Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Nebula Dialog
Introduction
Aims to create a trivial Task Dialog API for SWT as described at https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn742499.aspx.
Inspired by the Oxbow Project (https://github.com/eugener/oxbow)
Contents
Usage
Formatting
You can format the message using some pseudo-HTML tags :
-
<br/>for adding a line break -
<i>...</i>to render text in italic -
<u>...</u>to render text in underline -
<b>...</b>to render text in bold -
<size>...</size>to increase/decrease text size. You can use the following syntaxes :<size=10> (10px), <size=+4>, <size=-4> -
<color>...</color>to change foreground color. You can use the following syntaxes :<color=#FFCCAA>(HTML color code),<color=9,255,10>(RGB values) and<color=aliceblue> (HTML color code) -
<backgroundcolor>...</backgroundcolor>to change background color. You can use the following syntaxes :<backgroundcolor=#FFCCAA>(HTML color code),<backgroundcolor=9,255,10>(RGB values) and<backgroundcolor=aliceblue>(HTML color code)
Display an error
The Dialog class provides 2 static methods :
public static void error(final String title, final String errorMessage); public static void error(final Shell shell, final String title, final String errorMessage);
where title is the title of the dialog box, and errorMessage the error message to display. If no shell is specified, the dialog box will be an on-top window.
Example:
Dialog.error("CRASH AND BURN !", "The application has performed an illegal action. This action has been logged and reported.");
Display an information
The Dialog class provides 2 static methods :
public static void inform(final String title, final String text); public static void inform(final Shell shell, final String title, final String text);
where title is the title of the dialog box, and text is the text to display. If no shell is specified, the dialog box will be an on-top window.
Example:
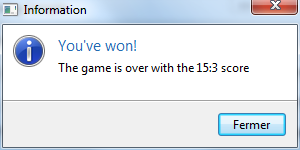
Dialog.inform("You've won!", "The game is over with the 15:3 score");
Display a confirmation
The Dialog class provides 4 static methods :
public static boolean isConfirmed(final String title, final String text); public static boolean isConfirmed(final Shell shell, final String title, final String text) public static boolean isConfirmed(final String title, final String text, final int timer) public static boolean isConfirmed(final Shell shell,final String title, final String text, final int timer)
where title is the title of the dialog box, and text is the text to display. If no shell is specified, the dialog box will be a on-top window. If a timer is specified, this is the time in second before the "Yes" button is enabled.
Example:
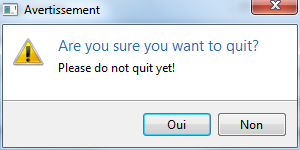
final boolean confirm = Dialog.isConfirmed("Are you sure you want to quit?", "Please do not quit yet!");
System.out.println("Choice is..." + confirm);
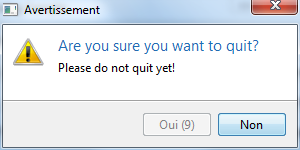
final boolean choice = Dialog.isConfirmed("Are you sure you want to quit?", "Please do not quit yet!", 10);
System.out.println("Choice is..." + choice);
Ask for a choice (radio button)
The Dialog class provides 2 static methods :
public static int radioChoice(final String title, final String text, final int defaultSelection, final String... values) public static int radioChoice(final Shell shell, final String title, final String text, final int defaultSelection, final String... values)
where title is the title of the dialog box, text is the text to display, defaultSelection is the index of the default selection (0-based index) and values is a list of propositions. If no shell is specified, the dialog box will be an on-top window.
Example:
final int choice = Dialog.radioChoice("You've got selection to make", "Go ahead", 1, "Yes", "No", "May be");
System.out.println("Choice is..." + choice);
Ask for a choice (vista style)
The Dialog class provides 2 static methods :
public static int choice(final String title, final String text, final int defaultSelection, final ChoiceItem... items); public static int choice(final Shell shell, final String title, final String text, final int defaultSelection, final ChoiceItem... items)
where title is the title of the dialog box, text is the text to display, defaultSelection is the index of the default selection (0-based index) and items is a list of propositions.
ChoiceItem is a POJO used to display the proposition, which is composed of a short text and a description.
If no shell is specified, the dialog box will be an on-top window.
