have the codebase in git format to work with. | You now have the codebase in git format to work with. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{note|Note:|You execute the "git svn clone" command only once. See below, "Using GIT From a Subversion User Point of View," to learn about more git commands.}} | ||
==Recommended Eclipse Plugins== | ==Recommended Eclipse Plugins== | ||
| − | Maven Integration - m2eclipse | + | We recommend these Eclipse plugins: |
| + | |||
| + | *Maven Integration - m2eclipse | ||
Update Site: http://m2eclipse.sonatype.org/update | Update Site: http://m2eclipse.sonatype.org/update | ||
| − | GIT Team Provider - jgit | + | *GIT Team Provider - jgit |
Update Site: http://www.jgit.org/updates | Update Site: http://www.jgit.org/updates | ||
| − | == | + | ==Importing into Eclipse== |
| − | + | {{tip|Build the checked out codebase on the command line to make the various dependencies available for use in Eclipse. See [[Building]] for details. (This is likely to improve in the future with more m2eclipse plugin releases).}} | |
To import Jetty into Eclipse do the following ... | To import Jetty into Eclipse do the following ... | ||
| − | # Start Eclipse | + | # Start Eclipse. |
| − | # Ensure | + | # Ensure that the recommended Eclipse plugins listed above are installed. |
| − | # Open the "Import Maven Projects" dialog by going to | + | # Open the "Import Maven Projects" dialog by going to F'''ile > Import ... > General > Maven Projects'''. |
# Browse to the 'git-svn' cloned directory for Jetty and import all projects. | # Browse to the 'git-svn' cloned directory for Jetty and import all projects. | ||
| − | ==GIT From a Subversion | + | ==Using GIT From a Subversion User Point of View== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | When you modify files and commit them, you are only commiting them to the local Git repository that you have recently checked out. | + | Git, like Subversion, is at home on the command line. Unlike Subversion, git can operate entirely without network access. When you modify files and commit them, you are only commiting them to the local Git repository that you have recently checked out. Those changes do not exist outside of your own personal git repository. |
| − | Those changes do not exist outside of your own personal git repository. | + | |
| − | The [http://git.or.cz/course/svn.html Git - SVN Crash Course] is a good | + | The [http://git.or.cz/course/svn.html Git - SVN Crash Course] is a good reference for those familiar with subversion, but new to git. The crash course gives a comparison of popular Subversion commands and what their Git equivalents are. |
| − | + | Here are a few of the most common git commands. | |
; git svn rebase | ; git svn rebase | ||
| − | : Performs an update from the | + | : Performs an update from the Subversion repository at dev.eclipse.org to your local Git repository, of the active branch, followed by a merge of active content into your local changes. |
; git svn dcommit | ; git svn dcommit | ||
| − | : Performs a push of the changes in your active | + | : Performs a push of the changes in your active Git repository branch to the Subversion repository at dev.eclipse.org. |
; git commit | ; git commit | ||
| − | : Performs a local commit of changes to your local | + | : Performs a local commit of changes to your local Git repository. |
; git status | ; git status | ||
| − | : Shows | + | : Shows the status of the changes made in your working directory (pending commits, modified files, untracked files, etc...) |
; git log | ; git log | ||
| − | : Shows a log of changes in your local | + | : Shows a log of changes in your local Git repository. |
| − | : NOTE: Your local changes | + | : NOTE: Your local changes are always at the top of this log; other entries below your changes show a 'git-svn-id' message indicating that it is content being tracked from the Subversion repository. |
; git add {filename} | ; git add {filename} | ||
| − | : Adds a file to the pending commit to your local | + | : Adds a file to the pending commit to your local Git repository. |
[[Image:Eclipse-git-flows.png]] | [[Image:Eclipse-git-flows.png]] | ||
Revision as of 17:35, 24 February 2012
Contents
Obtaining code via GIT
Jetty has its source control on dev.eclipse.org, which is accessible via two different urls.
- (Anonymous, read-only access) http://dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.jetty/
- (Developers, read-write, requires account on dev.eclipse.org) svn+ssh://{userid}@dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.jetty/
Choose your access technique and follow along ...
