Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
STEM Expression Language
Contents
STEM Expressions
The STEM Expression Language is designed to allow easy access to key components of the STEM modeling and simulation framework by using variable and function-driven equations. The variables and functions are designed to simplify access to STEM APIs for getting compartment values, model parameter values, as well as access to various denominator data through functions.
Operators and Keywords
Currently the expression language is primarily built around simple arithmetic operators, such as +, -, *, and / using infix notation. Parentheses ( and ) perform subexpression grouping and enforce operator precedence.
The equals operator = is used for assignment when defining local variables.
Statements are terminated with a semicolon ;
The delta keyword defines the final statement in an expression. This represents the "return value" for the expression.
Variables
There are four types of user variables that are visible to your expressions, three of which a user can change.
- Global Variables that represent key parts of the simulation state. These are fixed and cannot be edited.
- Model Parameter variables that represent the model parameters in your model
- Compartment variables that represent the absolute and relative values of compartments in your model
- Local variables
A fifth type of variable are system variables. These variables are not visible to the expression language and are only used by STEM API developers.
Global Variables
Global variables are system-defined variables that are helpful as input to determine rates relative to time.
Examples:
- t - absolute simulation time
- timeDelta - The time step (in ms) used in the simulation. t*timeDelta is the total (simulated) time (in ms) since the start of the simulation.
Model Parameter Variables
Model parameters provide access to the rate parameters defined in your disease model - and changeable by editing the value in your disease or as part of an experiment/automatic experiment. Model parameters are generally numeric (double) values and visible by their name as defined in the model.
Examples: transmissionRate, recoveryRate, immunityLossRate
Compartment Variables
Compartment variables provide access to your model's compartment values for each region for a step in the simulation. There are two types of compartment variables:
- Relative Compartment Value variables - lower case
- Absolute Compartment Value variables - upper case
Relative Value (lower case)
Relative compartment values are calculated as Compartment Value divided by Region Population Count. They are accessible to expressions using the compartment name beginning with a lower case letter.
Examples:
- s - relative population count in 'susceptible' compartment
- i - relative population count in 'infected' compartment
- r - relative population count in 'recovered' compartment
Absolute Value (upper case)
Absolute compartment values are the absolute number of population members in a given compartment for a node at the current time step. They are accessible to expressions using the compartment name beginning with an upper case letter.
Examples:
- S - absolute population count in 'susceptible' compartment
- I - absolute population count in 'infected' compartment
- R - absolute population count in 'recovered' compartment
Local Variables
Expression statements are "local" variables. A user may define statements above the "delta" line that then can be used in subsequent statements in the expression.
Example
myVariable = S*i; delta transmissionRate*myVariable;
Functions
Functions are special procedures/operations that provide access sophisticated data access and manipulation features in STEM. Functions accept zero or more parameters as inputs and return a single output, generally a floating point number. Some functions may not accept user inputs but are still context-sensitive based on the current region and time step, for example the Earth Science functions.
Functions are identified by a name with input parameters wrapped in parentheses. Examples:
- effective(s) - effective count for the susceptible compartment
- area() - area for the current region
In addition to the built-in functions listed below, many operations in the Java Math API are also available as STEM functions.
Current STEM Functions:
| Function Name | Input Type | Output Type | Description |
| Disease Modeling API Functions | |||
| effective | compartment | number | Calculates the effective count of the compartment, includes population mixing |
| vaccinations | none | number | Calculates the number of vaccinations for the region/time step |
| isolations | none | number | Calculates the number of isolations for the region/time step |
| Earth Science API Functions | |||
| area | none | number | Gets the area Earth Science label value |
| temperature | none | number | Gets the daylight temperature Earth Science label value for the region |
| nighttemp | none | number | Gets the night temperature Earth Science label value for the region |
| precipitation | none | number | Gets the precipitation Earth Science label value for the region |
| ndvi | none | number | Gets the vegetation index Earth Science label value for the region |
| elevation | none | number | Gets the elevation Earth Science label value for the region |
Comments
A "comment" - text that is not considered or evaluated as part of the expression - can be entered by prefixing a line with // . This creates a comment for the rest of the line.
Example
// This is a comment delta tranmissionRate*S*i;
Expression Editor
The Visual Editor's Expression Editor is a simple tool to enter the equations that describe the movement of a population between two compartments for each region for each step of the simulation. The transition value - the delta - as calculated by the equation entered represents a balanced decrease from the source compartment equal to the increase in the target compartment.
Select a Transition
To select a transition, a user may either:
- Select from the Visual Editor's canvas using the Chooser Tool
- Select from the Transition drop-down menu
Expressions
The expressions used in the Expression Editor follow the STEM Expression Language. For full details, see above
Delta
The last statement in the expression editor must start with the delta keyword/operator. This is the value used to compute the movement from source to target compartments.
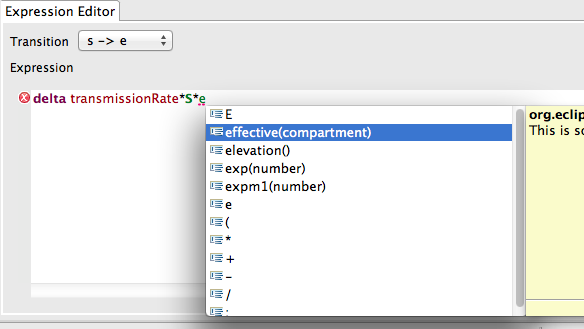
Contextual Content Assist
The content assist feature provides contextual suggestions to assist a user authoring expressions. This includes partial-completion of variables, functions, and operators. In the future, complete documentation will also be available from the content assist window.
Content assist is available at all times while editing an expression. To access the content assist prompt, simply type Control-<Space>. You can continue typing to further filter available syntax/semantic options.
Syntax Highlighting / Coloring
Incidences
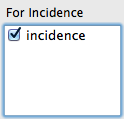
For internal and reporting purposes, the STEM simulation engine needs to know which transitions represent an increase in disease incidence. The (positive) delta value of the transition will be added to each incidence total after each step.
A transition can account to zero or more incidences that are included in a disease. Under For Incidence, check the box(es) next to the incidence name for a given transition.
Errors
Any problems with the syntax (structure) or semantic (types, etc) of your expression will result in an error.
Important note: Errors in the model will prevent the expression compiler from generating the code to update your disease/population model. Please fix any errors before trying to run the model in STEM.
The Expression Editor will notify you of an error in several ways:
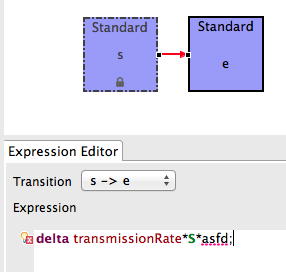
- The part of the expression that is not understood will be underlined in red
- A small red X icon will appear next to the line in the Expression Editor
- The transition connection in the Visual Editor will be highlighted red indicating an invalid expression
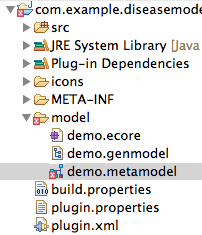
- If the Model is saved with an invalid expression, a red icon will appear next to the metamodel file in the Project Explorer
Error notification in the Visual Editor
Error notification in the Project Explorer