Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
EclipseLink/Examples/JPA/GlassFishV2 Web Tutorial
Contents
- 1 EclipseLink JPA Deployed on GlassFish 2.1 using Eclipse WTP
- 1.1 Development Environment
- 1.2 Prerequisites
- 1.3 GlassFish Configuration Changes
- 1.4 JNDI Datasource Setup
- 1.5 Persistence JAR location
- 1.6 EclipseLink JAR location
- 1.7 Downloading EclipseLink Libraries
- 1.8 JDBC JAR location
- 1.9 JSR-317 JPA 2.0 EJB 3.1 Support
- 1.10 Create J2EE application
- 1.11 JPA Entity Configuration
- 1.12 Persistence.xml
- 1.13 Start Server
- 1.14 Publish EAR
- 1.15 Perform CRUD operations: JPQL insert and query
- 1.16 Troubleshooting
- 1.17 References
- 1.18 Timeline
EclipseLink JPA Deployed on GlassFish 2.1 using Eclipse WTP
Having issues running JPA 2.0 on Glassfish V2 - use Glassfish V3 (The JPA 2.0 RI) and an application managed persitence unit (no EntityManagerProxy support for 2.0 in GF 2.1) and stay away from the persistence.xml 2.0 schema - see the JPA 2.0 reference page for Glassfish V3 and V2 or WebLogic Server (up to 10.3.3) support for JPA 2.0
Note: This tutorial' is under construction for the next week as of 20091207 as part of JPA 2.0 compliance for the Glassfish V3 server in enhancement #296269 .
If you want to get a small web application running quickly on GlassFish - the services provided by the Web Tools Project plugin in the Eclipse IDE can take care of the deployment details and set the server into debug mode for you.
This basic example details how to use Eclipse to run/debug a minimum J2EE web application servlet using EclipseLink JPA as the persistence provider. The goal of this example is to detail the minimum steps needed to run EclipseLink inside SUN GlassFish using the Eclipse IDE - at this point no presentation/controller layer such as JSF, Spring or Struts will be used beyond a basic HttpServlet so we can concentrate on the the integration layer JPA setup.
The DALI project was used to generate Entities from a schema with sequences already populated.
The details described here are valid for both GlassFish V2 2.1.1 and the SUN Java System Application Server 9
Development Environment
Software: Eclipse IDE for Java EE 3.4 Ganymede (June 2008 +) with all 5 packages (DTP 1.6, EMF 2.4, GEF 3.4, WTP 3.0, XSD 2.4), Derby Database 10.4, Java JDK 1.6.0_04, GlassFish V2.1.1
This example will run fine with any Database that EclipseLink supports.
Prerequisites
Install Eclipse EE
- I installed a clean version of Eclipse 3.5 32-bit EE edition.
Install a Database
- In this example I am using Derby 10.5.3.0, the table schemas have already been created by the following Java SE project in SVN - http://dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.persistence/trunk/examples/org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.common.ddlgen/
- GlassFish comes preconfigured with a JNDI datasource connection to Derby.
Install GlassFish
I installed the latest GlassFish V2.1.1 Final build and followed the instructions on that page.
- C:\opt>java -Xmx256m -jar glassfish-installer-v2.1.1-b31g-windows.jar
- C:\opt\glassfish>cd glassfish
- C:\opt\glassfish>ant -f setup.xml
Install GlassFish Eclipse 3.5 Server Plugin
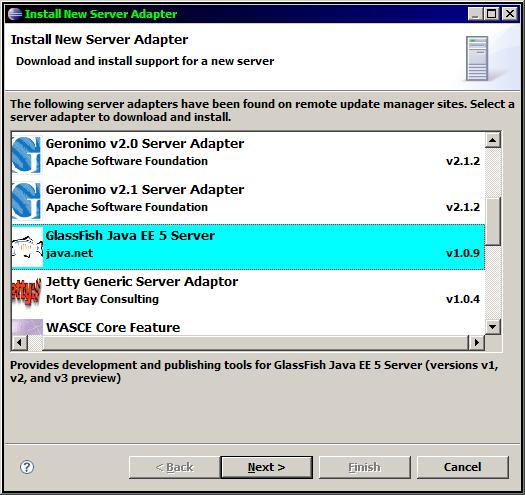
- The GlassFish server plugin is not shipped by default with Eclipse - you will need to update your Eclipse IDE to pick up the plugin.
