Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "DLTK IDE Guide:Step 3. Towards an IDE"
m (→Getting the code) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=== Requirements === | === Requirements === | ||
| − | * Eclipse 3.3 | + | * Eclipse 3.5, 3.6, 3.7 |
| − | * | + | * Latest DLTK 3.0 |
| − | * Plugins code from cvs | + | * Plugins code from cvs |
=== Plugin === | === Plugin === | ||
| Line 553: | Line 553: | ||
ScriptCompletionProposalCollector { | ScriptCompletionProposalCollector { | ||
| − | protected final static char[] VAR_TRIGGER = | + | protected final static char[] VAR_TRIGGER = { '\t', ' ', '=', ';', '.' }; |
| − | + | ||
protected char[] getVarTrigger() { | protected char[] getVarTrigger() { | ||
| Line 717: | Line 716: | ||
ScriptTemplateCompletionProcessor { | ScriptTemplateCompletionProcessor { | ||
| − | private static char[] IGNORE = | + | private static char[] IGNORE = {'.'}; |
public ExamplePythonTemplateCompletionProcessor( | public ExamplePythonTemplateCompletionProcessor( | ||
| Line 907: | Line 906: | ||
[[Image:Dltk_034_templates2.png]] | [[Image:Dltk_034_templates2.png]] | ||
| − | == Getting the code | + | == Getting the code == |
| − | The tutorial source code is available from Eclipse | + | The tutorial source code is available from Eclipse Git: |
| + | * http://git.eclipse.org/c/dltk/org.eclipse.dltk.examples.git/tree/eclipsecon08/org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.part4 | ||
| − | + | [[Category:DLTK]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Category:DLTK] | + | |
Latest revision as of 15:27, 13 October 2012
Contents
Summary
This tutorial describes the set of steps to create an integrated development environment (IDE) for a dynamically-typed language using Eclipse Dynamic Languages Toolkit (DLTK).
In this part we will add advanced features like search, selection, completion.
Requirements
- Eclipse 3.5, 3.6, 3.7
- Latest DLTK 3.0
- Plugins code from cvs
Plugin
We need to create another plugin names org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.part4 with following set of dependencies:
- org.eclipse.ui
- org.eclipse.core.runtime
- org.eclipse.dltk.core
- org.eclipse.dltk.ui
- org.eclipse.ui.ide
- org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python
- org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.part2
- org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.part3
- org.eclipse.search
- org.eclipse.jface.text
- org.eclipse.ui.editors
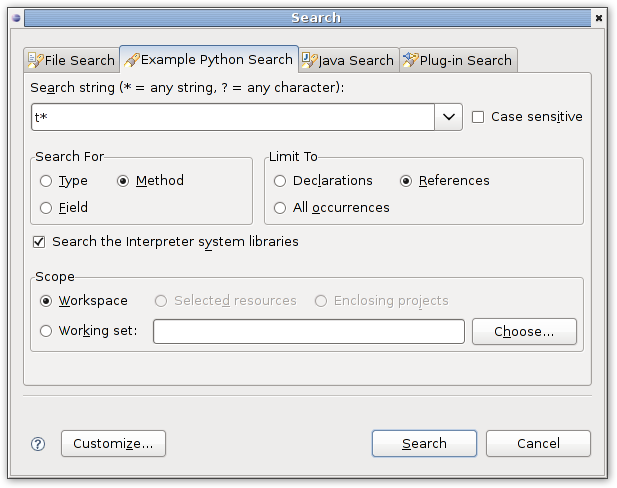
Search.
By default DLTK provides search for declarations. We only need to extend appropriate UI base classes.
<extension point="org.eclipse.search.searchPages"> <page canSearchEnclosingProjects="true" class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.search.ExamplePythonSearchPage" enabled="true" extensions="py:90" icon="/icons/search_obj.gif" id="org.eclipse.dltk.ui.ExamplePythonSearchPage" label="Example Python Search" showScopeSection="true" sizeHint="460,160"> </page> </extension>
And Page code: ExamplePythonSearchPage.java
public class ExamplePythonSearchPage extends ScriptSearchPage { protected IDLTKLanguageToolkit getLanguageToolkit() { return ExamplePythonLanguageToolkit.getDefault(); } }
Now we could execute Eclipse and try search for python class or method declarations.
