Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EEF/User Guide"
(→Editors available in the runtime) |
|||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope=row | Text | ! scope=row | Text | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope=row | Textarea | ! scope=row | Textarea | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:blue">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 166: | Line 166: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 177: | Line 177: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 190: | Line 190: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
|- | |- | ||
! scope=row | AdvancedTableComposition | ! scope=row | AdvancedTableComposition | ||
| Line 201: | Line 201: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
|- | |- | ||
! scope=row | FlatReferenceTable | ! scope=row | FlatReferenceTable | ||
| Line 209: | Line 209: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:green">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 215: | Line 215: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope=row | ImageViewer | ! scope=row | ImageViewer | ||
| − | | | + | |<span style="color:blue">✓</span> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 15:14, 17 January 2010
Contents
Introduction
The EEF workflow is the same than many others projects of the Eclipse Modeling Project :
- Modeling : In the first step, you have to define some models (conforms to EEF metamodels) describing the graphical components that will be generated by EEF.
- Generating : Once the EEF models defined, the second step in the EEF development is to call he EEF generating module. EEF bring an Acceleo module that generate the java classes for the components defined in the preceding step.
- Customization : An optional third step can be done by customizing java code to add features that aren't directly accessible by the EEF generation. The third component of EEF is the runtime that is used by the generated code. This runtime is extensible, so you can substitute the generated code by your code and bring new features.
The custom can also be done by adding custom code in dedicated area in the generated code (called "user code area"). Acceleo will keep this code in the next generators invocation.
This document will describes all these steps in the user point of view.
EEF Modeling
Introduction
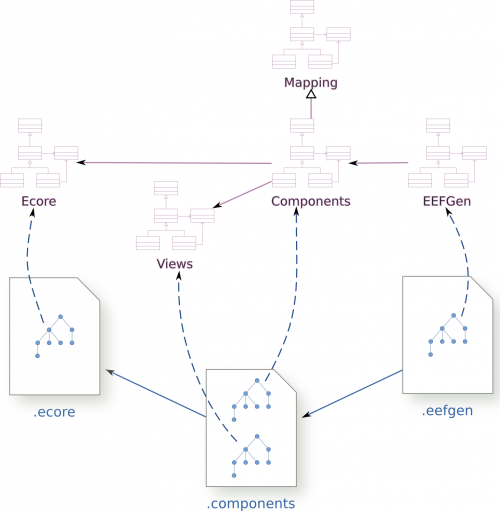
The EEF editing components are designed with three models conform to four metamodels. This models are :
- The views model : This is one or more ViewsRepository that we be used to edit the EMF models. These views can be stored in several categories.
- The components model : This a context PropertiesEditionContext that describes the controllers associating the elements of the views with the metamodel properties that they have to edit.
- The eefgen generation settings model : it allows the user to define settings for the generation. Thus, the target directory, the legal notice, and many other option can be set up in this model.
Warning : The EEF intializer create the two first models in only one file !
Views model
Concepts
The views modeling is made with a model conform to the EEF views metamodel. The root element of this model is a ViewsRepository. A ViewsRepository has a name and an optional documentation. A RepositoryKind property can be set but isn't used in the generation. This will be done in the next release.
A ViewsRepository contains Views and/or Categories. A Category doesn't step in the generation, it's just an element used to organize the Views. A Category only have a name and a documentation.
It's possible to create Views in a ViewsRepository of in a Category. A View represents a list of editors, called in EEF ElementEditor, which will be generated in the final editing component. A View shouldn't necessarily be defined for a particular element of the mapped meta-model and you don't have to create one ElementEditor for all the structural features of a given type. We'll see in next section that views can be referenced in several contexts. A View have a name, a documentation and can be defined as Explicit or not. A View is explicit when it is directly used by a component, not when it is referenced or compounded (see advanced topics).
The atomic part of a view is an ElementEditor. It's one or more widgets allowing to set the value of a EMF object property. Mostly, an ElementEditor is a label (for the name of the property) with a widget to enter the value and if the property has documentation a question mark displaying this documentation.
An editor have a name, a documentation and mainly a representation. This representation is a Widget of a Toolkit. This representation defines during the generation the widget to generated in the parts. The available widgets are listed in next sections.
The last concept for the view modeling is the Container. A Container group together widgets in order to generate graphical delimitation around these widgets or to change the default layout use by EEF. A container have a name, a documentation and a representation defining the behaviour of the container.
Editors available in the runtime
Table below describes editors available in EEF runtime and the kind of EObject properties they can manage. Green ticks indicate stable editors, blue ticks those under development.
| Widgets | Single EString EAttribute | Single EInt/EDouble EAttribute | Single EBool EAttribute | Single EEnum EAttribute | Multiple EAttribute | Single EReference | Multiple EReference | Simple containment | Multiple containment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| Textarea | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| Checkbox | ✓ | ||||||||
| Combo | ✓ | ||||||||
| Radio | ✓ | ||||||||
| EMFEnumViewer | ✓ | ||||||||
| MultiValuedEditor | ✓ | ||||||||
| EObjectFlatComboViewer | ✓ | ||||||||
| Advanced-EObjectFlatComboViewer | ✓ | ||||||||
| ReferenceTable | ✓ | ||||||||
| Advanced-ReferenceTable | ✓ | ||||||||
| TableComposition | ✓ | ||||||||
| AdvancedTableComposition | ✓ | ||||||||
| FlatReferenceTable | ✓ | ||||||||
| ImageViewer | ✓ |