- Goto the Servers tab in a Java EE view and right-click New | Server
- Select the link "Download additional Server adapters"
- Select the GlassFish Java EE 5 Server from java.net - make sure it is version 1.0.9+
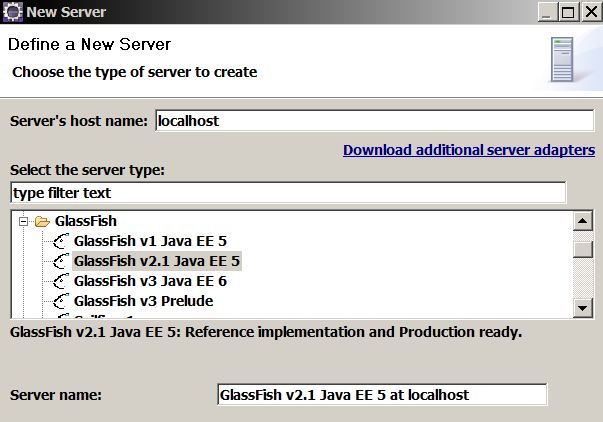
Validating the GlassFish/Eclipse configuration
- Use the V2.1.1 plugin when creating a server
- Create a default domain1 domain
- Start the server to test the plugin
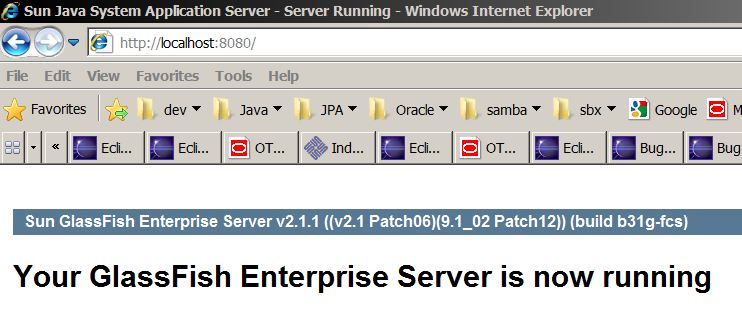
- You should see the following message when running http://localhost:8080
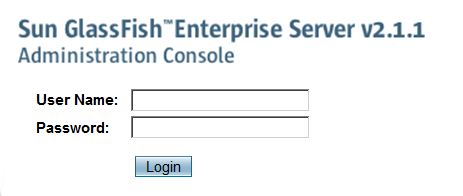
- You should see the following admin page when logging into the admin console at http://localhost:4848
- Create an empty EAR application using the Eclipse Java EE application wizard
- Create an EJB and Web subproject - do not add any facets for other servers - as GlassFish does not appear in the "Target Runtime" dropodown yet
- Switch the EAR version to 5.0 from 1.4
- Add a test.jsp page to the Web project
- Create an EJB and Web subproject - do not add any facets for other servers - as GlassFish does not appear in the "Target Runtime" dropodown yet
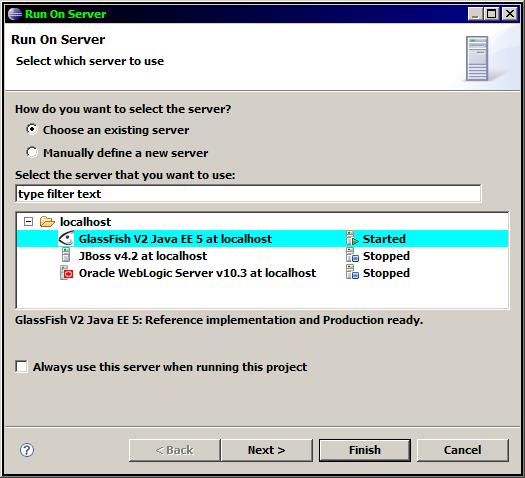
- Select the EAR project, right-click and "Run on Server" or previously associate the Targetted Runtimes with the server you just created.