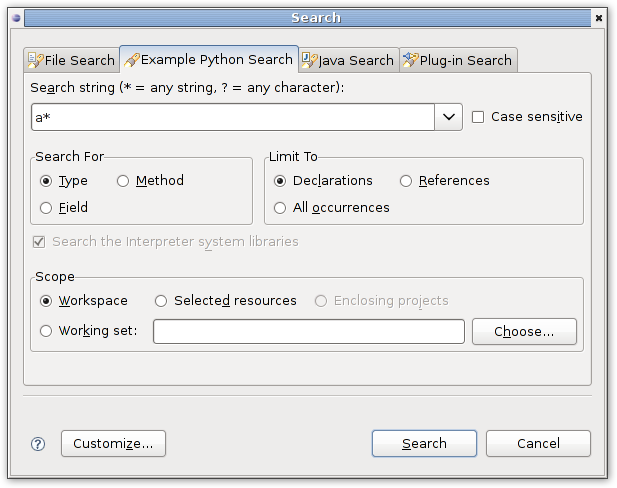
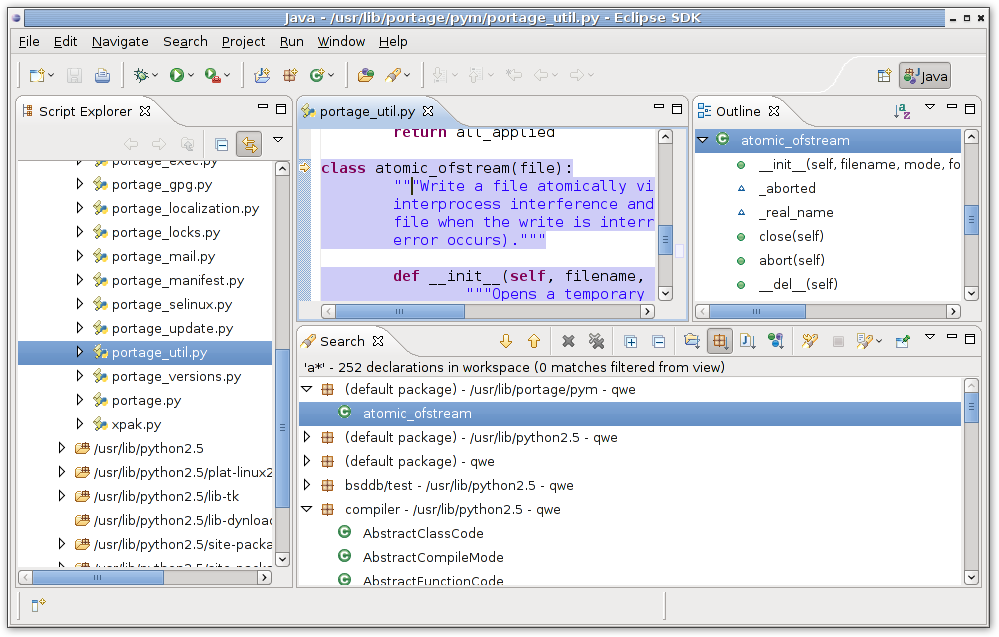
Search results will be available from default eclipse search view:
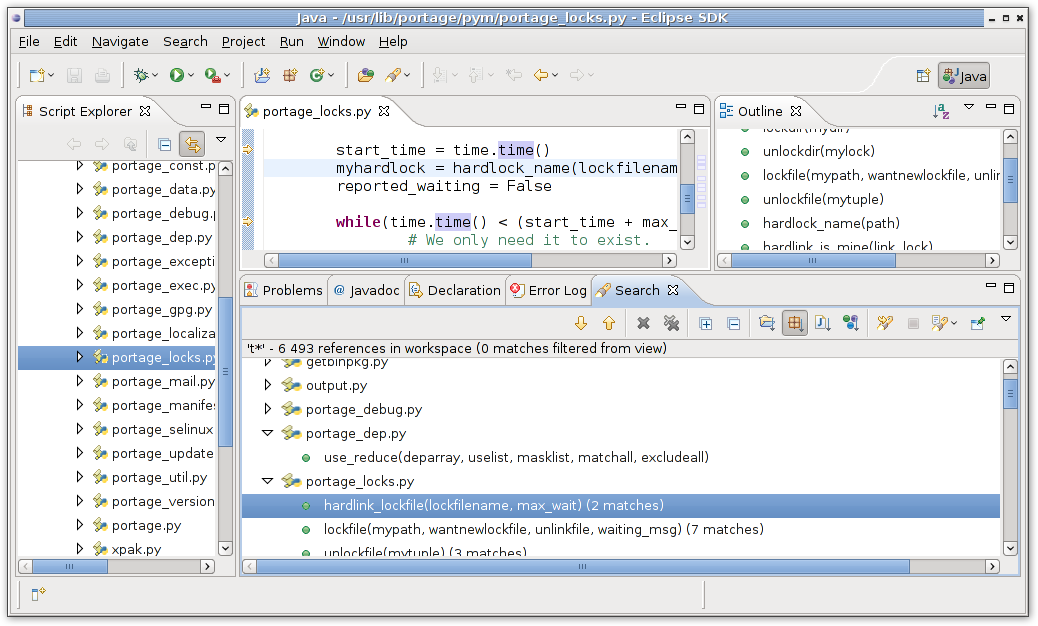
Search for References.
Search for references required adding additional code and declaration of search factory. Search factory provide language specific code to DLTK search infrastructure.
References requires two things to be done:
- SourceElementParser should report references to methods, fields, types. This class used by index manager to build index.
- Implementation of MatchLocatorParser base class to report references to search engine, then search operation are performed.
