Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Details on the JDBC data source"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| − | In order for the generator and the MySQL database to communicate, we will need a JDBC driver. We therefore download the MySQL JDBC driver (available [http://www.mysql.com/products/connector/j/ here]), and save it somewhere on our system. In addition, we will need to know the name of the JDBC driver, and the JDBC URL format. This information is usually found somewhere on the driver maker's website (for MySQL, it can be found [http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.0/en/connector-j-reference-configuration-properties.html here]; the driver name is <code>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, and the URL for our database is <code | + | In order for the generator and the MySQL database to communicate, we will need a JDBC driver. We therefore download the MySQL JDBC driver (available [http://www.mysql.com/products/connector/j/ here]), and save it somewhere on our system. In addition, we will need to know the name of the JDBC driver, and the JDBC URL format. This information is usually found somewhere on the driver maker's website (for MySQL, it can be found [http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.0/en/connector-j-reference-configuration-properties.html here]; the driver name is <code>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</code>, and the URL for our database is <code>jdbc:mysql://localhost/batchdata</code>). |
The user has to supply the JDBC driver and the database connection info. Token names are datbase column names, or column names qualified by table names. | The user has to supply the JDBC driver and the database connection info. Token names are datbase column names, or column names qualified by table names. | ||
Revision as of 11:58, 15 August 2007
The batch generator can use any JDBC-supported database as data source. This tutorial will walk you through setting up a MySQL database as a batch data source; setting up other databases works similarly.
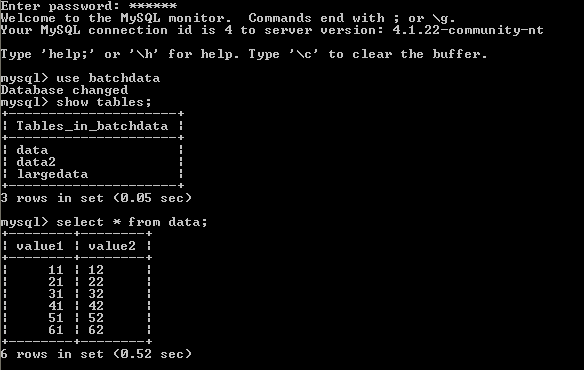
For this example, we assume that a MySQL is already installed on our system. Furthermore, a database called batchdata already exists. The database contains the table data, which is populated with some sample data (shown below). Finally, the database is accessible for reading to a user on the local system, using user as login name and password as password. See the MySQL manual for information on how to set up this kind of database.
In order for the generator and the MySQL database to communicate, we will need a JDBC driver. We therefore download the MySQL JDBC driver (available here), and save it somewhere on our system. In addition, we will need to know the name of the JDBC driver, and the JDBC URL format. This information is usually found somewhere on the driver maker's website (for MySQL, it can be found here; the driver name is com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, and the URL for our database is jdbc:mysql://localhost/batchdata).
The user has to supply the JDBC driver and the database connection info. Token names are datbase column names, or column names qualified by table names.
-appropriate databases
-jdbc information
-setting up the information in the preference page
-valid tokens, default tables
-multiple tables, joins
-sample jdbc connection info, driver names, database names