Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Papyrus/customizations/robotics/fta"
(Created page with "= System analysis via fault trees = A fault tree is a top down and deductive method that represents graphically and logically the combination of events and the paths leading...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | = Fault tree analysis = |
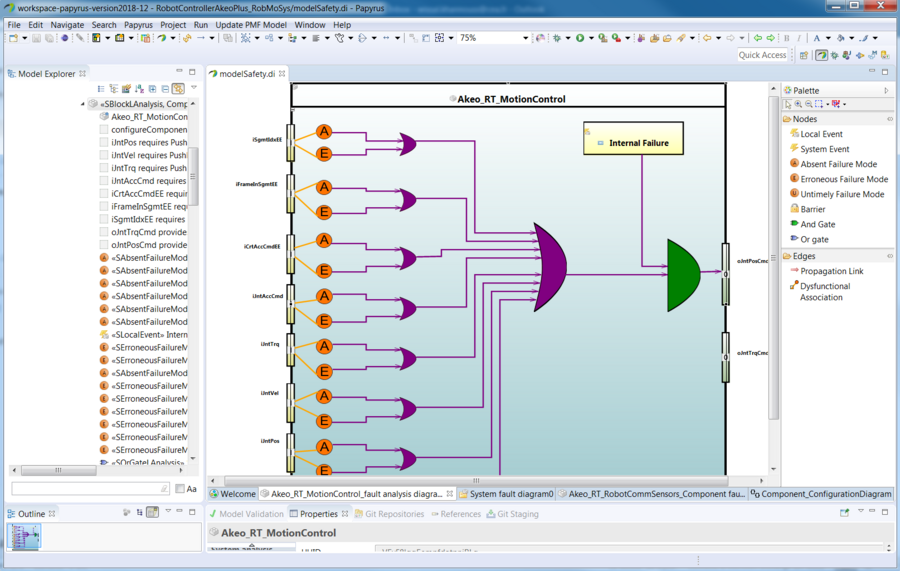
A fault tree is a top down and deductive method that represents graphically and logically the combination of events and the paths leading to the occurrence of an undesired event or state. To perform FTA on RobMoSys system models, each component is annotated with local safety analysis information. Failure modes are associated to the ports, component’s internal failures are defined and fault propagation is then done by combining logic gates (AND, OR) and propagation links. | A fault tree is a top down and deductive method that represents graphically and logically the combination of events and the paths leading to the occurrence of an undesired event or state. To perform FTA on RobMoSys system models, each component is annotated with local safety analysis information. Failure modes are associated to the ports, component’s internal failures are defined and fault propagation is then done by combining logic gates (AND, OR) and propagation links. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
After components fault annotation and fault propagation in the system, a top event is selected for fault tree generation and analysis. Fault trees are generated in openpsa standard format. | After components fault annotation and fault propagation in the system, a top event is selected for fault tree generation and analysis. Fault trees are generated in openpsa standard format. | ||
| + | |||
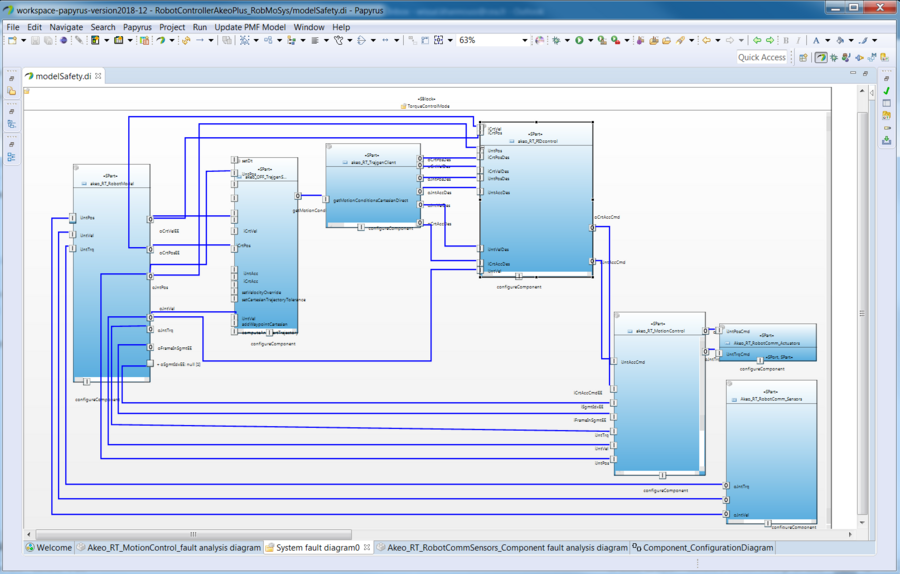