<extension point="org.eclipse.dltk.core.search"> <seachFactory class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.search.ExamplePythonSearchFactory" nature="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.nature" priority="0"> </seachFactory> </extension>
Search factory class return MatchLocator base class for our case. ExamplePythonSearchFactory.java
public class ExamplePythonSearchFactory extends AbstractSearchFactory { public IMatchLocatorParser createMatchParser(MatchLocator locator) { return new ExamplePythonMatchLocationParser(locator); } }
Python match locator: ExamplePythonMatchLocationParser.java
public class ExamplePythonMatchLocationParser extends MatchLocatorParser { protected ExamplePythonMatchLocationParser(MatchLocator locator) { super(locator); } protected void processStatement(ASTNode node, PatternLocator locator) { super.processStatement(node, locator); if (node instanceof ExtendedVariableReference) { ExtendedVariableReference ref = (ExtendedVariableReference) node; int expressionCount = ref.getExpressionCount(); for (int i = 0; i < expressionCount; i++) { Expression e = ref.getExpression(i); if (ref.isCall(i) && e instanceof VariableReference) { CallExpression call = new CallExpression(null, ((VariableReference) e).getName(), null); call.setStart(e.sourceStart()); call.setEnd(e.sourceEnd()); locator.match(call, getNodeSet()); } else if (e instanceof VariableReference) { locator.match(node, getNodeSet()); } } } if (node instanceof VariableReference) { locator.match(node, getNodeSet()); } } }
We could search for references now:
After search is finished we will get results:
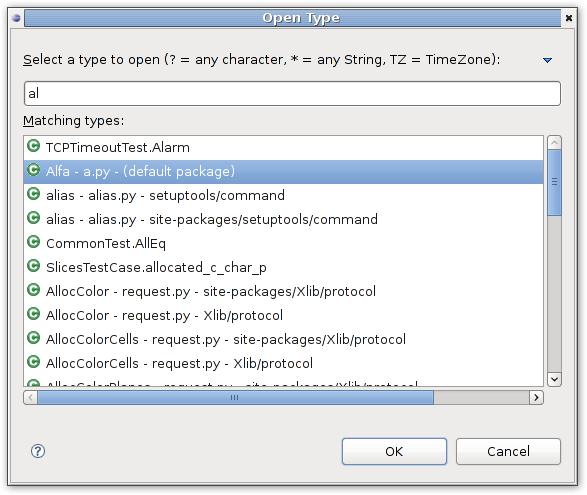
Open type feature.
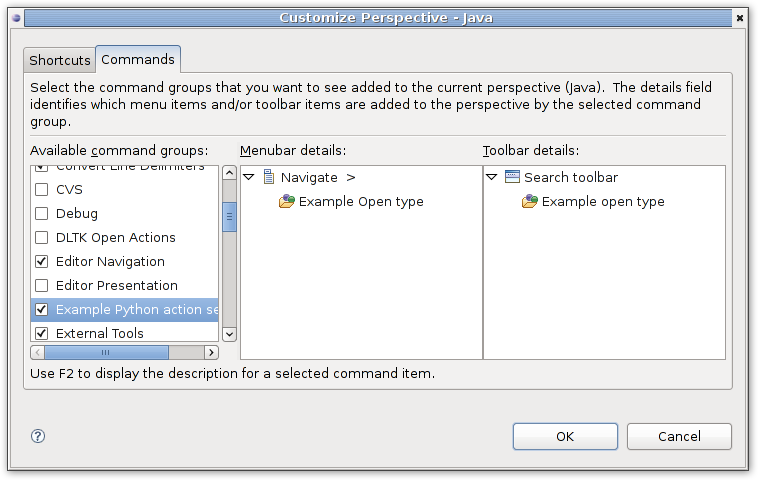
Open type feature allows easy navigation to any class in workspace. To add open types feature we need to declare action set:
<extension point="org.eclipse.ui.actionSets"> <actionSet id="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.actionSet" label="Example Python action set"> <action class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.ExamplePythonOpenTypeAction" icon="icons/opentype.gif" id="openType" label="Example Open type" menubarPath="navigate/open.ext2" toolbarPath="org.eclipse.search.searchActionSet/Search" tooltip="Example open type"> </action> </actionSet> </extension>
And action code: ExamplePythonOpenTypeAction.java
public class ExamplePythonOpenTypeAction extends OpenTypeAction { protected IDLTKUILanguageToolkit getUILanguageToolkit() { return new ExamplePythonUILanguageToolkit(); } }
After eclipse is started we need to configure current perspective and enable "Example Python action set" action set.
Open declaration feature.
Open declaration is a very powerful navigation feature, and also mostly used one. We need to declare "org.eclipse.dltk.core.selectionEngine" extension.
