Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Scout/Tutorial/3.7/Minicrm/Code Types"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ScoutPage|cat=Tutorial}} {{note|Scout Tutorial|This page belongs to the {{ScoutLink|Tutorial|Minicrm Step-by-Step|Minicrm Step-by-Step Tutorial}}. It explains how to add and use Code Types. You need to finish at least step {{ScoutLink|Tutorial|Add a form|Add a form}} in order to continue.}} | {{ScoutPage|cat=Tutorial}} {{note|Scout Tutorial|This page belongs to the {{ScoutLink|Tutorial|Minicrm Step-by-Step|Minicrm Step-by-Step Tutorial}}. It explains how to add and use Code Types. You need to finish at least step {{ScoutLink|Tutorial|Add a form|Add a form}} in order to continue.}} | ||
| − | == How to | + | == How to Create Code Types == |
Code Types always contain of an ID and a list of values. | Code Types always contain of an ID and a list of values. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[Image:Scout new company type codetype.jpg]] | [[Image:Scout new company type codetype.jpg]] | ||
| − | The Code ID needs to be an unique number, which helps to identify the values belonging to the Code Type. | + | The Code ID needs to be an unique number, which helps to identify the values belonging to the Code Type.Always leave enough space between the Code Type's IDs, because the Code Type's values need IDs as well. |
| − | + | ||
| − | Always leave enough space between the Code Type's IDs, because the Code Type's values need IDs as well. | + | |
Idea is that the IDs of Code Types and their values are close together (e.g. Code Type 10000 and Values from 10001 to 10099, next Code Type 10100). | Idea is that the IDs of Code Types and their values are close together (e.g. Code Type 10000 and Values from 10001 to 10099, next Code Type 10100). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Enter the information into the Code Type form according to the picture: | Enter the information into the Code Type form according to the picture: | ||
[[Image:Scout company type codetype form.jpg]] | [[Image:Scout company type codetype form.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Right-click on the newly created Code Type and choose New Code… | Right-click on the newly created Code Type and choose New Code… | ||
[[Image:Scout company type codetype new childcode.jpg]] | [[Image:Scout company type codetype new childcode.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Increase the CompanyType Code Type's ID by 1 and assign it to the Code ID field. Give it a name like Customer. | Increase the CompanyType Code Type's ID by 1 and assign it to the Code ID field. Give it a name like Customer. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 35: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | == How to | + | == How to Use Code Types == |
So let's use the code type inside the Company Form: we are going to add a Radio Button Group containing those two values. | So let's use the code type inside the Company Form: we are going to add a Radio Button Group containing those two values. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 46: | ||
[[Image:Scout company type codetype new radiobutton group.jpg]] | [[Image:Scout company type codetype new radiobutton group.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
