Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Context Data Model"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
| + | The model can provide data portability, interoperability and unification for three kinds of identity data about what we call [[Entity | Entities]] (e.g. people). These three kinds are ''identity'', ''profile'' and ''relationship.'' ''Identity'' information is related to identification, authentication, etc. ''Profile'' information can be preferences, interests, and associated objects like events and things, wishlists. ''Relations'' are links to other [[Entity]]s--they can be used to represent friends and other kinds of associations with other [[Digital Subject]]s. A key kind of relation introduced in the model is the a Higgins ''correlation''--a link between different representations of the same person in different contexts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rather than invent a new metamodel from scratch, the model is based on the W3C's Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL 1.0). We used RDF and OWL to express an abstract base ontology called higgins.owl or [[HOWL]] that in turn describe the domain of identity information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These domain concepts include: | ||
| + | # [[Attribute]] | ||
| + | # [[Context]] | ||
| + | # [[ContextId]] | ||
| + | # [[Correlation]] | ||
| + | # [[Entity]] | ||
| + | # [[Relation]] | ||
| + | # [[SubjectId]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Their semantics have been expressed in higgins.owl summarized here [HOWL]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An overview presentation on the data model can be found here: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.eclipse.org/higgins/images/Higgins_Data_Model.ppt Higgins Data Model Intro (PPT)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Extending HOWL == | ||
| + | HOWL is a base ontology. To be useful in real-world applications developers must develop specialized ontologies based on HOWL that describe a specific concrete domain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, if a developer wanted to describe a CRM database, she would create an OWL ontology that would describe the data objects in the CRM database. This CRM database is called a [[Context]] in Higgins. If, for example, the database contained records about customers and those customers had full-names and email addresses, then the developer would define "Customer" as a sub-class of [[Entity]] and "full-name" and "email" as kinds of [[Attribute]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here are some HOWL-based Ontologies: | ||
| + | * [[test-person Example Context Ontology]] | ||
| + | * [[Person-with-address Example Context Ontology]] | ||
| + | * [[Person-with-friend Example Context Ontology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == HOWL and IdAS == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Identity Attribute Service]] (IdAS) provides a Java API that exposes read/write-able data from a wide variety of external data sources in the common Higgins model. The IdAS API implements but does not define the semantics of the Higgins data model. [[Context Provider]] plug-ins to IdAS are used to adapt external system, site, database or other data source to the IdAS API. These [[Context Provider]]s are responsible for data transformation between the Higgins model and their own internal data model. Higgins does not constrain the [[Context Provider]]'s choice of data representation; it could be XML-based, object-oriented, relational, or anything else. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Context Provider]]s can be used to adapt data stores/sources such as: | ||
| + | * Directories: LDAP stores like eDirectory, Active Directory, OpenLDAP, etc... | ||
| + | * Relational databases used by enterprise apps to store identity/profile information. | ||
| + | * Digital social networks (node-edge graphs): data behind Facebook, MySpace, LinkedIn, etc; or the graphs created by mining email traffic | ||
| + | * Email/IM/collaboration client account data: email and IM client accounts, contact/buddy lists | ||
| + | * Identity/profile data stored in website "silos": personal information stored sites like eBay, Amazon, Google Groups, Yahoo Groups | ||
| + | |||
The Higgins Global Graph is built on existing, proven web and semantic web technologies. It extends these by defining conventions on their use within the context of Higgins. | The Higgins Global Graph is built on existing, proven web and semantic web technologies. It extends these by defining conventions on their use within the context of Higgins. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 53: | ||
=== Data Model === | === Data Model === | ||