<extension point="org.eclipse.dltk.core.selectionEngine"> <selectionEngine class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.selection.ExamplePythonSelectionEngine" nature="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.nature" priority="0"> </selectionEngine> </extension>
Example python selection engine. Engine is quite simple. It search for structure elements from field, method references. ExamplePythonSelectionEngine.java
public class ExamplePythonSelectionEngine implements ISelectionEngine { private org.eclipse.dltk.core.ISourceModule sourceModule; public IModelElement[] select(ISourceModule module, final int offset, int i) { sourceModule = (org.eclipse.dltk.core.ISourceModule) module .getModelElement(); ModuleDeclaration moduleDeclaration = SourceParserUtil .getModuleDeclaration(sourceModule, null); final List results = new ArrayList(); try { moduleDeclaration.traverse(new ASTVisitor() { public boolean visit(Expression s) throws Exception { if (s.sourceStart() <= offset && offset <= s.sourceEnd()) { if (s instanceof ExtendedVariableReference) { ExtendedVariableReference ref = (ExtendedVariableReference) s; int count = ref.getExpressionCount(); for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) { Expression e = ref.getExpression(j); if (e.sourceStart() <= offset && offset <= e.sourceEnd()) { if (e instanceof VariableReference) { findDeclaration(((VariableReference) e) .getName(), results); } } } } else if (s instanceof VariableReference) { findDeclaration(((VariableReference) s).getName(), results); } } return super.visit(s); } public boolean visit(MethodDeclaration s) throws Exception { if (s.getNameStart() <= offset && offset <= s.getNameEnd()) { findDeclaration(s.getName(), results); } return super.visit(s); } public boolean visit(TypeDeclaration s) throws Exception { if (s.getNameStart() <= offset && offset <= s.getNameEnd()) { findDeclaration(s.getName(), results); } return super.visit(s); } }); } catch (Exception e) { if (DLTKCore.DEBUG) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return (IModelElement[]) results.toArray(new IModelElement[results .size()]); } private void findDeclaration(final String name, final List results) { try { this.sourceModule.accept(new IModelElementVisitor() { public boolean visit(IModelElement element) { if (element.getElementName().equals(name)) { results.add(element); } return true; } }); } catch (ModelException e) { if (DLTKCore.DEBUG) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public void setOptions(Map options) { } }
In production qualify IDE this engine should know about code structure and search correct elements. It could use DLTK search for looking for external elements, etc.
Simple documentation provider for comments.
Lets create documentation provider for comments. DLTK provide easy way to show any documentation for structure model elements.
<extension point="org.eclipse.dltk.ui.scriptDocumentationProviders"> <provider class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.selection.ExamplePythonCommentDocumentationProvider" id="org.eclipse.dltk.tcl.ui.ExamplePythonCommentDocumentationProvider" nature="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.nature"/> </extension>
ExamplePythonCommentDocumentationProvider.java
public class ExamplePythonCommentDocumentationProvider implements IScriptDocumentationProvider { protected String getLine(Document d, int line) throws BadLocationException { return d.get(d.getLineOffset(line), d.getLineLength(line)); } protected String getHeaderComment(IMember member) { try { ISourceRange range = member.getSourceRange(); if (range == null) return null; IBuffer buf = null; ISourceModule compilationUnit = member.getSourceModule(); if (!compilationUnit.isConsistent()) { return null; } buf = compilationUnit.getBuffer(); final int start = range.getOffset(); String contents = buf.getContents(); String result = ""; Document doc = new Document(contents); try { int line = doc.getLineOfOffset(start); line--; if (line < 0) return null; boolean emptyEnd = true; while (line >= 0) { String curLine = getLine(doc, line); String curLineTrimmed = curLine.trim(); if ((curLineTrimmed.length() == 0 && emptyEnd) || curLineTrimmed.startsWith("#")) { if (curLineTrimmed.length() != 0) emptyEnd = false; result = curLine + result; } else break; line--; } } catch (BadLocationException e) { return null; } return result; } catch (ModelException e) { } return null; } public Reader getInfo(IMember member, boolean lookIntoParents, boolean lookIntoExternal) { String header = getHeaderComment(member); return new StringReader(convertToHTML(header)); } protected String convertToHTML(String header) { StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(); // result.append("<p>\n"); Document d = new Document(header); for (int line = 0;; line++) { try { String str = getLine(d, line).trim(); if (str == null) break; while (str.length() > 0 && str.startsWith("#")) str = str.substring(1); while (str.length() > 0 && str.endsWith("#")) str = str.substring(0, str.length() - 1); if (str.length() == 0) result.append("<p>"); else { if (str.trim().matches("\\w*:")) { result.append("<h4>"); result.append(str); result.append("</h4>"); } else result.append(str + "<br>"); } } catch (BadLocationException e) { break; } } return result.toString(); } public Reader getInfo(String content) { return null; } }
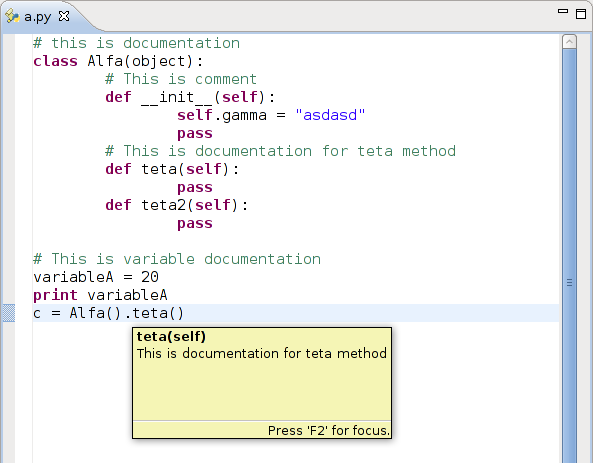
Selection in action.