In the properties editor go to the property Code Type and choose the Code Type CompanyTypeCodeType we have previously created. That’s all we need to do to fill the Code Type's values into the Radio Button Group. | In the properties editor go to the property Code Type and choose the Code Type CompanyTypeCodeType we have previously created. That’s all we need to do to fill the Code Type's values into the Radio Button Group. | ||
[[Image:Scout company type codetype radiobutton group add codetype.jpg]] | [[Image:Scout company type codetype radiobutton group add codetype.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
After adding this additional field, don't forget to update the form data: right-click on the CompanyForm and choose "Update Form Data" | After adding this additional field, don't forget to update the form data: right-click on the CompanyForm and choose "Update Form Data" | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | To write and read the values provided by the Radio Button from the database, we need to adjust the CompanyProcessService: | ||
<br> <source lang="java"> | <br> <source lang="java"> | ||
| Line 118: | Line 128: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | == Conditional | + | == Conditional Dependencies Between Fields == |
As already mentioned before, we need a Smart Field to choose a rating between A and D on the Company Form. This Smart Field must only be visible, when the company is type of Customer. | As already mentioned before, we need a Smart Field to choose a rating between A and D on the Company Form. This Smart Field must only be visible, when the company is type of Customer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
First we have to create another Code Type called CompanyRatingCodeType and add four Codes A, B, C and D to it. | First we have to create another Code Type called CompanyRatingCodeType and add four Codes A, B, C and D to it. | ||
| − | Go to [[# | + | Go to [[#How_to_create_Code_Types]] if you're lost. |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Scout company rating codetype overview.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | After creating the Code Type, we add another field to the Company Form: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Back in Scout Explorer expand the tree like: client | + | Back in Scout Explorer expand the tree like: client > Forms > CompanyForm > MainBox, right-click on MainBox and choose New Form Field… |
| − | The field's type is Smart Field. Enter the information provided by the picture in the wizard's next form. | + | The field's type is Smart Field. Enter the information provided by the picture in the wizard's next form. |
| − | [[Image:Scout company rating new smartfield.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Scout company rating new smartfield.jpg]] |
{{tip|Edit code directly|have a look at the properties and make sure that there is a Code Type assigned to the Code Type's field | {{tip|Edit code directly|have a look at the properties and make sure that there is a Code Type assigned to the Code Type's field | ||
| Line 141: | Line 157: | ||