* [[HOWL]] - Conventions on how W3C Web Ontology Langugage (OWL) is used to describe the attributes of [[Digital Subject]]s (nodes) in the graph --the [[Higgins Data Model]] | * [[HOWL]] - Conventions on how W3C Web Ontology Langugage (OWL) is used to describe the attributes of [[Digital Subject]]s (nodes) in the graph --the [[Higgins Data Model]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Open Issues== | ||
| + | * [[Data Model Open Issues]] | ||
| + | ** [[LDAP Issues and To-Dos]] --open issues specifically related to LDAP schema | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | ===RDF/OWL Related Resources=== | ||
| + | * OWL | ||
| + | ** W3C OWL working group: http://www.w3.org/2007/OWL/wiki/OWL_Working_Group | ||
| + | ** OWL 1.1 at Google Code: http://code.google.com/p/owl1-1/ | ||
| + | ** OWL 1.1 WD 8: http://www.w3.org/TR/owl11-syntax/ | ||
| + | * Intro to RDF/OWL: [[RDF-OWL Data Model]] | ||
| + | * Semantic Web (RDF/OWL) Resources | ||
| + | ** Toolkit: [http://www.wiwiss.fu-berlin.de/suhl/bizer/toolkits/ Developers Guide to Semantic Web Toolkits] | ||
| + | ** Reference documents: [http://www.w3.org/2001/sw/WebOnt/#Current W3C Web Ontology Working Group] | ||
| + | ** Tutorial: http://www.cs.man.ac.uk/~horrocks/ISWC2003/Tutorial/ | ||
| + | * Normalization to OWL/RDF | ||
| + | ** [http://www.ldap.com/1/spec/schema/ont.shtml Schemat] | ||
| + | ** Sebastian Dietzold, Generating RDF Models from LDAP Directories (PDF), [http://www.semanticscripting.org/SFSW2006/ 2nd Workshop on Scripting for the Semantic Web] co-located with the [http://www.eswc2006.org/ 3rd European Semantic Web Conference], June 12, 2006 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Misc Resources=== | ||
| + | * http://wiki.idcommons.net/index.php/Identity_Schemas | ||
| + | * "D3.2: Models" FIDIS, October, 2005, ([http://www.fidis.net/fileadmin/fidis/deliverables/fidis-wp2-del2.3.models.pdf PDF] 74 pages). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Summary: "The objective of this document is to present in a synthetic way different models of representation of a person ("person schema") that can be used in different application domains. | ||
| + | * [http://www.nmi-edit.org/eduPerson/internet2-mace-dir-eduperson-200604.html eduPerson spex] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
* [http://eclipse.org/higgins Higgins Home] | * [http://eclipse.org/higgins Higgins Home] | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 31 January 2008
Contents
Introduction
The model can provide data portability, interoperability and unification for three kinds of identity data about what we call Entities (e.g. people). These three kinds are identity, profile and relationship. Identity information is related to identification, authentication, etc. Profile information can be preferences, interests, and associated objects like events and things, wishlists. Relations are links to other Entitys--they can be used to represent friends and other kinds of associations with other Digital Subjects. A key kind of relation introduced in the model is the a Higgins correlation--a link between different representations of the same person in different contexts.
Rather than invent a new metamodel from scratch, the model is based on the W3C's Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL 1.0). We used RDF and OWL to express an abstract base ontology called higgins.owl or HOWL that in turn describe the domain of identity information.
These domain concepts include:
Their semantics have been expressed in higgins.owl summarized here [HOWL].
An overview presentation on the data model can be found here:
Higgins Data Model Intro (PPT)
Extending HOWL
HOWL is a base ontology. To be useful in real-world applications developers must develop specialized ontologies based on HOWL that describe a specific concrete domain.
For example, if a developer wanted to describe a CRM database, she would create an OWL ontology that would describe the data objects in the CRM database. This CRM database is called a Context in Higgins. If, for example, the database contained records about customers and those customers had full-names and email addresses, then the developer would define "Customer" as a sub-class of Entity and "full-name" and "email" as kinds of Attributes.
Here are some HOWL-based Ontologies:
- test-person Example Context Ontology
- Person-with-address Example Context Ontology
- Person-with-friend Example Context Ontology
HOWL and IdAS
The Identity Attribute Service (IdAS) provides a Java API that exposes read/write-able data from a wide variety of external data sources in the common Higgins model. The IdAS API implements but does not define the semantics of the Higgins data model. Context Provider plug-ins to IdAS are used to adapt external system, site, database or other data source to the IdAS API. These Context Providers are responsible for data transformation between the Higgins model and their own internal data model. Higgins does not constrain the Context Provider's choice of data representation; it could be XML-based, object-oriented, relational, or anything else.
Context Providers can be used to adapt data stores/sources such as:
- Directories: LDAP stores like eDirectory, Active Directory, OpenLDAP, etc...
- Relational databases used by enterprise apps to store identity/profile information.
- Digital social networks (node-edge graphs): data behind Facebook, MySpace, LinkedIn, etc; or the graphs created by mining email traffic
- Email/IM/collaboration client account data: email and IM client accounts, contact/buddy lists
- Identity/profile data stored in website "silos": personal information stored sites like eBay, Amazon, Google Groups, Yahoo Groups
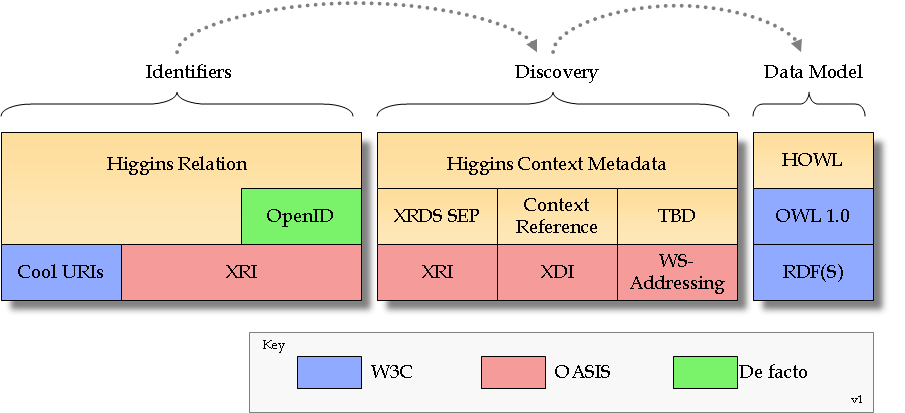
The Higgins Global Graph is built on existing, proven web and semantic web technologies. It extends these by defining conventions on their use within the context of Higgins.
Identifiers
- Relation - Conventions on how URIs, XRIs, and OpenIDs are used to point to nodes in the graph
Discovery
- Higgins XRDS Service Endpoint - Conventions on how XRDS is used to support access to Digital Subjects (nodes) in the graph referenced by Relations
- Higgins XDI Context Reference - As above but using XDI instead of XRDS
Data Model
- HOWL - Conventions on how W3C Web Ontology Langugage (OWL) is used to describe the attributes of Digital Subjects (nodes) in the graph --the Higgins Data Model
Open Issues
- Data Model Open Issues
- LDAP Issues and To-Dos --open issues specifically related to LDAP schema
References
RDF/OWL Related Resources
- OWL
- W3C OWL working group: http://www.w3.org/2007/OWL/wiki/OWL_Working_Group
- OWL 1.1 at Google Code: http://code.google.com/p/owl1-1/
- OWL 1.1 WD 8: http://www.w3.org/TR/owl11-syntax/
- Intro to RDF/OWL: RDF-OWL Data Model
- Semantic Web (RDF/OWL) Resources
- Toolkit: Developers Guide to Semantic Web Toolkits
- Reference documents: W3C Web Ontology Working Group
- Tutorial: http://www.cs.man.ac.uk/~horrocks/ISWC2003/Tutorial/
- Normalization to OWL/RDF
- Schemat
- Sebastian Dietzold, Generating RDF Models from LDAP Directories (PDF), 2nd Workshop on Scripting for the Semantic Web co-located with the 3rd European Semantic Web Conference, June 12, 2006
Misc Resources
- http://wiki.idcommons.net/index.php/Identity_Schemas
- "D3.2: Models" FIDIS, October, 2005, (PDF 74 pages).
Summary: "The objective of this document is to present in a synthetic way different models of representation of a person ("person schema") that can be used in different application domains.