Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Henshin/Parameters"
m (→Parameter creation and editing in graphical editor: Explain that kind and type are optional.) |
m (→Parameter mappings: Add remark about parameter kind UNKNOWN) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:Henshin]][[Category:Modeling]] | ||
| + | |||
'''Parameters''' allow to shape the behavior of [[Henshin/Units|units]], including rules, with variable information. | '''Parameters''' allow to shape the behavior of [[Henshin/Units|units]], including rules, with variable information. | ||
A unit can have an arbitary number of parameters. | A unit can have an arbitary number of parameters. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
! UNKOWN | ! UNKOWN | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! settable before application | + | ! settable externally before application |
| style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| style="background-color:#faa" | | | style="background-color:#faa" | | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
| style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! settable during application | + | ! settable automatically during application |
| style="background-color:#faa" | | | style="background-color:#faa" | | ||
| style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
| style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Examples: [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=bank Bank Accounts] (''in'', ''var''), [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=ecore2rdb Ecore2RDB] (''in'', ''out'', ''var''), [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=ecore2genmodel Ecore2Genmodel] (''in'', ''out'', ''var''), [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=combpattern Grid & Comb Pattern] (''in'', ''inout'', ''out''), [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=gossipinggirls Gossiping Girls] (''out''), [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=probbroadcast Probabilistic Broadcast] (''in'', ''var'') | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Parameter mappings == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Parameters that need to be set externally can be set by the user using the [[#Interpreter_API|API]] or the [[#Interpreter_Wizard|Interpreter Wizard]]. | ||
| + | In addition, they can be passed in from another unit using a '''parameter mapping'''. | ||
| + | A parameter mapping assigns a source parameter to a target parameter between a unit and its sub-unit. | ||
| + | Parameters that need to be set automatically during unit application are either set during the match finding process (in the case of LHS elements) or after the creation of new elements (in the case of RHS elements). | ||
| + | This behavior can be used to propagate values between LHS and RHS elements, as exemplified in the ''transferMoney'' rule in the [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=bank Bank Example]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+Allowed mappings | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! From → / to ↓ | ||
| + | ! IN | ||
| + | ! OUT | ||
| + | ! INOUT | ||
| + | ! VAR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! IN | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="background-color:#faa" | | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! OUT | ||
| + | | style="background-color:#faa" | | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! INOUT | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! VAR | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;background-color:#afa" | x | ||
| + | | style="background-color:#faa" | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The legacy parameter kind ''unknown'' can be mapped arbitrarily depending on its usage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Examples: [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=ecore2rdb Ecore2RDB] (''in''→''in'', ''out''→''out''), [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=ecore2genmodel Ecore2Genmodel] (''in''→''in'', ''out''→''out''), [https://www.eclipse.org/henshin/examples.php?example=combpattern Grid & Comb Pattern] (''in''→''in'', ''out''→''out'', ''in''→''inout'', ''inout''→''in'', ''inout''→''out'') | ||
== Usage during definition == | == Usage during definition == | ||
| Line 44: | Line 94: | ||
Parameters can be created using the tree-based or the [[Henshin/Graphical Editor|graphical]] editor. | Parameters can be created using the tree-based or the [[Henshin/Graphical Editor|graphical]] editor. | ||
They can be edited using the latter or the ''Properties'' view. | They can be edited using the latter or the ''Properties'' view. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Declared parameters are used inside the unit by referencing them by name. | ||
| + | Parameters can be used at any place in the unit where a string value is expected: | ||
| + | in rules, this is the case for node names, attribute values, edge indices, and attribute conditions. | ||
| + | In [[Henshin/Units#Iterated_Unit|iterated units]], this is the case for the iterations condition. | ||
=== Parameter creation and editing in graphical editor === | === Parameter creation and editing in graphical editor === | ||
| Line 59: | Line 114: | ||
=== Parameter creation in tree-based editor === | === Parameter creation in tree-based editor === | ||
| − | [[File:Henshin Parameters Creation TreeEditor.png]] | + | [[File:Henshin Parameters Creation TreeEditor.png|600px]] |
To create a parameter with the tree-based editor open the according ''*.henshin''-file. | To create a parameter with the tree-based editor open the according ''*.henshin''-file. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 122: | ||
=== Parameter editing in properties view === | === Parameter editing in properties view === | ||
| − | [[File:Henshin Parameters Editing PropertiesView.png]] | + | [[File:Henshin Parameters Editing PropertiesView.png|350px]] |
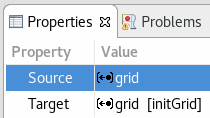
In the ''Properties'' view you can edit a parameter after selecting it in the tree-based editor. | In the ''Properties'' view you can edit a parameter after selecting it in the tree-based editor. | ||
To edit a value click in the according row of the ''Value'' column. | To edit a value click in the according row of the ''Value'' column. | ||
| − | === Parameter mapping === | + | === Parameter mapping creation === |
| + | |||
| + | In the graphical editor parameter mappings are maintained implicitely based on overlapping parameter names: | ||
| + | each parameter of a unit is mapped to all parameters of the same name in all sub-units; | ||
| + | mappings in the opposite direction exist as well. | ||
| − | [[File:Henshin ParameterMapping Creation TreeEditor.png| | + | [[File:Henshin ParameterMapping Creation TreeEditor.png|500px]] |
| − | + | Using the tree-based editor mappings for parameters can be created manually. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Therefore right-click the unit and select ''New Child → Parameter Mapping''. | Therefore right-click the unit and select ''New Child → Parameter Mapping''. | ||
The mapping can be edited using its ''Properties'' view. | The mapping can be edited using its ''Properties'' view. | ||
| Line 86: | Line 143: | ||
== Usage during execution == | == Usage during execution == | ||
| − | Before unit or rule execution parameters of kind ''in'' and ''inout'' have to be set. | + | Before unit or rule execution parameters of kind ''in'' and ''inout'' have to be set externally. |
| − | Parameters of kind ''unknown'' may be set depending on their usage in their units/rules. | + | Parameters of kind ''unknown'' may be set externally depending on their usage in their units/rules. |
This can be done using the [[Henshin/Interpreter#Interpreter_Wizard|Interpreter Wizard]] or the [[Henshin/Interpreter#Interpreter_API|Interpreter API]]. | This can be done using the [[Henshin/Interpreter#Interpreter_Wizard|Interpreter Wizard]] or the [[Henshin/Interpreter#Interpreter_API|Interpreter API]]. | ||
Revision as of 09:15, 23 April 2018
Parameters allow to shape the behavior of units, including rules, with variable information.
