|
|
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) |
| Line 14: |
Line 14: |
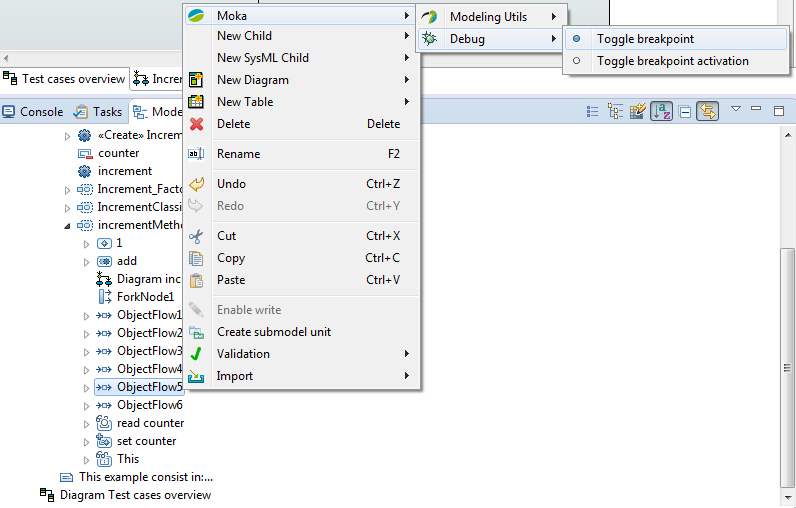
| | [[File:5 - ToggleBreakpointModelExplorer.png]] | | [[File:5 - ToggleBreakpointModelExplorer.png]] |
| | | | |
| − | == Code Generation Support ==
| |
| | | | |
| − | === Existing Code Generation Facilities ===
| |
| − | Currently, Papyrus supports code generation for the following programming languages:
| |
| − | * [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Java_Code_Generation Java code generation]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:GenerateJavaCode.jpg]]
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | * [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus/Codegen/Cpp_description C++ code generation]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:cdt-editor.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Adding a New Code Generator ===
| |
| − | Apart from the aforementioned programming language, it is also possible to develop and integrate other code generators to Papyrus.
| |
| − | To learn about how to add a new code generator to Papyrus, refer to the following [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus/Codegen/Adding_a_New_Code_Generator wikipage].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Reverse Engineering ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Java Reverse Engineering ===
| |
| − | In order to model your java code into UML, see [http://wiki.eclipse.org/Java_reverse_engineering Java reverse engineering]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:JavaReverseDnDResult.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Deploy your applications ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | If your want to deploy an application, see [https://wiki.eclipse.org/Papyrus_Software_Designer Papyrus Software Designer]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Fragment a Model ==
| |
| − | If you want to fragment your model by using Control Mode, see [[Papyrus/UserGuide/Submodel|Submodel Guide]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:ControlAction.png|center|Control Mode Menu]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | =Embedded Editors=
| |
| − | Papyrus provides embedded editors to edit UML Elements. Of course these editors allows to edit the name of the elements, but they allow to edit much more than this.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Textual Editor For Named Element==
| |
| − | Since Papyrus 1.1.0 (Eclipse Mars), Papyrus provides a new texutal editor to edit references to UML NamedElement. This editor works only for references which are not in containment. This editor has not been developed using XText. It use a custom string parser and provide a completion (CTRL+SPACE) to help the user to find the named elements to reference in the model.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | You can use this editor in Property View or in Papyrus table for example.
| |
| − | Developer documentation is available [[Papyrus_Developer_Guide/Papyrus_Embedded_Editors_Documentation/Textual_Editor_For_NamedElement|here]].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===Usage===
| |
| − | * This editors allows to find named element typing its name.
| |
| − | * In case of several elements to found, the separator to use is the comma <code>'</code>
| |
| − | * If the name of the element contains a comma, you should prefix and suffix its name by a quote <code>'</code>.
| |
| − | * The value will not be set if the element can't be found is the model
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===Example===
| |
| − | If you have 3 Classes in your model, named <code>Class1</code>, <code>Class2</code> and <code>Clas,s3</code>.