Example:
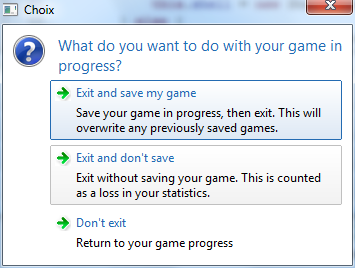
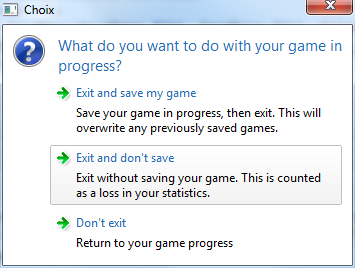
final int choice = Dialog.choice("What do you want to do with your game in\nprogress?", "", 1,
new ChoiceItem("Exit and save my game", "Save your game in progress, then exit. " + "This will\noverwrite any previously saved games."),
new ChoiceItem("Exit and don't save", "Exit without saving your game. " + "This is counted\nas a loss in your statistics."),
new ChoiceItem("Don't exit", "Return to your game progress"));
System.out.println("Choice is..." + choice);
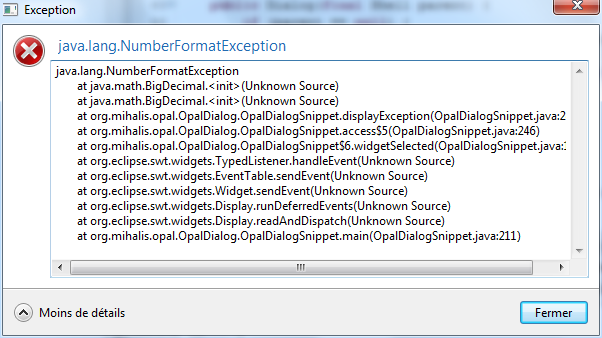
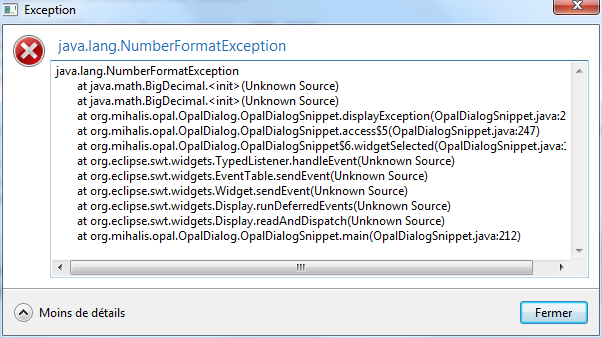
Display an exception
The Dialog class provides 1 static methods :
public static void showException(final Throwable exception)
where exception is the exception to display.
Example:
try {
new BigDecimal("seven");
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
Dialog.showException(ex);
}
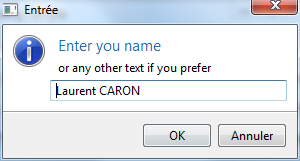
Display input
The Dialog class provides 2 static methods :
public static String ask(final String title, final String text, final String defaultValue) public static String ask(final Shell shell, final String title, final String text, final String defaultValue)
where title is the title of the dialog box, text is the text to display and defaultValue is the default value of the input box. If no shell is specified, the dialog box will be an on-top window.
Example:
final String input = Dialog.ask("Enter you name", "or any other text if you prefer", "Laurent CARON");
System.out.println("Choice is..." + input);
More complex stuffs
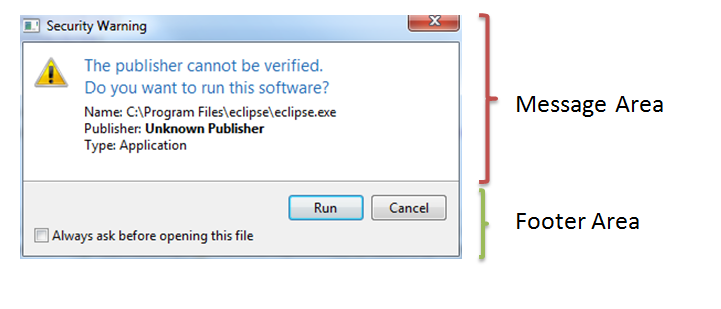
A dialog box is composed of 2 parts :
- A message area
- A footer area
Message Area
A message area is composed of 3 or 4 parts :
- A title
- An icon
- A text
- Possibly a progress bar
Each setter returns the message area object, so you can join statements.
Footer Area
A footer area is composed of different optional parts
- A checkbox : use by the method
addCheckbox(text, default selection) - A list of button labels : use the method
setButtonLabels (String... labels) - A collapsable section
- Use
setExpanded(boolean expanded)to set the collapse/expanded state - Use
setDetailText(String text)to set the text displayed when the panel is expanded
- Use
- A footer
- Use
setFooterText(String text)to set the text displayed in the footer - Use
setImage(Image image)to set the image displayed in the footer, on the left side
- Use
Each setter returns the footer area object, so you can join statements.
End
Once the message area and the footer area are built, use the method show() to open the dialog box. It returns the zero-based index of the selected button. You can also set the minimum height and width of the dialog box (by using the appropriate setters) or specifiy the buttons (by using a value of the enumeration OpalDialogType : CLOSE, NO_BUTTON, OK, OK_CANCEL, SELECT_CANCEL, SELECT_CANCEL, YES_NO).
Examples
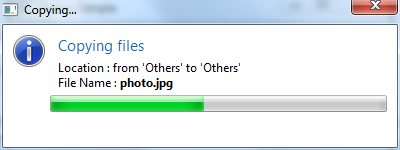
final Dialog dialog = new Dialog();
dialog.setTitle("Copying...");
dialog.setMinimumWidth(400);
dialog.getMessageArea().setTitle("Copying files") //
.setIcon(Display.getCurrent().getSystemImage(SWT.ICON_INFORMATION)) //
.setText("Location : from 'Others' to 'Others'
" + //
"File Name : photo.jpg").//
addProgressBar(0, 100, 0);
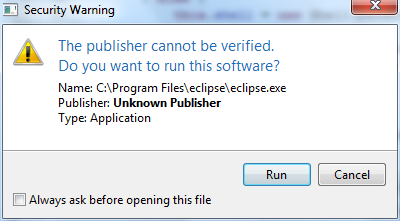
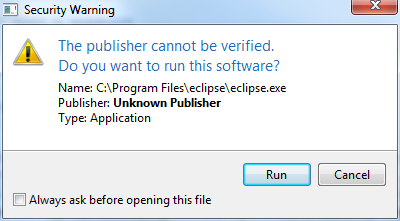
final Dialog dialog = new Dialog();
dialog.setTitle("Security Warning");
dialog.setMinimumWidth(400);
dialog.getMessageArea().setTitle("The publisher cannot be verified.\nDo you want to run this software?") //
.setIcon(Display.getCurrent().getSystemImage(SWT.ICON_WARNING)) //
.setText("Name: C:\\Program Files\\eclipse\\eclipse.exe
" + //
"Publisher: Unknown Publisher
" + //
"Type: Application
");
dialog.getFooterArea().addCheckBox("Always ask before opening this file", false).setButtonLabels("Run", "Cancel");
dialog.show();
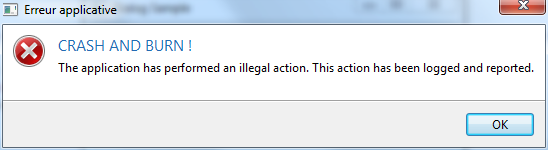
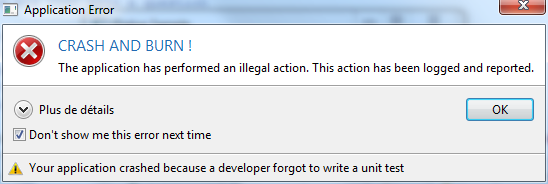
final Dialog dialog = new Dialog();
dialog.setTitle("Application Error");
dialog.getMessageArea().setTitle("CRASH AND BURN !").//
setText("The application has performed an illegal action. This action has been logged and reported.").//
setIcon(Display.getCurrent().getSystemImage(SWT.ICON_ERROR));
dialog.setButtonType(OpalDialogType.OK);
dialog.getFooterArea().setExpanded(false).addCheckBox("Don't show me this error next time", true).setDetailText("More explanations to come...");
dialog.getFooterArea().setFooterText("Your application crashed because a developer forgot to write a unit test").//
setIcon(SWTGraphicUtil.createImage("org/mihalis/opal/OpalDialog/warning.png"));
dialog.show();
i18n
Common text in the dialog can be shown in any language by putting locale specific resource bundle named opal_<locale_id>.properties on the classpath and switching default locale. The library has following built-in bundles under ’src/main/resources’: (pari Bundle/Locale)
- Default /en
- Spanish/es
- French/fr
- Italian/it
- German/de
- Polish/pl
- Chinese/cn
- Portuguese Brazil/pt_BR
More info about on Java i18n support can be found at https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/i18n/resbundle/propfile.html
Example
An example called OpalDialogSnippet.java is available in the plugin org.eclipse.nebula.widgets.opal.dialog.snippets.
An example is also available here : OpalDialogSnippet.java