A unit can have an arbitary number of parameters.
Parameters have a name, a description, a kind, and, optionally, a type.
Parameter kinds
The kind specifies the time when the parameter is bound to a concrete value, and whether the parameter is intended to be accessed after the unit has been applied. There are four parameter kinds (in, out, inout, var) and an additional legacy parameter kind (unknown)
| Parameter kind | IN | OUT | INOUT | VAR | UNKOWN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| settable externally before application | x | x | x | ||
| settable automatically during application | x | x | x | ||
| readable after application | x | x | x |
Examples: Bank Accounts (in, var), Ecore2RDB (in, out, var), Ecore2Genmodel (in, out, var), Grid & Comb Pattern (in, inout, out), Gossiping Girls (out), Probabilistic Broadcast (in, var)
Parameter mappings
Parameters that need to be set externally can be set by the user using the API or the Interpreter Wizard. In addition, they can be passed in from another unit using a parameter mapping. A parameter mapping assigns a source parameter to a target parameter between a unit and its sub-unit. Parameters that need to be set automatically during unit application are either set during the match finding process (in the case of LHS elements) or after the creation of new elements (in the case of RHS elements). This behavior can be used to propagate values between LHS and RHS elements, as exemplified in the transferMoney rule in the Bank Example.
| From → / to ↓ | IN | OUT | INOUT | VAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN | x | x | x | |
| OUT | x | x | x | |
| INOUT | x | x | x | x |
| VAR | x | x | x |
The legacy parameter kind unknown can be mapped arbitrarily depending on its usage.
Examples: Ecore2RDB (in→in, out→out), Ecore2Genmodel (in→in, out→out), Grid & Comb Pattern (in→in, out→out, in→inout, inout→in, inout→out)
Usage during definition
Parameters can be created using the tree-based or the graphical editor. They can be edited using the latter or the Properties view.
Declared parameters are used inside the unit by referencing them by name. Parameters can be used at any place in the unit where a string value is expected: in rules, this is the case for node names, attribute values, edge indices, and attribute conditions. In iterated units, this is the case for the iterations condition.
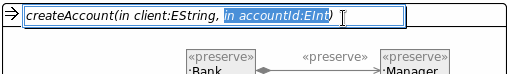
Parameter creation and editing in graphical editor
To create or edit a parameter with the graphical editor open the according *.henshin_diagram file. Select the name of a unit or rule by clicking on it. Click a second time to edit the name. You can now - text-based - add, edit and remove parameters which follow the unit/rule name encompassed by parentheses and separated by commas. The parameter entries adhere to the following scheme: <kind> <name>:<type> . Both kind and type are optional. If you omit a kind the parameter kind will be unknown.
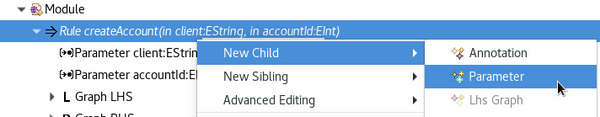
Parameter creation in tree-based editor
To create a parameter with the tree-based editor open the according *.henshin-file. Right-click on the desired rule or unit and navigate to New Child → Parameter. You can continue with editing the parameter in its Properties view.
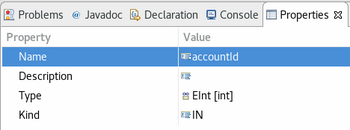
Parameter editing in properties view
In the Properties view you can edit a parameter after selecting it in the tree-based editor. To edit a value click in the according row of the Value column.
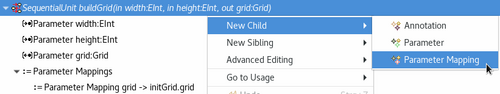
Parameter mapping creation
In the graphical editor parameter mappings are maintained implicitely based on overlapping parameter names: each parameter of a unit is mapped to all parameters of the same name in all sub-units; mappings in the opposite direction exist as well.
Using the tree-based editor mappings for parameters can be created manually. Therefore right-click the unit and select New Child → Parameter Mapping. The mapping can be edited using its Properties view.
Usage during execution
Before unit or rule execution parameters of kind in and inout have to be set externally. Parameters of kind unknown may be set externally depending on their usage in their units/rules. This can be done using the Interpreter Wizard or the Interpreter API.
Interpreter Wizard
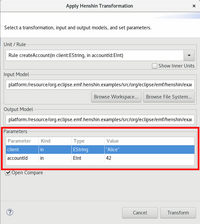
To set parameters using the interpreter wizard you have to open the wizard for your unit or rule of interest. In the lower part of the popup window is a table with the available parameters. You can set them by editing the cells in the Values column.
Interpreter API
See Setting and Getting Parameter Values in Henshin/Interpreter#Transforming_and_more.