- You should see an empty jsp page when running http://127.0.0.1:8080/glassFishTestWeb/test.jsp
GlassFish Configuration Changes
The following configuration changes will need to be done within the GlassFish [http:/127.0.0.1"4848 admin] console.
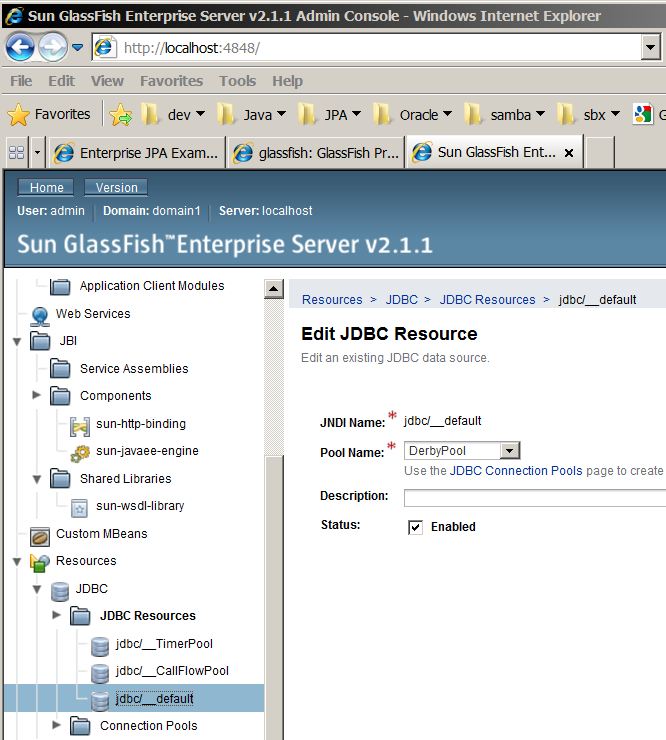
JNDI Datasource Setup
Global Scoped Datasource Setup
After logging into the admin console navigate to the following 2 sections to setup the JDBC connection pool and DataSource.
Setup GlassFish JDBC Connection Pool
- 1 - create your own connection pool and datasource
Resource | JDBC | Connection Pools | New Connection Pool Resource | JDBC | Connection Pools | New JDBC DataSource
- 2 - or use the preconfigured datasource "jdbc/__default" that comes with GlassFish
- You may want to remove the property ;create=true to manage your own database state.
- You should see the following logs on predeploy
[EL Config]: 2008.09.15 15:20:52.611--ServerSession(20983130)--Connection(4519815)--Thread(Thread[main,5,main])--connecting(DatabaseLogin( platform=>DerbyPlatform user name=> "APP" datasource URL=> "jdbc:derby:C:/opt/derby104/sun-appserv-samples;create=true" )) [EL Config]: 2008.09.15 15:20:54.200--ServerSession(20983130)--Connection(22611277)--Thread(Thread[main,5,main])--Connected: jdbc:derby:C:/opt/derby104/sun-appserv-samples User: APP Database: Apache Derby Version: 10.3.2.1 - (599110) Driver: Apache Derby Embedded JDBC Driver Version: 10.3.2.1 - (599110)
Persistence JAR location
- You will not need to add a jar for the Persistence API 1.0 - GlassFish already includes it.
- However, your project will need a reference to $EclipseLink\plugins\javax.persistence_*.jar
EclipseLink JAR location
- GlassFish V2 Build 32+ is aware of EclipseLink - however you still need to copy the latest eclipselink.jar into GlassFish.
- The eclipselink.jar should be placed off of the container lib directory $GLASSFISH_HOME/lib
- It is not recommended that the EAR include its own version of eclipselink.jar.
- Your eclipse project should reference but not include this jar.
Downloading EclipseLink Libraries
Download EclipseLink using HTTP - recommended
- Proceed to the following URL and download the latest eclipselink.zip which contains everything you need.