# open the Company Form class, go to the inner class CompanyRatingField, which represents the Smart Field. | # open the Company Form class, go to the inner class CompanyRatingField, which represents the Smart Field. | ||
# Type getConfiguredCodeType and press ctrl + space what automatically creates the method according to the super class' ones. | # Type getConfiguredCodeType and press ctrl + space what automatically creates the method according to the super class' ones. | ||
| − | # Change the return value to CompanyRatingCodeType.class or whatever your Code Type's name is.}} | + | # Change the return value to CompanyRatingCodeType.class or whatever your Code Type's name is.}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | As there is a dependency between fields, we have to define a master – slave – relation. This happens by telling the slave who's its master. | |
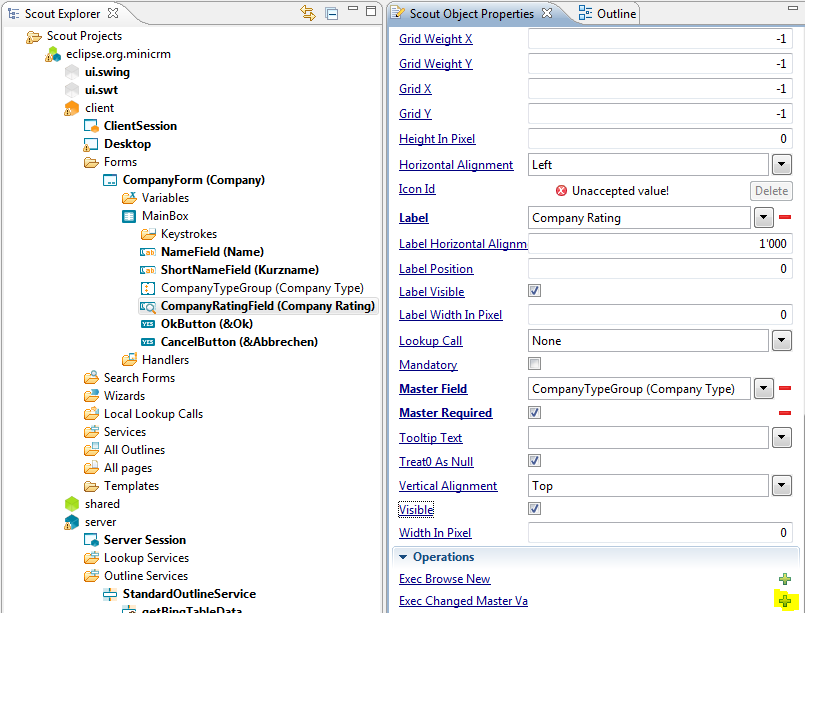
| − | + | Expand the tree in the Scout Explorer like: client > Forms > CompanyForm > MainBox > CompanyRatingField. Set the Master Field and Master Required (see picture) and click on Exec Changed Master Value. | |
| − | + | [[Image:Scout company rating codetype smartfield master.jpg]] | |
| − | Code Type and Code IDs can get accessed very easily because they are defined as static. | + | |
| + | |||
| + | Open the CompanyForm class and go to the inner class CompanyRatingField. We need to adjust the execChangedMasterValue method, which is called whenever something happens in the CompanyTypeGroup Field, this because of the master – slave – relation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When execChangedMasterValue is called, we check if the customer type value equals the Customer code. If so, the fields is set visible and enabled. In all other cases the field has to be invisible and disabled, as well as set to null nothing must be written to the database. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Code Type and Code IDs can get accessed very easily because they are defined as static. | ||
<source lang="java"> | <source lang="java"> | ||
| Line 171: | Line 191: | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| − | </source> | + | </source> |
{{tip|Scout Utility Classes|calling a member means to make sure that the object is not null. Standard operations like comparisons etc. always follow the same pattern: first check for null values, second call the actual operation. To prevent the programmer from coding the same thing all over again, Scout often provides so called Utility classes, which make sure that no unnecessary Exceptions will be thrown. | {{tip|Scout Utility Classes|calling a member means to make sure that the object is not null. Standard operations like comparisons etc. always follow the same pattern: first check for null values, second call the actual operation. To prevent the programmer from coding the same thing all over again, Scout often provides so called Utility classes, which make sure that no unnecessary Exceptions will be thrown. | ||
| − | Have a look at those Utility classes by pressing ctrl + alt + T and type *Utility. It's highly recommended to use these classes whenever possible.}} | + | Have a look at those Utility classes by pressing ctrl + alt + T and type *Utility. It's highly recommended to use these classes whenever possible.}} |
| − | Now that the Form works, we have to make sure that the rating value can be read and written from and to the database. So let's change the CompanyProcessService once more. | + | Now that the Form works, we have to make sure that the rating value can be read and written from and to the database. So let's change the CompanyProcessService once more. |
<source lang="java"> | <source lang="java"> | ||
| Line 247: | Line 267: | ||
return formData; | return formData; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | </source> | + | </source> |