- Make sure you have git-svn installed. You can do that by checking if there is help for you:
git svn --help
- Use git-svn to clone the subversion tree to your local disk. This pulls the jetty tree from Subversion, from the HEAD revision, via git-svn, to your local disk as a directory called "jetty".
The command line is a bit long, so here is a helper bash script to make this task a bit easier:
#!/bin/bash JETTYSVNROOT=http://dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.jetty/jetty git svn clone -r HEAD \ --branches $JETTYSVNROOT/branches \ --tags $JETTYSVNROOT/tags \ --trunk $JETTYSVNROOT/trunk \ $JETTYSVNROOT
You now have the codebase in git format to work with.
Recommended Eclipse Plugins
We recommend these Eclipse plugins:
- Maven Integration - m2eclipse
Update Site: http://m2eclipse.sonatype.org/update
- GIT Team Provider - jgit
Update Site: http://www.jgit.org/updates
Importing into Eclipse
To import Jetty into Eclipse do the following ...
- Start Eclipse.
- Ensure that the recommended Eclipse plugins listed above are installed.
- Open the "Import Maven Projects" dialog by going to File > Import ... > General > Maven Projects.
- Browse to the 'git-svn' cloned directory for Jetty and import all projects.
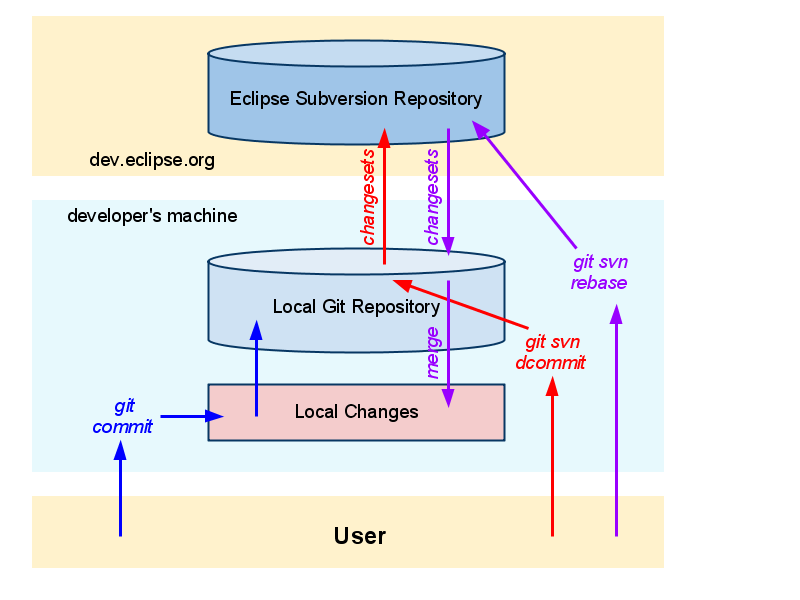
Using GIT From a Subversion User Point of View
Git, like Subversion, is at home on the command line. Unlike Subversion, git can operate entirely without network access. When you modify files and commit them, you are only commiting them to the local Git repository that you have recently checked out. Those changes do not exist outside of your own personal git repository.
The Git - SVN Crash Course is a good reference for those familiar with subversion, but new to git. The crash course gives a comparison of popular Subversion commands and what their Git equivalents are.
Here are a few of the most common git commands.
- git svn rebase
- Performs an update from the Subversion repository at dev.eclipse.org to your local Git repository, of the active branch, followed by a merge of active content into your local changes.
- git svn dcommit
- Performs a push of the changes in your active Git repository branch to the Subversion repository at dev.eclipse.org.
- git commit
- Performs a local commit of changes to your local Git repository.
- git status
- Shows the status of the changes made in your working directory (pending commits, modified files, untracked files, etc...)
- git log
- Shows a log of changes in your local Git repository.
- NOTE: Your local changes are always at the top of this log; other entries below your changes show a 'git-svn-id' message indicating that it is content being tracked from the Subversion repository.
- git add {filename}
- Adds a file to the pending commit to your local Git repository.