Lets write some python code, and test goto declaration and documentation.
# this is documentation class Alfa(object): # This is comment def __init__(self): self.gamma = "asdasd" pass # This is documentation for teta method def teta(self): pass def teta2(self): pass # This is variable documentation variableA = 20 print variableA c = Alfa().teta()
We will see documentation if we hover element:
Code assistance
To add code assistance we need to make few things:
- Create completion engine and declare it to DLTK
- Create completion proposal computer
- Modify source viewer configuration and return correct completion proposal computer
Completion engine.
To declare completion engine we need to extend "org.eclipse.dltk.core.completionEngine" extension point.
<extension point="org.eclipse.dltk.core.completionEngine"> <completionEngine class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.completion.ExamplePythonCompletionEngine" nature="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.nature" priority="0"> </completionEngine> </extension>
ExamplePythonCompletionEngine.java
public class ExamplePythonCompletionEngine implements ICompletionEngine { IScriptProject project; private CompletionRequestor requestor; private int actualCompletionPosition; private int offset; public void complete(ISourceModule module, int position, int pos) { this.actualCompletionPosition = position; this.offset = pos; String[] keywords = new String[] { "and", "del", "for", "is", "raise", "assert", "elif", "from", "lambda", "break", "else", "global", "not", "try", "class", "except", "if", "or", "while", "continue", "exec", "import", "pass", "yield", "def", "finally", "in", "print", "self", "return" }; for (int j = 0; j < keywords.length; j++) { createProposal(keywords[[j]], null); } // Completion for model elements. try { module.getModelElement().accept(new IModelElementVisitor() { public boolean visit(IModelElement element) { if (element.getElementType() > IModelElement.SOURCE_MODULE) { createProposal(element.getElementName(), element); } return true; } }); } catch (ModelException e) { if (DLTKCore.DEBUG) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void createProposal(String name, IModelElement element) { CompletionProposal proposal = null; try { if (element == null) { proposal = this.createProposal(CompletionProposal.KEYWORD, this.actualCompletionPosition); } else { switch (element.getElementType()) { case IModelElement.METHOD: proposal = this.createProposal( CompletionProposal.METHOD_DECLARATION, this.actualCompletionPosition); proposal.setFlags(((IMethod) element).getFlags()); break; case IModelElement.FIELD: proposal = this.createProposal( CompletionProposal.FIELD_REF, this.actualCompletionPosition); proposal.setFlags(((IField) element).getFlags()); break; case IModelElement.TYPE: proposal = this.createProposal(CompletionProposal.TYPE_REF, this.actualCompletionPosition); proposal.setFlags(((IType) element).getFlags()); break; default: proposal = this.createProposal(CompletionProposal.KEYWORD, this.actualCompletionPosition); break; } } proposal.setName(name.toCharArray()); proposal.setCompletion(name.toCharArray()); proposal.setReplaceRange(actualCompletionPosition - offset, actualCompletionPosition - offset); proposal.setRelevance(20); proposal.setModelElement(element); this.requestor.accept(proposal); } catch (Exception e) { } } public void setOptions(Map options) { } public void setProject(IScriptProject project) { this.project = project; } public void setRequestor(CompletionRequestor requestor) { this.requestor = requestor; } protected CompletionProposal createProposal(int kind, int completionOffset) { return CompletionProposal.create(kind, completionOffset - this.offset); } }
Completion proposal computer declaration:
<extension point="org.eclipse.dltk.ui.scriptCompletionProposalComputer" id="ExamplePythonTypeCompletionProposalComputer"> <scriptCompletionProposalComputer class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.completion.ExamplePythonCompletionProposalComputer" categoryId="org.eclipse.dltk.ui.scriptTypeProposalCategory" toolkitId="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.nature"> <partition type="__dftl_partition_content_type"/> </scriptCompletionProposalComputer> </extension>