| − | == Display Code Types in Tables == | + | == Display Code Types in Tables == |
| − | Whenever we want to display a Code Type in a table, we cannot just use the value returned by the database query. This out of the reason that Code Types IDs are stored and displaying IDs would mean nothing to a user. | + | Whenever we want to display a Code Type in a table, we cannot just use the value returned by the database query. This out of the reason that Code Types IDs are stored and displaying IDs would mean nothing to a user. |
| − | Instead we use a Smart Column, tell it which Code Type will be returned and let it translate the ID into a name. | + | Instead we use a Smart Column, tell it which Code Type will be returned and let it translate the ID into a name. So let's add a new column to the CompanyTablePage and extend the StandardOutlineService. |
| − | So let's add a new column to the CompanyTablePage and extend the StandardOutlineService. | + | |
| − | Expand the tree in Scout Explorer like: client | + | Expand the tree in Scout Explorer like: client > All pages and right-click on CompanyTablePage > Table > Columns and choose New Column… |
| − | {{tip|All roads lead to Rome|Wherever CompanyTablePage has been linked to, we'll find it (e.g. client > Desktop > StandardOutline > Child Pages > CompanyTablePage). Nevertheless, all pages, no matter where they are linked to, are situated in: client > All pages.}} | + | {{tip|All roads lead to Rome|Wherever CompanyTablePage has been linked to, we'll find it (e.g. client > Desktop > StandardOutline > Child Pages > CompanyTablePage). Nevertheless, all pages, no matter where they are linked to, are situated in: client > All pages.}} |
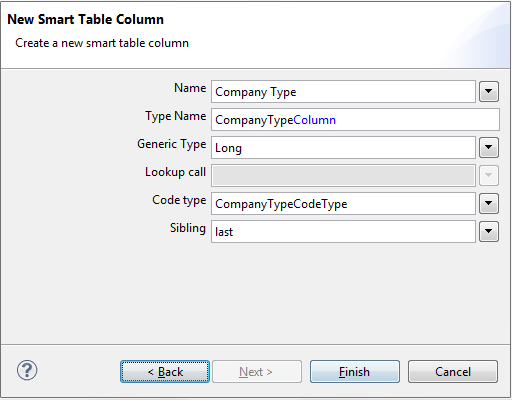
| − | Choose type Smart Column and fill in the information according to the picture. | + | Choose type Smart Column and fill in the information according to the picture. |
[[Image:Scout company rating codetype smartcolumn.jpg]] | [[Image:Scout company rating codetype smartcolumn.jpg]] | ||
| − | Adjust the getCompanyTableData method in the StandardOutlineService (server | + | |
| + | |||
| + | Adjust the getCompanyTableData method in the StandardOutlineService (server > Outline Services > StandardOutlineService): | ||
<source lang="java"> | <source lang="java"> | ||
| Line 277: | Line 298: | ||
" FROM COMPANY " + | " FROM COMPANY " + | ||
" WHERE 1 = 1 "); | " WHERE 1 = 1 "); | ||
| − | </source> | + | </source> |
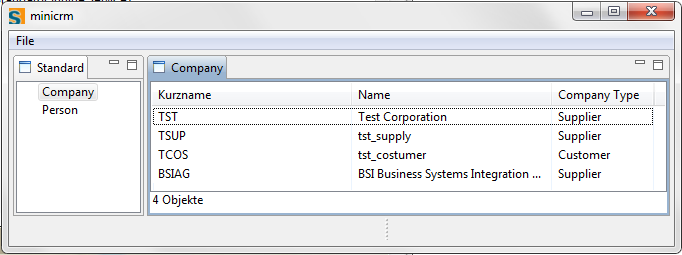
[[Image:Scout company type rating codetype table.jpg]] | [[Image:Scout company type rating codetype table.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 09:06, 21 February 2011
The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.
Contents
How to Create Code Types
Code Types always contain of an ID and a list of values.
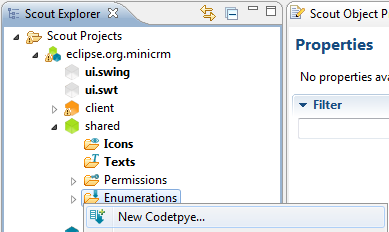
Open the shared node in Eclipse Scout and expand the tree until you reach the Enumerations node. Right-click on the node and choose "New Codetype…" menu.
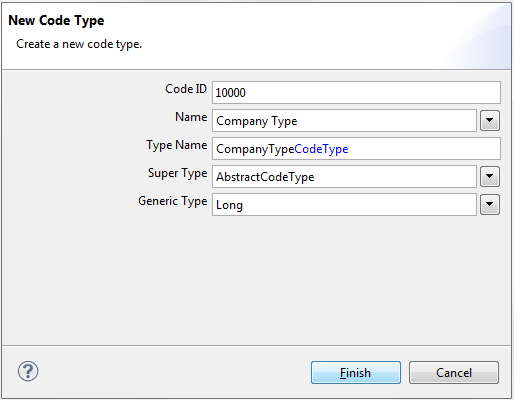
The Code ID needs to be an unique number, which helps to identify the values belonging to the Code Type.Always leave enough space between the Code Type's IDs, because the Code Type's values need IDs as well.
Idea is that the IDs of Code Types and their values are close together (e.g. Code Type 10000 and Values from 10001 to 10099, next Code Type 10100).
