Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Introduction to EclipseLink (ELUG)"
m |
m (→Introduction to EclipseLink) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction to EclipseLink== | ==Introduction to EclipseLink== | ||
| − | <div style="float:right;">__TOC__</div> | + | <div style="float:right;border:1px solid #000000;padding:5px">__TOC__ |
| + | [[Special:Whatlinkshere/Eclipse/Developer's Guide/EclipseLink Introduction|Related Topics]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
EclipseLink is an advanced, object-persistence and object-transformation framework that provides development tools and run-time capabilities that reduce development and maintenance efforts, and increase enterprise application functionality. | EclipseLink is an advanced, object-persistence and object-transformation framework that provides development tools and run-time capabilities that reduce development and maintenance efforts, and increase enterprise application functionality. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Using EclipseLink , you can integrate persistence and object-transformation into your application, while staying focused on your primary domain problem by taking advantage of an efficient, flexible, and field-proven solution (see "[[#What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch]]"). | Using EclipseLink , you can integrate persistence and object-transformation into your application, while staying focused on your primary domain problem by taking advantage of an efficient, flexible, and field-proven solution (see "[[#What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch]]"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sample crosslink: [[Eclipse/Developer's Guide/Acquiring and using Sessions at Runtime|Acquiring and using Sessions at Runtime]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch=== | ===What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch=== | ||
Revision as of 09:21, 19 October 2007
Introduction to EclipseLink
Contents
EclipseLink is an advanced, object-persistence and object-transformation framework that provides development tools and run-time capabilities that reduce development and maintenance efforts, and increase enterprise application functionality.
What Is EclipseLink?
EclispeLink builds high-performance applications that store persistent object-oriented data in a relational database. It successfully transforms object-oriented data into either relational data or Extensible Markup Language (XML) elements.
Using EclipseLink , you can integrate persistence and object-transformation into your application, while staying focused on your primary domain problem by taking advantage of an efficient, flexible, and field-proven solution (see "#What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch").
Sample crosslink: Acquiring and using Sessions at Runtime
What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch
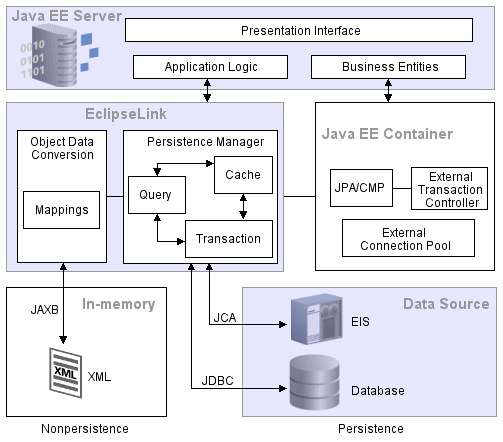
Java-to-data source integration is a widely underestimated problem when creating enterprise Java applications. This complex problem involves more than simply reading from and writing to a data source. The data source elements include tables, rows, columns, and primary and foreign keys. The Java and Java EE include entity classes (regular Java classes or Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) entity beans), business rules, complex relationships, and inheritance. In a nonrelational data source, you must match your Java entities with EIS records or XML elements and schemas. These differences (as shown in Figure 1-2) are known as the object-persistence impedance mismatch.
EclipseLink Key Features
EclipseLink provides an extensive and thorough set of features. Java developers can use these features to rapidly build high-performance enterprise applications that are both scalable and maintainable.
Some of the primary features of EclipseLink are the following:
- feature
- feature
- feature
EclipseLink Application Architectures
You can use EclipseLink in a variety of application architectures, including three- and two-tier architectures, with or without J2EE, to access a variety of data types on both relational and nonrelational data sources.
Copyright © 2007 Oracle. EclipseLink Developer's Guide License.