- http://www.eclipse.org/eclipselink/downloads/index.php
- Click on the "EclipseLink Installer Zip link which resolves to http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/download.php?file=/rt/eclipselink/releases/n.n.n/eclipselink-n.n.n.zip
- http://www.eclipse.org/eclipselink/downloads/index.php
- Expand the zip file and get the following 2 files
- eclipselink-*\eclipselink\jlib\eclipselink.jar
- eclipselink-*\eclipselink\jlib\jpa\javax.persistence_*.jar
Download EclipseLink using Maven
See the repository on http://www.eclipse.org/eclipselink/downloads/index.php
Download EclipseLink using SVN - developers only
- Get the following eclipselink.jar and javax.persistence*.jar from http://www.eclipselink.org ready for your EclipseLink shared library.
- The following page details four different ways to either obtain the binary jars or download the source and build them yourself with an anon account.
- http://wiki.eclipse.org/EclipseLink/Source
JDBC JAR location
Jars for Derby 10, Oracle 11, MySQL 5 and Sybase 5.5/6.0 should be placed off the container lib directory $GLASSFISH_HOME/lib if they don't already exist.
JSR-317 JPA 2.0 EJB 3.1 Support
- EclipseLink 1.2 and 2.0+ fully implement the JPA 2.0 specification via enhancement # 248291 and are the RI for the GlassFish V3 Java EE 6 server.
- See 296269 for details on JPA 2.0 on Glassfish V2 and V3
- See the following design page details on Glassfish Server support for JPA 2.0
Create J2EE application
Either checkout the 3 source projects attached to this tutorial or create your own J2EE Enterprise Application as below. File | new | project | J2EE | Enterprise Application Project Select server, use 5.0 Ear version
Create a new Web and an optional EJB project
Select generate deployment descriptor if you want to change the context-root
- Path changes
<classpathentry combineaccessrules="false" kind="src" path="/org.eclipse.persistence.core"/> <classpathentry combineaccessrules="false" kind="src" path="/org.eclipse.persistence.jpa"/> or <classpathentry combineaccessrules="false" kind="src" path="/eclipselink.jar"/>
- After EAR project creation - reference the org.eclipse.peristence.core and jpa projects or include a reference to eclipselink.jar in your EJB project and reference the EJB project from your WAR project.
- If you don't reference the eclipselink.* projects then include a classpath reference to persistence.jar and an Oracle (or other Database) JDBC driver jar for your DB - You will need to put this JDBC driver jar in your /domains/domain1/lib directory as well.
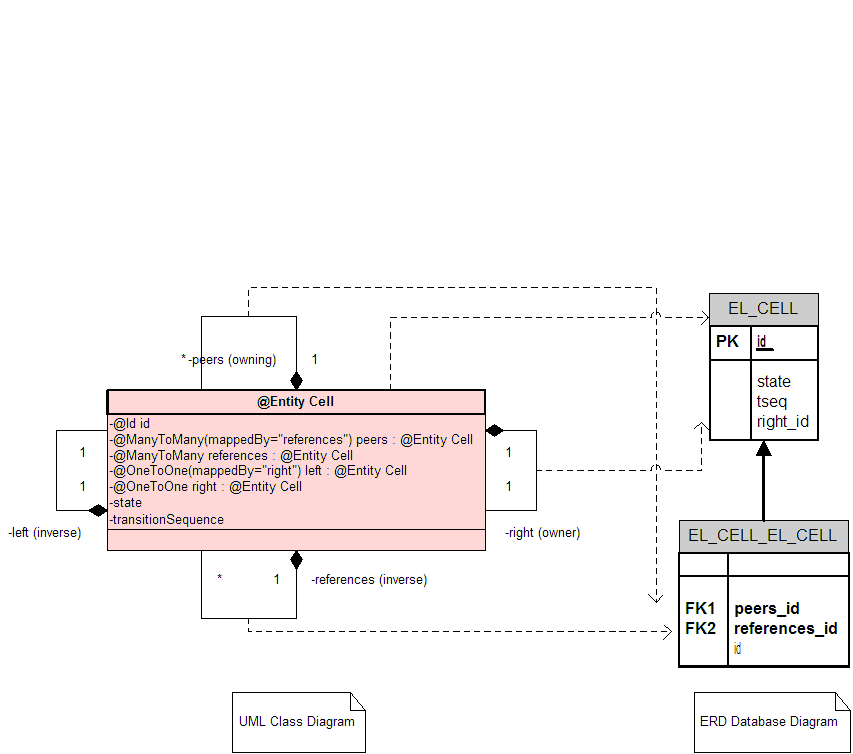
UML Data Model
The following single entity Cell has a @ManyToMany bidirectional relationship to itself.