Enter the information into the Code Type form according to the picture:
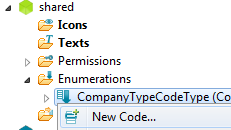
Right-click on the newly created Code Type and choose New Code…
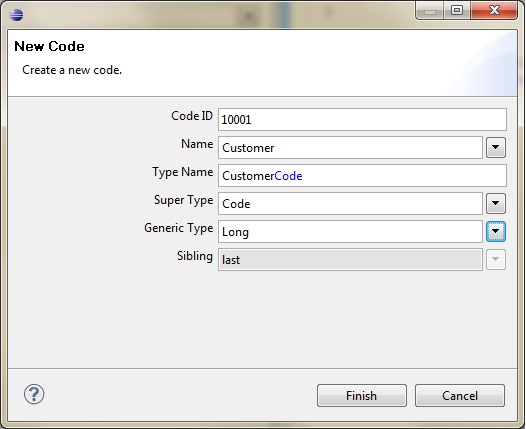
Increase the CompanyType Code Type's ID by 1 and assign it to the Code ID field. Give it a name like Customer.
Repeat these last two steps for another code called Supplier (Code ID: 10002).
How to Use Code Types
So let's use the code type inside the Company Form: we are going to add a Radio Button Group containing those two values.
In a Radio Button Group only one item can be selected at a time. This is exactly what we need here, as we don't like a company being both, customer and supplier.
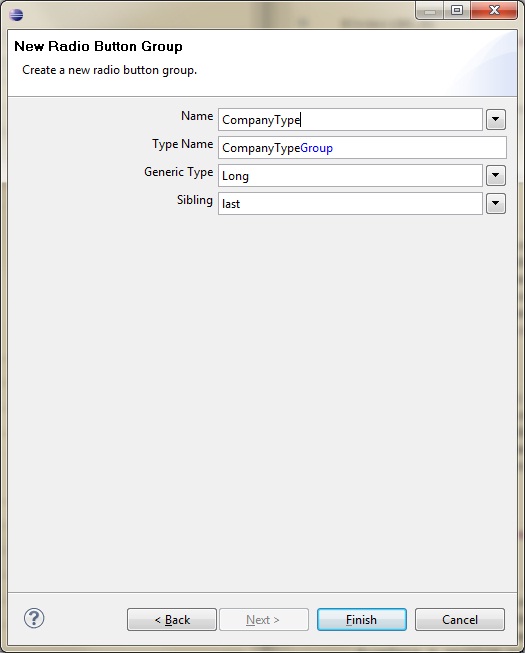
Back in Scout Explorer we expand the tree like: client > Forms > CompanyForm and right-click on MainBox to choose New Form Field…
Choose Radio Button Group as Type, give it a name like CompanyType and press Finish.
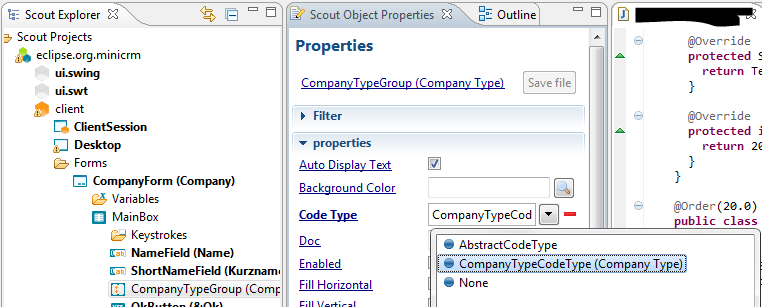
In the properties editor go to the property Code Type and choose the Code Type CompanyTypeCodeType we have previously created. That’s all we need to do to fill the Code Type's values into the Radio Button Group.