| + | Whereas the previous screenshot shows the fault-propagation analysis on the component level, the following shows fault propagation on the system level. | ||
[[Image:Papyrus-robotics-system-analysis-diagram.png|900px]] | [[Image:Papyrus-robotics-system-analysis-diagram.png|900px]] | ||
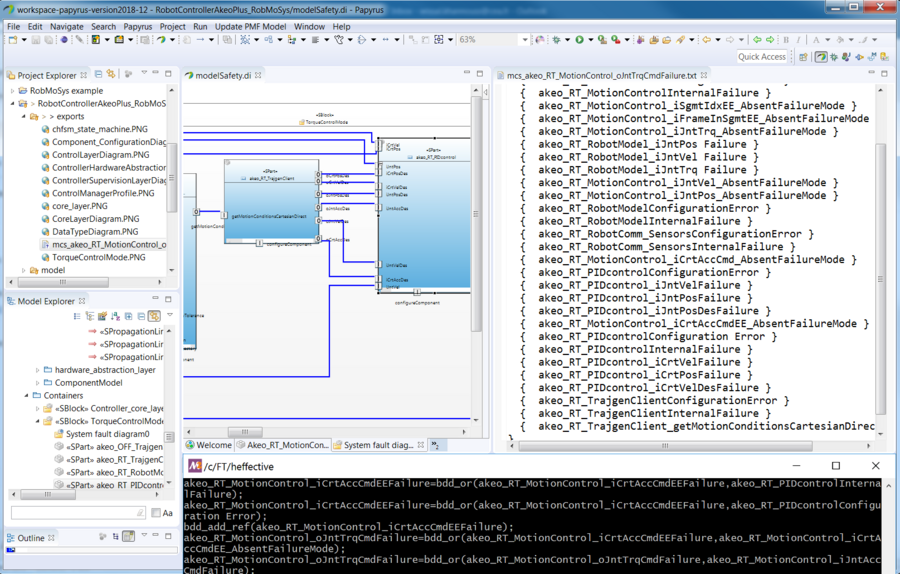
| − | + | Using the information from system-level faults, a fault tree analysis is performed using HEffective, a tool developed by CEA for Heterogeneous Effects Inferences and Verification. The minimal cut-set is calculated, as shown in the following screen-shot. | |
[[Image:Papyrus-robotics-min-cut-set.png|900px]] | [[Image:Papyrus-robotics-min-cut-set.png|900px]] | ||
Revision as of 10:13, 11 April 2019
Fault tree analysis
A fault tree is a top down and deductive method that represents graphically and logically the combination of events and the paths leading to the occurrence of an undesired event or state. To perform FTA on RobMoSys system models, each component is annotated with local safety analysis information. Failure modes are associated to the ports, component’s internal failures are defined and fault propagation is then done by combining logic gates (AND, OR) and propagation links.
After components fault annotation and fault propagation in the system, a top event is selected for fault tree generation and analysis. Fault trees are generated in openpsa standard format.
Whereas the previous screenshot shows the fault-propagation analysis on the component level, the following shows fault propagation on the system level.
Using the information from system-level faults, a fault tree analysis is performed using HEffective, a tool developed by CEA for Heterogeneous Effects Inferences and Verification. The minimal cut-set is calculated, as shown in the following screen-shot.