Tutorial Design
The goal of the tutorial is to demonstrate a quick start end-to-end deployment on a specific application server of an EclipseLink JPA application. To accomplish this...
- The web framework is a simple servlet so we avoid container specific issues around JSF implementation.
- The data model is very simple (@ManyToMany) - as the other tutorials get into more advanced JPA entity concepts and annoations
- The entitymanager is container managed where possible by injection
- The schema is generated by DDL generation in a separate common application managed SE app.
- The application context name is standard across servers
- The datasource is globally defined (by the user) on the server - with the only configuration setting being the jta-data-source element in persistence.xml
DDL/Schema Generation
- The database schema for this example can be automatically generated using the DDL generation capability of EclipseLink (normally only used by development or for demos). The following project in SVN can be run as an application managed stand-alone JPA project that has ddl-generation turned on in the persistence.xml.
- http://dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.persistence/trunk/examples/org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.common.ddlgen
- Note: DDL Generation is not possible on a container managed entity manager connected to a JTA datasource - hence the use of a separate project that is server agnostic and sharable by all the JPA Web application tutorials in this section of the Wiki.
JPA Entity Configuration
For all other application servers that support JPA 1.0 profiled so far (WebLogic, OC4J, Tomcat and JBoss) - I was able to use BigDecimal as the @Id for entity classes. In GlassFish 2 I had to switch to using BigInteger (or Long) as the entity @Id.
@Entity @Table(name="EL_CELL") public class Cell implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8865917134914502125L; @Id // keep the sequence column name under 30 chars to avoid an ORA-00972 @SequenceGenerator(name="EL_SEQUENCE_CELL", sequenceName="EL_CELL_SEQ", allocationSize=25) @GeneratedValue(generator="EL_SEQUENCE_CELL") private BigInteger id; ....
Persistence.xml
The GlassFish V2 server is defined as the SUN Application Server 9 in JPA as "SunAS9"
Verify in particular that you have the eclipselink.target-server property set - especially if you are migrating from TopLink Essentials to EclipseLink - where the provider and target-server were defaulted.
- JTA : Put persistence.xml beside your JPA entities in yourProjectEJB/ejbModule/META-INF
- The provider must be specified or it will default to TopLink Essentials
<persistence version="1.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_1_0.xsd"> <persistence-unit name="enterprise" transaction-type="JTA"> <provider>org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider</provider> <jta-data-source>jdbc/__default</jta-data-source> <properties> <property name="eclipselink.target-server" value="SunAS9"/> <property name="eclipselink.logging.level" value="FINEST"/> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
- RESOURCE_LOCAL : non-JTA : Put persistence.xml beside your JPA entities in yourProjectEJB/ejbModule/META-INF
- This one is used by a local SE Java app to create and pre-populated the derby database
<persistence-unit name="stat.create.tables" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <provider>org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider</provider> <class>entity..</class> <properties> <property name="eclipselink.jdbc.platform" value="org.eclipse.persistence.platform.database.DerbyPlatform"/> <property name="eclipselink.jdbc.driver" value="org.apache.derby.jdbc.EmbeddedDriver"/> <property name="eclipselink.target-database" value="Derby"/> <property name="eclipselink.jdbc.url" value="jdbc:derby:C:/opt/derby104/sun-appserv-samples;create=true"/> <property name="eclipselink.jdbc.user" value="APP"/> <property name="eclipselink.jdbc.password" value="APP"/> <property name="eclipselink.logging.level" value="FINEST"/> <property name="eclipselink.ddl-generation" value="drop-and-create-tables"/> <property name="eclipselink.ddl-generation.output-mode" value="database"/> </properties> </persistence-unit>
Start Server
- Steps: Select the EAR and [Run on Server].
- The first "Run on Server" may not start the server, in this case you "Start Server" and then "Run on Server".