After adding this additional field, don't forget to update the form data: right-click on the CompanyForm and choose "Update Form Data"
To write and read the values provided by the Radio Button from the database, we need to adjust the CompanyProcessService:
public CompanyFormData create(CompanyFormData formData) throws ProcessingException { if (!ACCESS.check(new CreateCompanyPermission())) { throw new VetoException(Texts.get("AuthorizationFailed")); } SQL.selectInto("" + "SELECT MAX(COMPANY_NR)+1 " + "FROM COMPANY " + "INTO :companyNr" , formData); /* * NEW: TYPE_UID behind INSERT INTO * NEW: :companyTypeGroup in VALUES, field is named according to the inner class CompanyTypeGroup * of CompanyForm */ SQL.insert("" + "INSERT INTO COMPANY (COMPANY_NR, SHORT_NAME, NAME, TYPE_UID) " + "VALUES (:companyNr, :shortName, :name, :companyTypeGroup)" , formData); return formData; } public CompanyFormData load(CompanyFormData formData) throws ProcessingException { if (!ACCESS.check(new ReadCompanyPermission())) { throw new VetoException(Texts.get("AuthorizationFailed")); } /* * NEW: TYPE_UID in SELECT * NEW: :companyTypeGroup behind INTO, field is named according to the inner class CompanyTypeGroup * of CompanyForm */ SQL.selectInto("" + "SELECT SHORT_NAME, " + " NAME," + " TYPE_UID " + "FROM COMPANY " + "WHERE COMPANY_NR = :companyNr " + "INTO :shortName," + " :name, " + " :companyTypeGroup" , formData); return formData; } public CompanyFormData store(CompanyFormData formData) throws ProcessingException { if (!ACCESS.check(new UpdateCompanyPermission())) { throw new VetoException(Texts.get("AuthorizationFailed")); } /* * NEW: TYPE_UID = :companyTypeGroup in SET, field is named according to * the inner class CompanyTypeGroup of CompanyForm */ SQL.update("" + "UPDATE COMPANY " + " SET SHORT_NAME = :shortName, " + " NAME = :name, " + " TYPE_UID = :companyTypeGroup " + "WHERE COMPANY_NR = :companyNr " , formData); return formData; }
Conditional Dependencies Between Fields
As already mentioned before, we need a Smart Field to choose a rating between A and D on the Company Form. This Smart Field must only be visible, when the company is type of Customer.
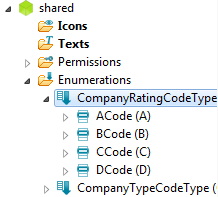
First we have to create another Code Type called CompanyRatingCodeType and add four Codes A, B, C and D to it.
Go to #How_to_create_Code_Types if you're lost.
After creating the Code Type, we add another field to the Company Form:
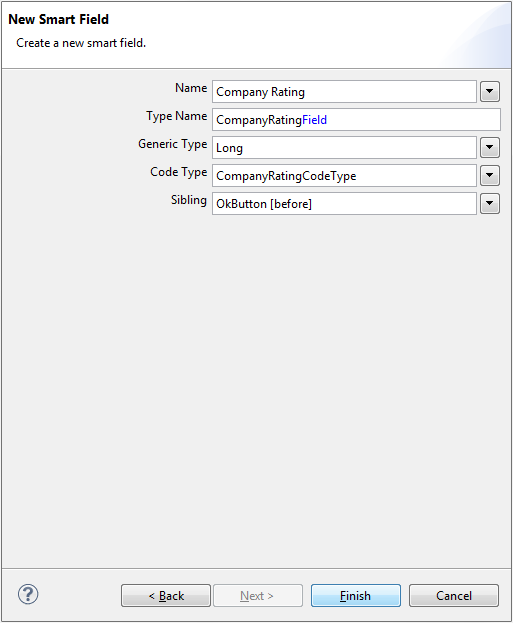
Back in Scout Explorer expand the tree like: client > Forms > CompanyForm > MainBox, right-click on MainBox and choose New Form Field…
The field's type is Smart Field. Enter the information provided by the picture in the wizard's next form.
As there is a dependency between fields, we have to define a master – slave – relation. This happens by telling the slave who's its master.
Expand the tree in the Scout Explorer like: client > Forms > CompanyForm > MainBox > CompanyRatingField. Set the Master Field and Master Required (see picture) and click on Exec Changed Master Value.