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | typed text
| |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | completion proposal
| |
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | explanation
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | empty string
| |
| − | | <Undefined>, ...
| |
| − | | we look for nothing, so we provide the <code><Undefined></code> value and <code>...</code> to ask to the user to write more text
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | Clas
| |
| − | | <Undefined>,Class1,Class2,Clas,s3
| |
| − | | 3 classes matches the string, <code><Undefined></code> is always proposed
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | Class
| |
| − | | <Undefined>,Class1,Class2
| |
| − | | 3 classes matches the string, <Undefined>is always proposed
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 'Clas
| |
| − | | <Undefined>, Clas,s3
| |
| − | | the string starts with a quote and Clas,s3 contains a comma, so we propose <code>Clas,s3</code>; <code><Undefined></code> is always proposed
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | Clas,
| |
| − | | <Undefined>,...
| |
| − | | interpreted as a list of value, the first value is <code>Clas</code>, and we have no information for the second one, for the completion it is an empty string
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | =Property View=
| |
| − | ==Multiplicity Editor==
| |
| − | ===Description===
| |
| − | The multiplicity editor contains two modes of edition:
| |
| − | * The '''simple''' mode which allows to edit the lower and the upper values from a unique editor
| |
| − | * The '''advanced''' mode which allows to edit the lower and the upper values from two editors of ValueSpecification.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===Usage===
| |
| − | ====Simple mode====
| |
| − | The simple mode is represented as the following:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:simpleMode.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This editor must be filled by the following pattern:
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0"
| |
| − | ! Value filled
| |
| − | ! Lower value
| |
| − | ! Upper value
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 1
| |
| − | | <code>null</code> (default value is '''1''')
| |
| − | | <code>null</code> (default value is '''1''')
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | x..y
| |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code> with value '''x'''
| |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> with value '''y'''
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | x..*
| |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code> with value '''x'''
| |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> with value '''-1''' (interpreted as <code>*</code>)
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | x
| |
| − | | <code>LiteralInteger</code> with value '''x'''
| |
| − | | <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> with value '''x'''
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The values set as lower and upper are always positive (except the <code>*</code> for the upper which is valued as '''-1''').
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This editor is usable only when the lower ValueSpecification is a <code>LiteralInteger</code> or <code>null</code> and when the upper ValueSpecification is a <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> or <code>null</code>.
| |
| − | On the other hand, this editor will be displayed like the following:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:simpleModeDisabled.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====Advanced mode====
| |
| − | =====Simple ValueSpecification editor=====
| |
| − | The advanced mode with simple ValueSpecificatiton editors is represented as the following:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:advancedMode.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The lower and the upper ValueSpecification can be created/edited/deleted by the buttons:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:buttonsEdit.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | =====XText ValueSpecification editor=====
| |
| − | The advanced mode with XText ValueSpecification editors is represented as the following:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:advancedModeXText.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This editor use the XText ValueSpecification editors (explain [[Papyrus_User_Guide#UML_ValueSpecification_editor|here]]) with some specificities depending on lower or upper value edition.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The specificity of the '''lower''' ValueSpecification edition is when the value filled is an integer, this one will be handled as <code>LiteralInteger</code> instead of <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> or <code>LiteralInteger</code> (the <code>*</code> value will create an <code>OpaqueExpression</code>).
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The specificity of the '''upper''' ValueSpecification edition is when the value filled is an integer or <code>*</code>:
| |
| − | * if the integer is '''positive or -1''', a <code>LiteralUnlimitedNatural</code> will be created
| |
| − | * if the integer is '''negative''', an <code>OpaqueExpression</code> will be created instead of <code>LiteralInteger</code>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====Switch modes====
| |
| − | This is possible to switch between the two modes by two ways:
| |
| − | * The button in the multiplicity editor:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:buttonSwitch.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * The '''multiplicity editor''' preferences in the '''property views''' preferences:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:preferencesMultiplicityEditor.png]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Regarless of the way used to switch modes, the mode used is saved in the preferences and will be used for each multiplicity in Papyrus.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | = Tips =
| |
| − | [[Papyrus_Key_Binding|Key Bindings]]
| |
| − | = Extra Components =
| |
| | == Papyrus for Requirements == | | == Papyrus for Requirements == |
| | | | |
Papyrus for Requirements helps you to specify and analyze requirements in the context of systems modeling. It aims to cover the Specification, Management, Analysis and Validation-Verification activities of Requirements Engineering. Papyrus for Requirements depends on the components Papyrus for SysML and Papyrus for Metrics.