Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EclipseLink/UserGuide/MOXy/Relationships/Privately Owned/One-to-Many"
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{EclipseLink_UserGuide | {{EclipseLink_UserGuide | ||
|info=y | |info=y | ||
| − | }} | + | }} |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | = One-to-Many Composite Collection Mapping = | |
| + | Use XML composite collection mappings to represent one-to-many relationships. Composite collection XML mappings can reference any class that has an EclipseLink descriptor. The attribute in the object mapped must implement either the Java <tt>Collection</tt> interface (for example, <tt>Vector</tt> or <tt>HashSet</tt>) or <tt>Map</tt> interface (for example, <tt>Hashtable</tt> or <tt>TreeMap</tt>). The <tt>CompositeCollectionMapping</tt> class allows a reference to the mapped class and the indexing type for that class. | ||
| − | <span id=" | + | Given the XML schema in this example, [[#Figure_58-27|XML Composite Collection Mapping]] illustrates an XML composite collection mapping to different elements by position in a corresponding XML document. [[#Example_58-49|Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Collection Attribute]] shows how to configure this mapping in Java for a <tt>Collection</tt> attribute and [[#Example_58-50|Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Map Attribute]] shows how to configure this mapping in Java for a <tt>Map</tt> attribute. |
| + | |||
| + | <br> <span id="Example_58-48"> | ||
''''' Schema for XML Composite Collection Mapping''''' | ''''' Schema for XML Composite Collection Mapping''''' | ||
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
</xsd:schema> | </xsd:schema> | ||
| − | </source> | + | </source></span> |
| − | <span id=" | + | <span id="Figure_58-27" /> '''''XML Composite Collection Mapping''''' |
| − | ''''' XML Composite Collection Mapping''''' | + | |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Ccxm.gif|XML Composite Collection Mapping]]<br><br> |
| − | <span id=" | + | <span id="Example_58-49" /> '''''Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Collection Attribute''''' <source lang="java"> |
| − | ''''' Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Collection Attribute''''' | + | |
| − | <source lang="java"> | + | |
XMLCompositeCollectionMapping phoneNumbersMapping = new XMLCompositeCollectionMapping(); | XMLCompositeCollectionMapping phoneNumbersMapping = new XMLCompositeCollectionMapping(); | ||
phoneNumbersMapping.setAttributeName("phoneNumbers"); | phoneNumbersMapping.setAttributeName("phoneNumbers"); | ||
| Line 48: | Line 46: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | + | <br> <span id="Example_58-50" /> '''''Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Map Attribute''''' <source lang="java"> | |
| − | <span id=" | + | |
| − | ''''' Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Map Attribute''''' | + | |
| − | <source lang="java"> | + | |
XMLCompositeCollectionMapping phoneNumbersMapping = new XMLCompositeCollectionMapping(); | XMLCompositeCollectionMapping phoneNumbersMapping = new XMLCompositeCollectionMapping(); | ||
phoneNumbersMapping.setAttributeName("phoneNumbers"); | phoneNumbersMapping.setAttributeName("phoneNumbers"); | ||
| Line 57: | Line 52: | ||
phoneNumbersMapping.setReferenceClass(PhoneNumber.class); | phoneNumbersMapping.setReferenceClass(PhoneNumber.class); | ||
phoneNumbersMapping.useMapClass(HashMap.class, "getType"); | phoneNumbersMapping.useMapClass(HashMap.class, "getType"); | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id="annotations" />'''''Using EclipseLink Annotations''''' | ||
| + | Use the '''@OneToMany''' annotation: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | @Entity | ||
| + | public class Employee { | ||
| + | |||
| + | @OneToMany(mappedBy="contact") | ||
| + | private List<PhoneNumber> contactNumber; | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | Use the EclipseLink extension '''@XmlInverseReference''' to map the back-pointer: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | @Entity | ||
| + | public class PhoneNumber { | ||
| + | |||
| + | @ManyToOne | ||
| + | @JoinColumn(name="E_ID", referencedColumnName = "E_ID") | ||
| + | @XmlInverseReference(mappedBy="contactNumber") | ||
| + | private Employee contact; | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
{{EclipseLink_MOXy | {{EclipseLink_MOXy | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 12:05, 10 December 2010
| EclipseLink | |
| Website | |
| Download | |
| Community | |
| Mailing List • Forums • IRC • mattermost | |
| Issues | |
| Open • Help Wanted • Bug Day | |
| Contribute | |
| Browse Source |
One-to-Many Composite Collection Mapping
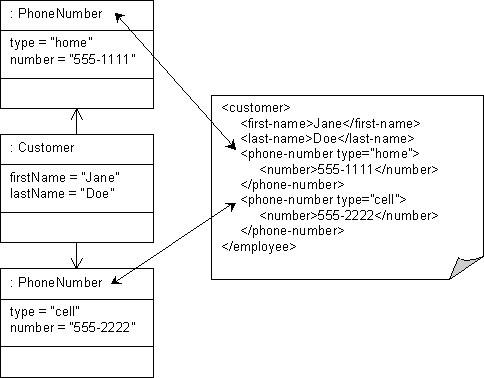
Use XML composite collection mappings to represent one-to-many relationships. Composite collection XML mappings can reference any class that has an EclipseLink descriptor. The attribute in the object mapped must implement either the Java Collection interface (for example, Vector or HashSet) or Map interface (for example, Hashtable or TreeMap). The CompositeCollectionMapping class allows a reference to the mapped class and the indexing type for that class.
Given the XML schema in this example, XML Composite Collection Mapping illustrates an XML composite collection mapping to different elements by position in a corresponding XML document. Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Collection Attribute shows how to configure this mapping in Java for a Collection attribute and Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Map Attribute shows how to configure this mapping in Java for a Map attribute.
Schema for XML Composite Collection Mapping
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="first-name" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:element name="last-name" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:element name="phone-number"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="number" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:sequence> <xsd:attribute name="type" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
<span id="Figure_58-27" /> XML Composite Collection Mapping
<span id="Example_58-49" /> Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Collection AttributeXMLCompositeCollectionMapping phoneNumbersMapping = new XMLCompositeCollectionMapping(); phoneNumbersMapping.setAttributeName("phoneNumbers"); phoneNumbersMapping.setXPath("phone-number"); phoneNumbersMapping.setReferenceClass(PhoneNumber.class);
<span id="Example_58-50" /> Java for XML Composite Collection Mapping for a Map Attribute
XMLCompositeCollectionMapping phoneNumbersMapping = new XMLCompositeCollectionMapping(); phoneNumbersMapping.setAttributeName("phoneNumbers"); phoneNumbersMapping.setXPath("phone-number"); phoneNumbersMapping.setReferenceClass(PhoneNumber.class); phoneNumbersMapping.useMapClass(HashMap.class, "getType");
<span id="annotations" />Using EclipseLink Annotations Use the @OneToMany annotation:
@Entity public class Employee { @OneToMany(mappedBy="contact") private List<PhoneNumber> contactNumber; }
Use the EclipseLink extension @XmlInverseReference to map the back-pointer:
@Entity public class PhoneNumber { @ManyToOne @JoinColumn(name="E_ID", referencedColumnName = "E_ID") @XmlInverseReference(mappedBy="contactNumber") private Employee contact; }
|
|
|
|
| How to contribute to this guide... | ||