Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Papyrus/Tester/RCPTT
Introduction
RCPTT is an Eclipse Project that provides a testing tool for Eclipse RCP application. RCPTT allows to run GUI tests based on ECL. Several functions as the "Record actions" make RCPTT easy to handle and use for beginners. After a bit of experience, it will be easy to understand the different commands and make more complex scripts.
A quick Start guide is available here : Getting Started with RCPTT:
The RCPTT "framework" has been put in place in Papyrus RT. Some tests are arleady created and could base as example.
How to use RCPTT
RCPTT Eclipse can be found Download RCPTT
This demo shows how to create a test for papyrus RT:RCPTT Demo for PapyrusRT
Good Practices
Here are some tips to have an homogeneous practice around RCPTT. This is a certain way to work, maybe not the best one. If you have other opinion, please share it here.
Root Structure
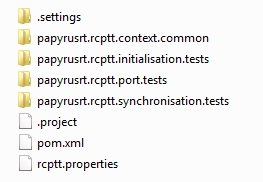
In the rcptt root in org.eclipse.papyrus-rt\releng\rcptt of the project we should have the following elements:
Folder Structure
After importing the rcptt folder into the RCPTT eclipse IDE, the the tests created should respect architecture to make this folder easy to maintain.
Project Properties file
rcptt.properties is shown as Project Settings file in the Test Explorer and contains Description, default contexts and default Validations.
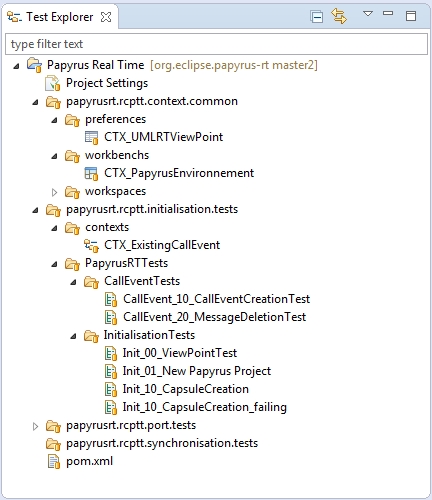
Contexts
There are several type of contexts :
- Preferences contexts
- Like the UMLRTViewPoint
- Workbenchs contexts
- For exemple: Perspective to use
- Workspaces contexts
- To clear the workspace
- Inital projects to be used for the further tests
- Procedures contexts
- ECL procedures that will be used as common library for RCPTT test
Naming Convention
Contexts Name
In order to quickly identify a Context file, the context name should be prefixed with the string "CTX_".
CTX_[ContextName]
For example:
CTX_UMLRTViewPoint
Test Name
All tests are executed alphabetically and this should work as each test must be independant ! But in order to have a better overview during execution, it would be a good practice to regroup test by feature. For this reason here is a naming convention used as for now:
[FeatureName]_[XY]_[TestName]
- X = Type of the test (e.i.: 0: initialisation, 1: creation, 2: deletion, 3: modification , ...)
- Y = Number of this test of this type X
For Example:
CallEvent_15_CreateCallEventTest
Represents a test around CallEvent, 1 = creation , 5 = fifth test of Creation of CallEvent.
Workspace initialisation with model files
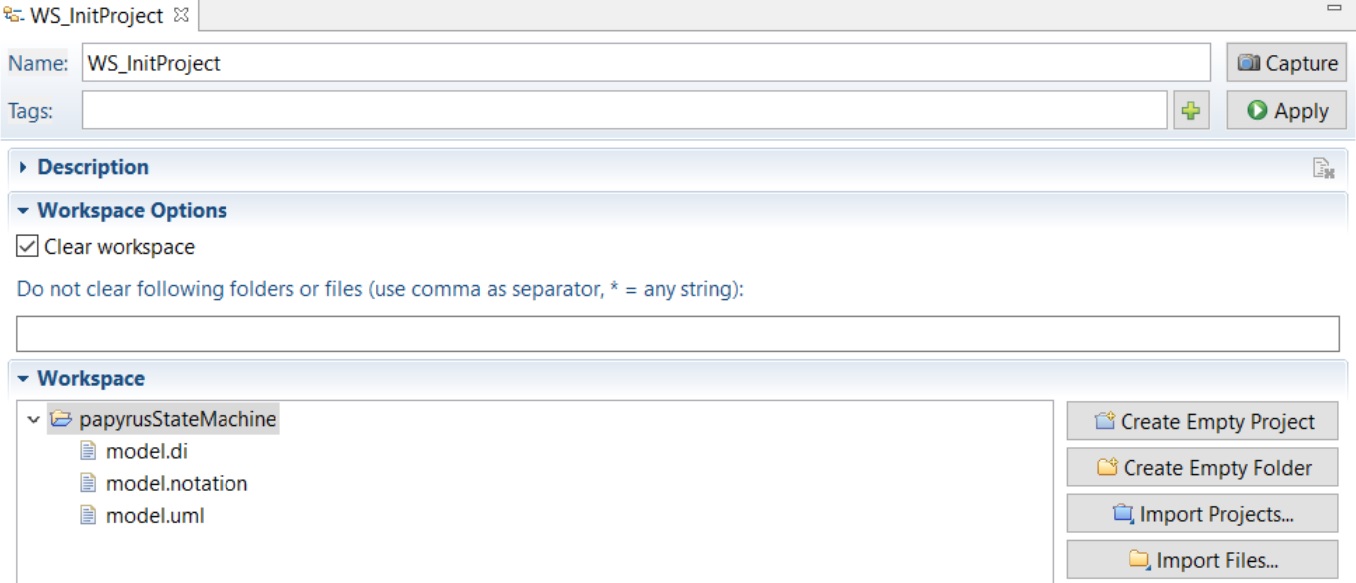
When you want to test Papyrus, you need to initialize your application’s workspace. For that you can use Papyrus model files.
First, export or copy model files of the papyrus project that you want use to start your tests and place them in a folder named //models// at the root of your rcptt project.
Then, create a new workspace context, open it and create an empty project. Once the project created, import files from the Papyrus model onto the created project.
Then, if you launch a test linked with your workspace context or if it is add by default in your project settings, the AUT’s workspace will be initialized with model files and creates a project with elements you need to start the test. (But the model steal must be opened ).
Super Contexts
Sometimes you have to execute the same tests with variant parameters, with super contexts it’s possible to launch the same script with different values.
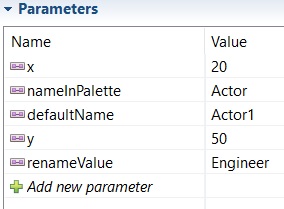
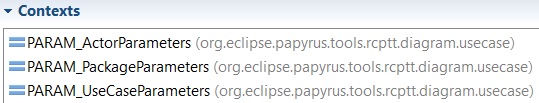
For example if you want to use a procedure which create a node on a diagram:
For each possible node, you create a parameter context which contains the node’s label in the palette and the coordinates of the node, for each value, the parameter’s name must be the same in each context.
Link all contexts to a super context of the same type as them and in the test, use the super context by using the parameters’ names in your test script.
RCPTT will launch your test script for each context link to your super context.
The super context is execute with each context successively and give different parameters to your test and give you the possibility to test different elements with the same test.
Open points
Naming Convention
- What should be that best naming convention to make the tests structured ?
Directory Structure
- How deep should be the test folder
Common Library
- How this library can be put in place (ECL, Java, ???)
- What will be added into this library ?
Industrialization
- Should we create a special Hudson job to run the RCPTT
- On which version of Papyrus should be based the AUT ?
- On which version of Papyrus RT should be based the AUT ?