Open the CompanyForm class and go to the inner class CompanyRatingField. We need to adjust the execChangedMasterValue method, which is called whenever something happens in the CompanyTypeGroup Field, this because of the master – slave – relation.
When execChangedMasterValue is called, we check if the customer type value equals the Customer code. If so, the fields is set visible and enabled. In all other cases the field has to be invisible and disabled, as well as set to null nothing must be written to the database.
Code Type and Code IDs can get accessed very easily because they are defined as static.
@Override
protected void execChangedMasterValue(Object newMasterValue) throws
ProcessingException {
if (CompareUtility.equals(getCompanyTypeGroup().getValue(),
CompanyTypeCodeType.CustomerCode.ID)) {
setEnabled(true);
setVisible(true);
}
else {
setEnabled(false);
setVisible(false);
setValue(null);
}
}
Now that the Form works, we have to make sure that the rating value can be read and written from and to the database. So let's change the CompanyProcessService once more.
public CompanyFormData create(CompanyFormData formData) throws ProcessingException { if (!ACCESS.check(new CreateCompanyPermission())) { throw new VetoException(Texts.get("AuthorizationFailed")); } SQL.selectInto("" + "SELECT MAX(COMPANY_NR)+1 " + "FROM COMPANY " + "INTO :companyNr" , formData); /* * NEW: RATING_UID behind INSERT INTO * NEW: :companyRating in VALUES, field is named according to the inner class CompanyRating * of CompanyForm */ SQL.insert("" + "INSERT INTO COMPANY (COMPANY_NR, SHORT_NAME, NAME, TYPE_UID, RATING_UID) " + "VALUES (:companyNr, :shortName, :name, :companyTypeGroup, :companyRating)" , formData); return formData; } public CompanyFormData load(CompanyFormData formData) throws ProcessingException { if (!ACCESS.check(new ReadCompanyPermission())) { throw new VetoException(Texts.get("AuthorizationFailed")); } /* * NEW: RATING_UID in SELECT * NEW: :companyRating behind INTO, field is named according to the inner class CompanyRating * of CompanyForm */ SQL.selectInto("" + "SELECT SHORT_NAME, " + " NAME," + " TYPE_UID, " + " RATING_UID " + "FROM COMPANY " + "WHERE COMPANY_NR = :companyNr " + "INTO :shortName," + " :name, " + " :companyTypeGroup, " + " :companyRating " , formData); return formData; } public CompanyFormData store(CompanyFormData formData) throws ProcessingException { if (!ACCESS.check(new UpdateCompanyPermission())) { throw new VetoException(Texts.get("AuthorizationFailed")); } /* * NEW: RATING_UID = :companyRating in SET, field is named according to * the inner class CompanyRating of CompanyForm */ SQL.update("" + "UPDATE COMPANY " + " SET SHORT_NAME = :shortName, " + " NAME = :name, " + " TYPE_UID = :companyTypeGroup, " + " RATING_UID = :companyRating " + "WHERE COMPANY_NR = :companyNr " , formData); return formData; }
Display Code Types in Tables
Whenever we want to display a Code Type in a table, we cannot just use the value returned by the database query. This out of the reason that Code Types IDs are stored and displaying IDs would mean nothing to a user.
Instead we use a Smart Column, tell it which Code Type will be returned and let it translate the ID into a name. So let's add a new column to the CompanyTablePage and extend the StandardOutlineService.
Expand the tree in Scout Explorer like: client > All pages and right-click on CompanyTablePage > Table > Columns and choose New Column…
Choose type Smart Column and fill in the information according to the picture.
Adjust the getCompanyTableData method in the StandardOutlineService (server > Outline Services > StandardOutlineService):
/* * NEW: TYPE_UID behind SELECT */ statement.append( "SELECT COMPANY_NR, " + " SHORT_NAME, " + " NAME, " + " TYPE_UID " + " FROM COMPANY " + " WHERE 1 = 1 ");