Publish EAR
- You will see the following in the server.log redirected to Eclipse.
Buildfile: C:\wse\w35d\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.jst.server.generic.core\serverdef\sunappsrv-ant.xml
replace.module.name.space:
[delete] Deleting: C:\wse\w35d\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.jst.server.generic.core\serverdef\fooFile2.properties
deploy.j2ee.ear:
resourcesfile.check:
replace.module.name.space:
[delete] Deleting: C:\wse\w35d\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.jst.server.generic.core\serverdef\fooFile2.properties
tools:
addresources:
[jar] Building jar: C:\wse\w35d\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.wst.server.core\tmp2\org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.glassfishv2.EnterpriseEAR.ear
replace.module.name.space:
[delete] Deleting: C:\wse\w35d\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.jst.server.generic.core\serverdef\fooFile2.properties
tools:
deploy:
[exec] Command deploy executed successfully.
deploy-url-message:
[echo] Application Deployed at: http://localhost:8080/org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.glassfishv2.EnterpriseEAR
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 3 seconds
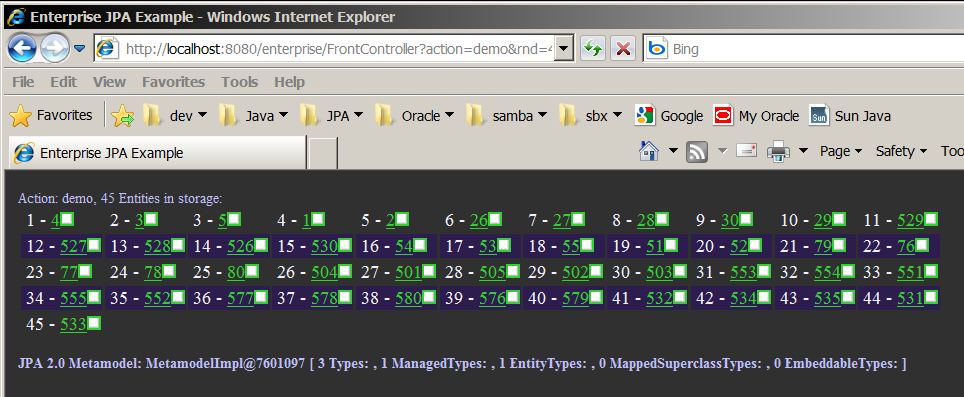
Perform CRUD operations: JPQL insert and query
Browser Output
Troubleshooting
EJBException on valid JPA 2.0 API
- The following exception will occur if you are running the default JPA 1.0 API that ships with Glassfish V2 because it is Java EE 5 compliant - you will need the JPA 2.0 API specification jar higher in your server classpath.
javax.ejb.EJBException at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.processSystemException(BaseContainer.java:3903) at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.completeNewTx(BaseContainer.java:3803) at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvokeTx(BaseContainer.java:3605) at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvoke(BaseContainer.java:1388) at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvoke(BaseContainer.java:1325) at com.sun.ejb.containers.EJBLocalObjectInvocationHandler.invoke(EJBLocalObjectInvocationHandler.java:205) at com.sun.ejb.containers.EJBLocalObjectInvocationHandlerDelegate.invoke(EJBLocalObjectInvocationHandlerDelegate.java:127) at $Proxy32.getMetamodel(Unknown Source
References
- See JPA 2.0 page for Glassfish Server http://wiki.eclipse.org/EclipseLink/Development/JPA_2.0/glassfish
- See Integrating EclipseLink with an Application Server in the ELUG
- See Developing JPA Projects in the EclipseLink User's Guide.
- http://dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.persistence/trunk/examples/org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.glassfishv2.enterpriseEAR
- http://dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.persistence/trunk/examples/org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.glassfishv2.enterpriseEJB
- http://dev.eclipse.org/svnroot/rt/org.eclipse.persistence/trunk/examples/org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.glassfishv2.enterpriseWeb
- EclipseLink Architecture and UML Diagrams
Timeline
- 20080915 - Originated on build 20080915 - Michael O'Brien
- 20091207 - retrofitting for JPA 2.0 usage