Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
E4/DeclarativeUI/XAML Roundup
Contents
Name of Technology
eXAML - eclipse XAML
Purpose
Adopt XAML technology as UI XML serialization and provide a direct mapping to SWT/JFace with the support of JFace DataBinding
Contact
Committers
Yves YANG, Thomas Guiu and others
Current License
XAML specification is licensed under OSP license (Open Specification Promesses)
eXAML is an Open Source under EPL Licnese.
Description
Extensible Application Markup Language (XAML) is a markup language for declarative application programming. Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) implements a XAML loader and provides XAML language support for Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) types such that you can create the majority of your application UI in XAML markup. Silverlight uses the same technology for Declarative UI.
Soyatec has developed a solution for Java: eFace, which is compatible with XAML/WPF. Obviously, XAML is a generic solution that can be used not only in .NET environment, but also in Java/Eclipse.
"eXAML" under license EPL is a specific solution of using XAML grammar for SWT/JFace directly. It is a combination of XAML serialization technology with SWT/JFace semantic.
Precisely, XAML simplifies creating a UI programming model. You can create visible UI elements in the declarative XAML markup, and then separate the UI definition from the run-time logic by using code-behind files. The ability to mix code with markup in XAML is important because XML by itself is declarative. An XML based declarative language is very intuitive for creating interfaces ranging from prototype to production, especially for people with a background in web design and technologies. Unlike most other markup languages, XAML directly represents the instantiation of managed objects. This general design principle enables simplified code and debugging access for objects that are created in XAML.
There are two ways to apply XAML to e4:
- SWT Centric
- Abstraction UI Model
eXAML implements "SWT Centric" approach.
The benefices of XAML for e4 are following:
- XAML is more human-readable and light-weight markup without ambiguity between properties and child type
- High Extensible
- Well defined and complete specification
- Mature and Generic Declarative UI solution
- Share the common tools like eclipse SLDT
Examples of eXAML
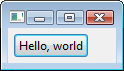
1. Hello, world
Here is a simple example.
<Shell xmlns=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt/presentation” xmlns:x=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt”> <Shell.layout> <FillLayout/> </Shell.layout> <Button text="Hello, world!"> </Button> </Shell>
The same UI can be developed in Java corresponding:
Shell parent = new Shell(); parent.setLayout(new FillLayout()); Button button = new Button(parent, SWT.NONE); button.setText("Hello, world!");
To load and start a simple application, we use the class EXaml:
Shell shell = EXaml.load(file).getShell(); shell.pack(); shell.open(); while (!shell.isDisposed()) { if (!shell.getDisplay().readAndDispatch()) { shell.getDisplay().sleep(); } }
It is possible to load a UI resource under a Composite:
EXaml.load(parent, uri);
2. Appearance and Event
In the previous example, we just rewrite Java code in XML. This example illustrates the separation between UI and event handling.
The appearance is defined in XAML.
<Shell xmlns=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt/presentation” xmlns:x=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt” x:Class="ui.EventHandler"> <Shell.layout> <GridLayout/> </Shell.layout> <Button text="Click Me!" SelectionEvent="clickButton"> </Button> </Shell>
The extension attribute x:Class declares the Java class to handle all events. The Button event is handled by clickButton method in the class ui.EventHandler. The association is setup during the loading:
package ui; import org.eclipse.swt.Event; import org.eclipse.swt.Button; public class EventHandler { protected void clickButton(Event event) { Button button = (Button )event.widget; button.setText("Hello, world!"); } }
When the button gets selected, the method clickButton is invoked to change the Button text to "Hello, world!".
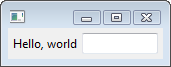
3. Layout
<Composite xmlns=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt/presentation” xmlns:x=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt”> <Composite.layout> <GridLayout numColumns="2"/> </Composite.layout> <Label text="Hello, world"/> <Text x:style="BORDER"> <Text.layoutData> <GridData horizontalAlignment="FILL" grabExcessHorizontalSpace="true"/> </Text.layoutData> </Text> </Composite>
- The simple element name (<Composite>) corresponds to a class name.
- The qualified element name (i.g. <Composite.layout>) corresponds to a property defined by an element.
- The default namespace corresponds to system packages.
- User defined package can be declared as a namespace in the format: ”clr-namespace:<package>=<jar>”
This is functionally equivalent to:
Composite parent = new Composite(shell, SWT.NONE); parent.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, false); Label label = new Label(parent, SWT.NULL); label.setText("Hello, world"); Text text = new Text(parent, SWT.BORDER); text.setLayoutData(new GridData(GridData.FILL_HORIZONTAL | GridData.GRAB_HORIZONTAL));
4. Extensibility and Re-usability
In case, if you have your own layout named as ui.MyGridLayout, it can be used directly. The code will be:
<Composite xmlns=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt/presentation” xmlns:x=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt” xmlns:y=”cls-namespace:ui”> <Composite.layout> <y:MyGridLayout numColumns="2"/> </Composite.layout> <Label text="Hello, world"/> <Text x:style="BORDER"> <Text.layoutData> <GridData horizontalAlignment="FILL" grabExcessHorizontalSpace="true"/> </Text.layoutData> </Text> </Composite>
In the same way, a customized UI component can be used directly:
<Composite xmlns=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt/presentation” xmlns:x=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt” xmlns:y=”cls-namespace:ui”> <Composite.layout> <GridLayout numColumns="2"/> </Composite.layout> <y:PersonView /> <y:PersonView.layoutData> <GridData horizontalAlignment="FILL" grabExcessHorizontalSpace="true"/> </y:PersonView.layoutData> </y:PersonView> </Composite>
Where the ui.PersonView is a UI component developed by two files:
XAML file PersonView.xaml
<Composite xmlns=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt/presentation” xmlns:x=”http://www.eclipse.org/swt” x:Class="ui.PersonView" xmlns:y=”cls-namespace:ui”> <Composite.layout> <GridLayout numColumns="2"/> </Composite.layout> <Label text="Name"/> <Text x:style="BORDER"> <Text.layoutData> <GridData horizontalAlignment="FILL" grabExcessHorizontalSpace="true"/> </Text.layoutData> </Text> </Composite>
Java class PersonView.java
package ui; import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite; public class PersonView extends Composite { ... }
5. Data Binding
The DataBinding engine relies on Eclipse DataBinding component.
If we bind the text attribute of Label to a property “Name” of a Person, here is the data binding expression:
<Label text="{binding path=Name}"/>It has the same result as following, but the expression is in pure XML:
<Label> <Label.text> <Binding path=”Name”/> </Label.text> <Label>
The data context of Label should be a person.
6. JFace integration
The following example shows the JFace direct integration with ListViewer.
We have a Class Company that has a name and a collection of Employee. The company is bound to the root Composite object. The child Text is bound to Name of company and ListViewer to property employees of type Java Collection.
<Composite xmlns="http://www.eclipse.org/swt/presentation" xmlns:x="http://www.eclipse.org/swt" xmlns:j="clr-namespace:jface.listviewer" x:DataContext="{StaticResource myCompany}"> <Composite.layout> <GridLayout numColumns="2"/> </Composite.layout> <x:Composite.Resources> <j:Company x:Key="myCompany" Name="Soyatec"> <j:Company.employees> <j:Employee Name="Thomas"/> <j:Employee Name="Jin"/> </j:Company.employees> </j:Company> </x:Composite.Resources> <Label text="Name"/> <Text text="{Binding Path=Name}"/> <ListViewer input="{Binding Path=employees}"> <ListViewer.contentProvider> <j:ContentProvider/> </ListViewer.contentProvider> <ListViewer.labelProvider> <j:LabelProvider/> </ListViewer.labelProvider> <ListViewer.control.layoutData> <GridData horizontalAlignment="FILL" grabExcessHorizontalSpace="true" horizontalSpan="2"/> </ListViewer.control.layoutData> </ListViewer> </Composite>