Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Papyrus/customizations/robotics/bt"
(Created page with "= Task and skill concepts = The skill abstraction interfaces the task level and the level in which software components are executed (called the service level in the RobMoSys p...") |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
= How to define a new skill = | = How to define a new skill = | ||
| + | Papyrus for Robotics provides a graphical modeling language that enables the definition of skills as specified by the [https://robmosys.eu/wiki/modeling:metamodels:skill-definition RobMoSys Skill Definition Metamodel]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once the skill definition artifact is selected from the palette and dropped into a skill definition set element, it can easily be renamed and its attributes can conveniently be specified via the <code>Skills</code> tab in the property view. Configurable properties of skill attributes include <code>Name</code> and <code>Attribute Type</code>, which is normally a communication object in a [[Papyrus/customizations/robotics/servicedef|Service Definition Model]]. Several skill results can be defined, with configurable name, type and description. | ||
| + | |||
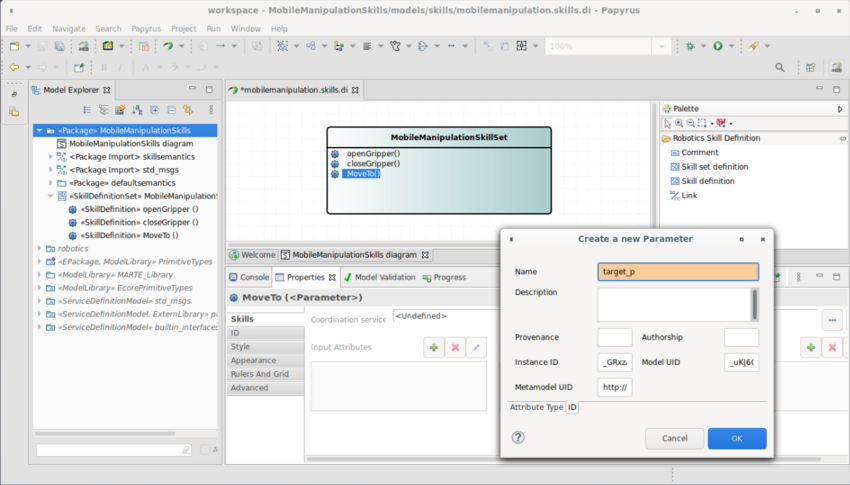
| + | The video below (click on the picture to open the animated gif) shows the definition of skill <code>MoveTo</code>, which takes one input attribute named <code>target_p</code> of type <code>Pose</code> (from ROS <code>geometry_msgs</code> package). | ||
[[Image:Papyrus-customizations-robotics-DefinitionOfSkillStatic.png|850px|link=https://wiki.eclipse.org/images/d/db/Papyrus-customizations-robotics-DefinitionOfSkillVideo.gif]] | [[Image:Papyrus-customizations-robotics-DefinitionOfSkillStatic.png|850px|link=https://wiki.eclipse.org/images/d/db/Papyrus-customizations-robotics-DefinitionOfSkillVideo.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 29 September 2020
Contents
Task and skill concepts
The skill abstraction interfaces the task level and the level in which software components are executed (called the service level in the RobMoSys parlance, see Separation of Levels and Concerns in RobMoSys).
Skills make the functionalities realized by components accessible to the task level, without binding the behavior models to concrete components. The system sequencer, which is in charge of executing the task description, demands to the components the execution of their skills by means of a well-defined configuration and coordination interface. This approach conforms to the RobMoSys Architectural Patterns for Task-Plot Coordination and for Component Coordination.
How to define a new skill
Papyrus for Robotics provides a graphical modeling language that enables the definition of skills as specified by the RobMoSys Skill Definition Metamodel.
Once the skill definition artifact is selected from the palette and dropped into a skill definition set element, it can easily be renamed and its attributes can conveniently be specified via the Skills tab in the property view. Configurable properties of skill attributes include Name and Attribute Type, which is normally a communication object in a Service Definition Model. Several skill results can be defined, with configurable name, type and description.
The video below (click on the picture to open the animated gif) shows the definition of skill MoveTo, which takes one input attribute named target_p of type Pose (from ROS geometry_msgs package).