ExamplePythonCompletionProposalComputer.java
public class ExamplePythonCompletionProposalComputer extends ScriptCompletionProposalComputer { public ExamplePythonCompletionProposalComputer() { } protected ScriptCompletionProposalCollector createCollector( ScriptContentAssistInvocationContext context) { return new ExamplePythonCompletionProposalCollector(context.getSourceModule()); } protected TemplateCompletionProcessor createTemplateProposalComputer( ScriptContentAssistInvocationContext context) { return null; } }
ExamplePythonCompletionProposalCollector.java
public class ExamplePythonCompletionProposalCollector extends ScriptCompletionProposalCollector { protected final static char[] VAR_TRIGGER = { '\t', ' ', '=', ';', '.' }; protected char[] getVarTrigger() { return VAR_TRIGGER; } public ExamplePythonCompletionProposalCollector(ISourceModule module) { super(module); } // Specific proposals creation. May be use factory? protected ScriptCompletionProposal createScriptCompletionProposal( String completion, int replaceStart, int length, Image image, String displayString, int i) { return new ExamplePythonCompletionProposal(completion, replaceStart, length, image, displayString, i); } protected ScriptCompletionProposal createScriptCompletionProposal( String completion, int replaceStart, int length, Image image, String displayString, int i, boolean isInDoc) { return new ExamplePythonCompletionProposal(completion, replaceStart, length, image, displayString, i, isInDoc); } protected ScriptCompletionProposal createOverrideCompletionProposal( IScriptProject scriptProject, ISourceModule compilationUnit, String name, String[] paramTypes, int start, int length, String displayName, String completionProposal) { return new ExamplePythonOverrideCompletionProposal(scriptProject, compilationUnit, name, paramTypes, start, length, displayName, completionProposal); } }
ExamplePythonCompletionProposal.java
public class ExamplePythonCompletionProposal extends ScriptCompletionProposal { public ExamplePythonCompletionProposal(String replacementString, int replacementOffset, int replacementLength, Image image, String displayString, int relevance) { super(replacementString, replacementOffset, replacementLength, image, displayString, relevance); } public ExamplePythonCompletionProposal(String replacementString, int replacementOffset, int replacementLength, Image image, String displayString, int relevance, boolean isInDoc) { super(replacementString, replacementOffset, replacementLength, image, displayString, relevance, isInDoc); } protected boolean isSmartTrigger(char trigger) { if (trigger == '.') { return true; } return false; } protected boolean insertCompletion() { IPreferenceStore preference = PythonCorePlugin.getDefault() .getPreferenceStore(); return preference .getBoolean(PreferenceConstants.CODEASSIST_INSERT_COMPLETION); } }
Also we need to create class ExamplePythonCompletionProcess to editor plugin and update ExamplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration. ExamplePythonCompletionProcessor.java
public class ExamplePythonCompletionProcessor extends ScriptCompletionProcessor { public ExamplePythonCompletionProcessor(IEditorPart editor, ContentAssistant assistant, String partition) { super(editor, assistant, partition); } protected String getNatureId() { return ExamplePythonNature.PYTHON_NATURE; } protected CompletionProposalLabelProvider getProposalLabelProvider() { return new CompletionProposalLabelProvider(); } protected IPreferenceStore getPreferenceStore() { return PythonCorePlugin.getDefault().getPreferenceStore(); } }
This method should be added to ExamplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration
protected void alterContentAssistant(ContentAssistant assistant) { // IDocument.DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE IContentAssistProcessor scriptProcessor = new ExamplePythonCompletionProcessor( getEditor(), assistant, IDocument.DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE); assistant.setContentAssistProcessor(scriptProcessor, IDocument.DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE); }
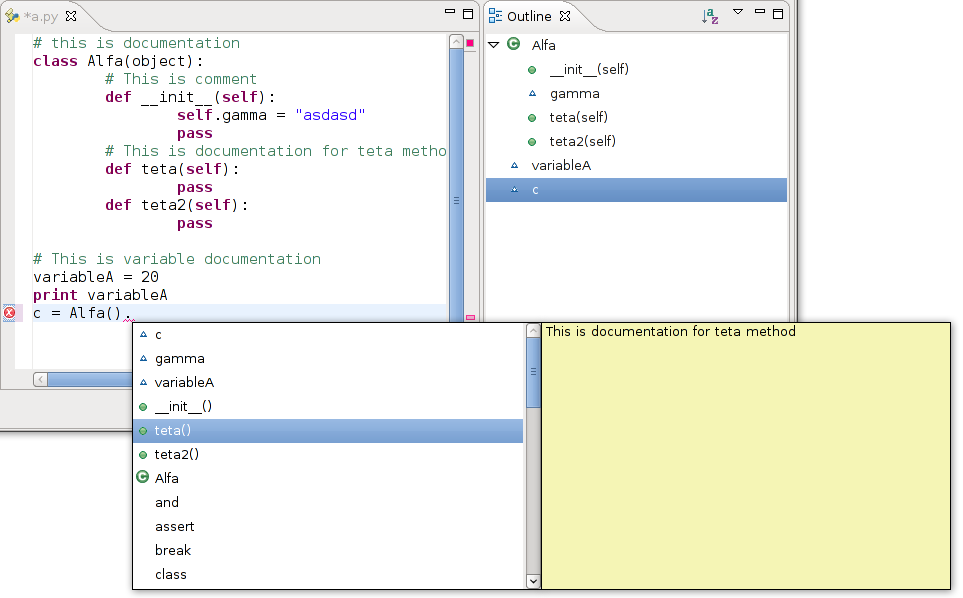
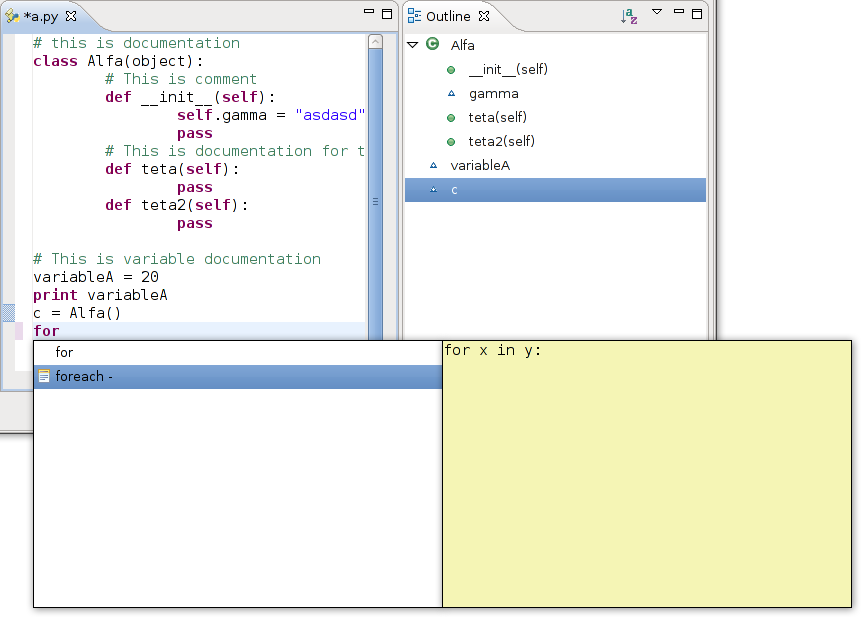
Now we could test completion.
Notice: DLTK not autoactive plugins with completion engines. As in this example. To autoactivate plugin selection could be used.
Code templates
To add code templates we need to extend "org.eclipse.ui.editors.templates" extension point.
<extension point="org.eclipse.ui.editors.templates"> <contextType class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.completion.templates.ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType" id="examplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType" name="Python Template content"> </contextType> <include file="templates/templates.xml" translations="templates/templates.properties"> </include> </extension> </plugin>
Template context type implementation ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType.java
public class ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType extends ScriptTemplateContextType { public static final String CONTEXT_TYPE_ID = "examplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType"; public ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType() { } public ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType(String id, String name) { super(id, name); } public ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType(String id) { super(id); } public ScriptTemplateContext createContext(IDocument document, int completionPosition, int length, ISourceModule sourceModule) { return new ExamplePythonTemplateContext(this, document, completionPosition, length, sourceModule); } }
Template context class ExamplePythonTemplateContext.java
public class ExamplePythonTemplateContext extends ScriptTemplateContext { protected ExamplePythonTemplateContext(TemplateContextType type, IDocument document, int completionOffset, int completionLength, ISourceModule sourceModule) { super(type, document, completionOffset, completionLength, sourceModule); } }
And to implement templates proposal computer class. This class instance should be created from ExamplePythonCompletionProposalComputer.createTemplateProposalComputer() method. ExamplePythonTemplateCompletionProcessor.java
public class ExamplePythonTemplateCompletionProcessor extends ScriptTemplateCompletionProcessor { private static char[] IGNORE = {'.'}; public ExamplePythonTemplateCompletionProcessor( ScriptContentAssistInvocationContext context) { super(context); } protected String getContextTypeId() { return ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType.CONTEXT_TYPE_ID; } protected char[] getIgnore() { return IGNORE; } protected ScriptTemplateAccess getTemplateAccess() { return ExamplePythonTemplateAccess.getInstance(); } }
Next class will implement access to templates store. ExamplePythonTemplateAccess.java
public class ExamplePythonTemplateAccess extends ScriptTemplateAccess { private static final String CUSTOM_TEMPLATES_KEY = "org.eclipse.dtlk.example.python.Templates"; private static ExamplePythonTemplateAccess instance; public static ExamplePythonTemplateAccess getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new ExamplePythonTemplateAccess(); } return instance; } protected String getContextTypeId() { return ExamplePythonUniversalTemplateContextType.CONTEXT_TYPE_ID; } protected String getCustomTemplatesKey() { return CUSTOM_TEMPLATES_KEY; } protected IPreferenceStore getPreferenceStore() { return ExamplePythonUI.getDefault().getPreferenceStore(); } }
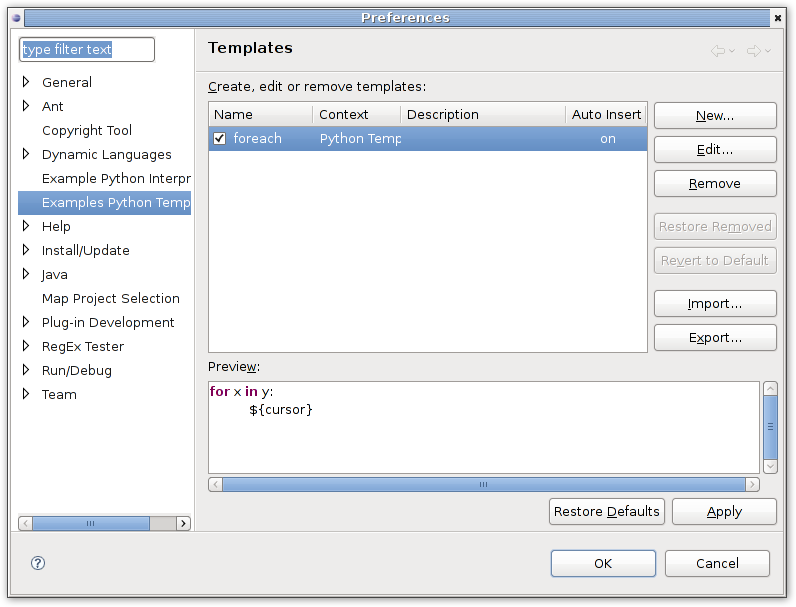
Also we need to add template preference configuration page:
<extension point="org.eclipse.ui.preferencePages"> <page class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.completion.templates.ExamplePythonCodeTemplatesPreferencePage" id="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.ui.editor.Templates" name="Examples Python Templates"/> </extension>
And page itselt: ExamplePythonCodeTemplatesPreferencePage.java
public class ExamplePythonCodeTemplatesPreferencePage extends ScriptTemplatePreferencePage { protected ScriptSourceViewerConfiguration createSourceViewerConfiguration() { return new ExampleSimplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration(getTextTools() .getColorManager(), getPreferenceStore(), null, IExamplePythonPartitions.PYTHON_PARTITIONING, false); } protected void setDocumentParticioner(IDocument document) { getTextTools().setupDocumentPartitioner(document, IExamplePythonPartitions.PYTHON_PARTITIONING); } protected void setPreferenceStore() { setPreferenceStore(ExamplePythonUI.getDefault().getPreferenceStore()); } protected ScriptTemplateAccess getTemplateAccess() { return ExamplePythonTemplateAccess.getInstance(); } private ExamplePythonTextTools getTextTools() { return ExamplePythonUI.getDefault().getTextTools(); } }
Templates support has one requirement IDLTKUILanguageToolkit class should return not null source viewer configuration from createSourceViewerConfiguration() method. We need to overwrite ui language toolkit declared in second part and return correct source viewer configuration:
<extension point="org.eclipse.dltk.ui.language"> <language class="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.internal.ui.ExamplePythonUILanguageToolkit2" nature="org.eclipse.dltk.examples.python.nature" priority="1"> </language> </extension>
ExamplePythonUILanguageToolkit2.java
public class ExamplePythonUILanguageToolkit2 extends ExamplePythonUILanguageToolkit { public ScriptSourceViewerConfiguration createSourceViewerConfiguration() { return new ExampleSimplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration(getTextTools() .getColorManager(), getPreferenceStore(), null, getPartitioningId(), false); } }
ExampleSimplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration.java
public class ExampleSimplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration extends ExamplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration { private boolean fConfigureFormatter; public ExampleSimplePythonSourceViewerConfiguration( IColorManager colorManager, IPreferenceStore preferenceStore, ITextEditor editor, String partitioning, boolean configureFormatter) { super(colorManager, preferenceStore, editor, partitioning); fConfigureFormatter = configureFormatter; } public IAutoEditStrategy[] getAutoEditStrategies( ISourceViewer sourceViewer, String contentType) { return null; } public IAnnotationHover getAnnotationHover(ISourceViewer sourceViewer) { return null; } public IAnnotationHover getOverviewRulerAnnotationHover( ISourceViewer sourceViewer) { return null; } public int[] getConfiguredTextHoverStateMasks(ISourceViewer sourceViewer, String contentType) { return null; } public ITextHover getTextHover(ISourceViewer sourceViewer, String contentType, int stateMask) { return null; } public ITextHover getTextHover(ISourceViewer sourceViewer, String contentType) { return null; } public IContentFormatter getContentFormatter(ISourceViewer sourceViewer) { if (fConfigureFormatter) return super.getContentFormatter(sourceViewer); else return null; } public IInformationControlCreator getInformationControlCreator( ISourceViewer sourceViewer) { return null; } public IInformationPresenter getInformationPresenter( ISourceViewer sourceViewer) { return null; } public IInformationPresenter getOutlinePresenter( ISourceViewer sourceViewer, boolean doCodeResolve) { return null; } public IInformationPresenter getHierarchyPresenter( ISourceViewer sourceViewer, boolean doCodeResolve) { return null; } public IHyperlinkDetector[] getHyperlinkDetectors(ISourceViewer sourceViewer) { return null; } }
Now we could test templates:
Templates configuration page:
Completion with templates:
Getting the code
The tutorial source code is available from Eclipse Git: