Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
GEF/GEF4/MVC
Note to non-wiki readers: This documentation is generated from the Eclipse wiki - if you have corrections or additions it would be awesome if you added them in the original wiki page.
Introduction
The GEF4 MVC component provides support for building up graphical editors and views based on a model-view-controller architecture and is the intended replacement for GEF (MVC) 3.x. It is internally composed out of four modules, which provide toolkit-independent base abstractions and implementations (MVC), JavaFX-specific specializations (MVC.FX), and Eclipse UI-integration for both (MVC.UI, MVC.FX.UI). In addition there is a deployed MVC Logo Example.
MVC
- feature: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc
- bundle: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc
The MVC module of GEF4 MVC offers those core concepts that are independent of any concrete rendering toolkit as well as of the Eclipse UI. As indicated by its name, the module provides a model-view-controller architecture that can be used to build up graphical editors and views. In good tradition with GEF (MVC) 3.x, 'controllers' are referred to as 'parts' (while the term 'visual part' instead of 'edit part' is used here, to depict that the MVC framework is not limited to editors alone).
A graphical application is thus composed of one or more viewers, where each viewer (IViewer) is populated by a set of visual parts (IVisualPart), which control the visuals that are rendered inside the viewer's controls. Those visual parts that are responsible of controlling to be visualized contents, are referred to as content parts (IContentPart). They are accompanied by feedback parts (IFeedbackPart) and handle parts (IHandlePart), which do not control visualized contents but feedback or handle visuals that are needed for user interaction. All visual parts are arranged in a hierarchy (which resembles the hierarchy of visuals) that is rooted by a 'root part' (IRootPart).
Besides the parent-child relationship that establishes the hierarchy, visual parts may also be related to each other by means of an anchorage-anchor relationship. That is, a visual part that is placed at an arbitrary location within the hierarchy may be anchored on another anchorage part. As the visual part hierarchy has to correspond to the visual hierarchy, this mechanism is very useful when parts that control visuals that are placed in arbitrary places within the visual hierarchy have to be related to each other. In a graphical application that usually organizes visuals into layers, it can for instance be used to update feedback or handles. By explicitly anchoring a feedback part on an underlying (anchorage) target content part, the feedback part inter alia obtains the necessary hooks to listen for changes of the content part visual (e.g. position changes) and to update its own feedback visual accordingly.
Tools (ITool) are used to interact with the parts inside a viewer. Each tool should be responsible of handling a certain interaction gesture (e.g. mouse click/drag or touch-based pinch/spread), by locating respective target parts (e.g. via hit-testing on the visual) and forwarding the interaction to them. While a tool should not have own interaction logic, it is responsible of handling the interaction, to which several parts may contribute e.g. by updating their visuals and contents, as a whole. That is, the tool has to ensure that all modifying operations that result from a certain interaction, are executed in a single (undoable) transaction. As an interaction may span several viewers (e.g. a drag/drop operation), tools are bound to a domain (IDomain), to which also all viewers that make up a graphical application are bound. The domain maintains a global operation history and facilities to initialize and commit transactions.
The handling of an interaction is not performed directly by the target visual parts themselves, but by respective policies (IPolicy) that are bound to them. A policy is a (passive) strategy that encapsulates a certain undoable logic. The active tool that handles an interaction takes this into account, as it locates target parts also by evaluating their supported policies, and interacts with these (interaction) policies instead of the visual part itself. Each (interaction) policy is related to one or more gestures (e.g. what to do on click/drag) and may thus be accessed by several tools. It may handle the response to an interaction directly, e.g. by manipulating the viewer state (e.g. changing the current selection when the target part gets clicked), or can delegate it to certain (transaction) policies that manipulate the contents as a result of an interaction (and have to do this by means of executing operations within the currently active transaction, the respective interaction tool has opened via the domain).
The viewer state (e.g. the current selection), which might be manipulated as the result of an interaction, is represented by means of dedicated models (e.g. ContentModel or SelectionModel), which are bound to each viewer. As changes to the viewer state, as well as to the visualized contents, may lead to necessary viewer updates as well, behaviors (IBehavior) may be bound to parts similar to policies. In contrast to policies, behaviors are active themselves, that is they will actively listen for changes (e.g. newly added content) and perform a certain. Behaviors are also responsible of creating and disposing respective visual parts as needed (e.g. to update selection feedback as a result of changes to the selection model). In contrast to policies, the reactions performed by behaviors are not executed on the operation history and are thus not undoable.
{Root}
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc
The {Root} package contains a com.google.inject.Module] that defines default bindings for MVC.
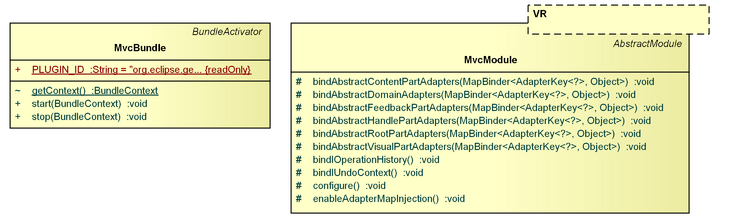
MvcModule
The MvcModule defines methods that register certain default bindings, which can be refined (overridden) by sub-classes. It also defines a couple of (empty) hook methods for bindings that subclasses should define.
Behaviors
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.behaviors
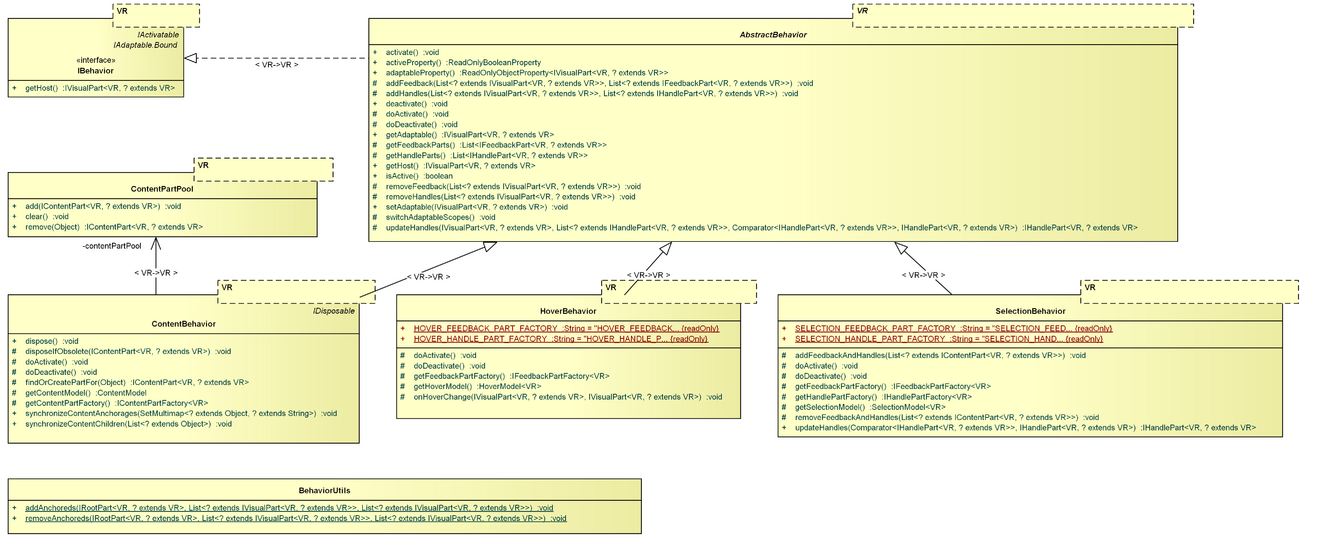
The Behaviors package contains the IBehavior and AbstractBehavior definitions. Additionally, it provides various IBehavior implementations and a related utility class.
IBehavior, AbstractBehavior
An IBehavior is bound to an IVisualPart, referred to as the host of the behavior. It actively listens to changes (usually of a viewer model like the SelectionModel or ContentModel) that affect its host and encapsulates a (not undoable) reaction to these changes, like showing or hiding feedback or handles. The SelectionBehavior for instance listens to changes of the SelectionModel and generates (or removes) selection feedback and handles in case its host is selected or deselected. To support proper registration of listeners, IBehavior extends org.eclipse.gef4.common.activate.IActivatable, so it is activated/deactivated by its host whenever the host itself is activated/deactivated. Registering and unregistering listeners can thus be performed during the activation and deactivation respectively.
An IBehavior is similar to an IPolicy in that it is bound to an IVisualPart. However, policies are not active by themselves (they are always called from the outside). Further, the response of an IBehavior is not meant to be undoable, whereas the response of an IPolicy is.
The AbstractBehavior handles activation and deactivation and provides methods to add/remove feedback and handle parts using the IFeedbackPartFactory and IHandlePartFactory of the IViewer.
BehaviorUtils
The BehaviorUtils class provides utility methods for establishing/unestablishing anchored-anchorage relations. These methods are used by the AbstractBehavior when adding/removing feedback or handles.
ContentBehavior, ContentPartPool
The ContentBehavior is listening for ContentModel changes to initiate a content synchronization upon changes. During a content synchronization, the currently active content parts are checked against the current content objects, i.e. content parts are created or removed based on the parent-child and anchored-anchorage relations between the content objects as defined by the content parts.
A content part that is removed is stored in a ContentPartPool, so that it can be re-used if it is needed later, and does not have to be re-created.
HoverBehavior
The HoverBehavior reacts to HoverModel changes. It can be bound to all content parts that should generate feedback/handles when the mouse hovers the part.
SelectionBehavior
The SelectionBehavior reacts to SelectionModel changes. It can be bound to all content parts that should generate feedback/handles when the part is selected.
Domain
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.domain
The Domain package contains the IDomain abstraction and its related AbstractDomain realization.
IDomain, AbstractDomain
The IDomain represents the collective state of a graphical application, i.e. it is composed of all IViewers and ITools. Additionally, the IDomain provides an org.eclipse.core.commands.operations.IOperationHistory and org.eclipse.core.commands.operations.IUndoContext, which are used by policies to change the state of the application.
Models
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.models
The Models package contains all viewer models, i.e. the data constituting a viewer state.
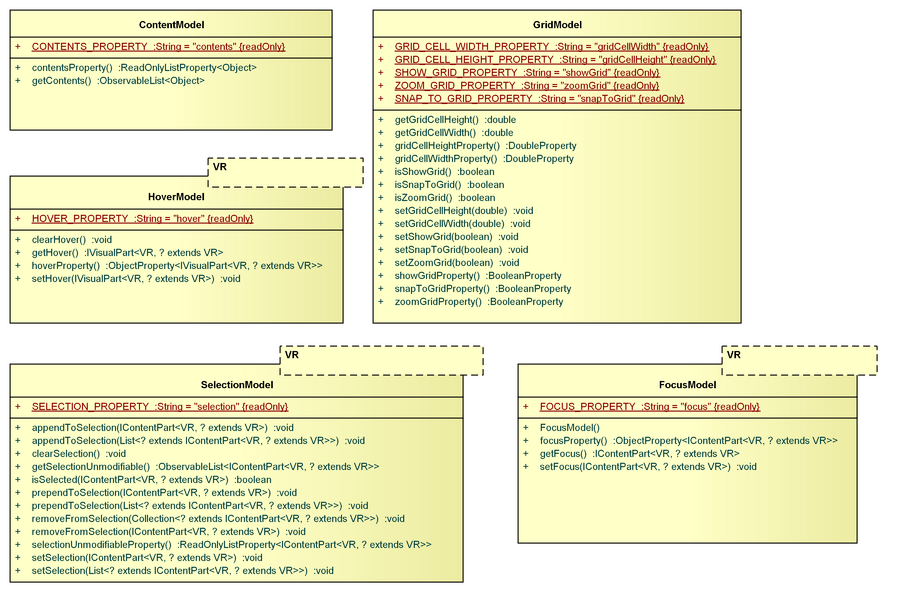
ContentModel
The ContentModel stores the viewer's contents, i.e. the data that is processed by your application.
FocusModel
The FocusModel stores the IVisualPart with keyboard focus, i.e. the part that will receive all keyboard input.
GridModel
The GridModel stores the viewer's background grid settings:
- snap-to-grid,
trueorfalse, indicates whether the visualization should snap to grid points. - show-grid,
trueorfalse, indicates whether to show the grid, or not. - zoom-grid,
trueorfalse, indicates whether to zoom the grid, or not. - grid-cell-width,
Double, specifies the width of grid cells. - grid-cell-height,
Double, specifies the height of grid cells.
HoverModel
The HoverModel stores the currently hovered IVisualPart.
SelectionModel
The SelectionModel stores all currently selected IContentParts.
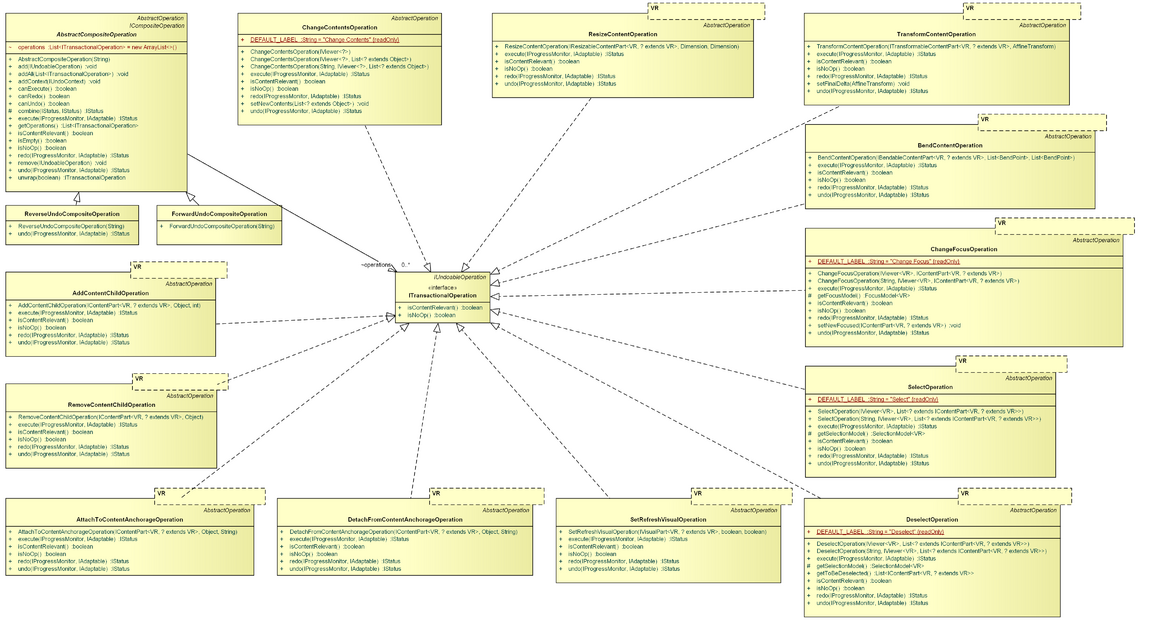
Operations
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.operations
The Operations package contains implementations of IUndoableOperation which can be used to manipulate the default models, especially content creation and removal.
ITransactionalOperation
The ITransactionalOperation is a specialization of org.eclipse.core.commands.operations.IUndoableOperation, which further supports querying for content relevance and effect of the encapsulated operation.
AbstractCompositeOperation
The AbstractCompositeOperation is the base class for two concrete org.eclipse.core.commands.operations.ICompositeOperation implementations: ForwardUndoCompositeOperation and ReverseUndoCompositeOperation.
AddContentChildOperation
The AddContentChildOperation can be used to add a content child to an IContentPart. It relies on the IContentPart's addContentChild() method for doing this.
This operation is the counterpart of the RemoveContentChildOperation.
AttachToContentAnchorageOperation
The AttachToContentAnchorageOperation can be used to attach an IContentPart to a content anchorage. It relies on the IContentPart's attachToContentAnchorage() method for doing this.
This operation is the counterpart of the DetachFromContentAnchorageOperation.
BendContentOperation
The BendContentOperation allows to bend the content of an BendableContentPart.
ChangeContentsOperation
The ChangeContentsOperation allows to exchange the contents hold by the ContentModel.
ChangeFocusOperation
The ChangeFocusOperation can be used to set the currently focused part by manipulating the FocusModel.
DeselectOperation
The DeselectOperation can be used to clear the currently selected parts by manipulating the SelectionModel.
DetachFromContentAnchorageOperation
The DetachFromContentAnchorageOperation can be used to detach an IContentPart from a content anchorage. It relies on the IContentPart's detachFromContentAnchorage() method for doing this.
This operation is the counterpart of the AttachToContentAnchorageOperation.
ForwardUndoCompositeOperation
The ForwardUndoCompositeOperation is a specific AbstractCompositeOperation. It will execute(), redo(), and undo() its operations in the order they were added to the composite operation.
RemoveContentChildOperation
The RemoveContentChildOperation can be used to remove a content child from an IContentPart. It relies on the IContentPart's removeContentChild() method for doing this.
This operation is the counterpart of the AddContentChildOperation.
ResizeContentOperation
The ResizeContentOperation allows to resize the contents of an ResizableContentPart.
ReverseUndoCompositeOperation
The ReverseUndoCompositeOperation is a specific AbstractCompositeOperation. It will execute() and redo() its operations in the order they were added to the composite operation, however it will undo() its operations in reverse order.
SelectOperation
The SelectOperation can be used to manipulate the currently selected parts by manipulating the SelectionModel.
SetRefreshVisualOperation
The SetRefreshVisualOperation can be used to enable/disable the #refreshVisual() method for a specific IVisualPart.
TransformContentOperation
The TransformContentOperation can be used to transform the content of an ITransformableContentPart.
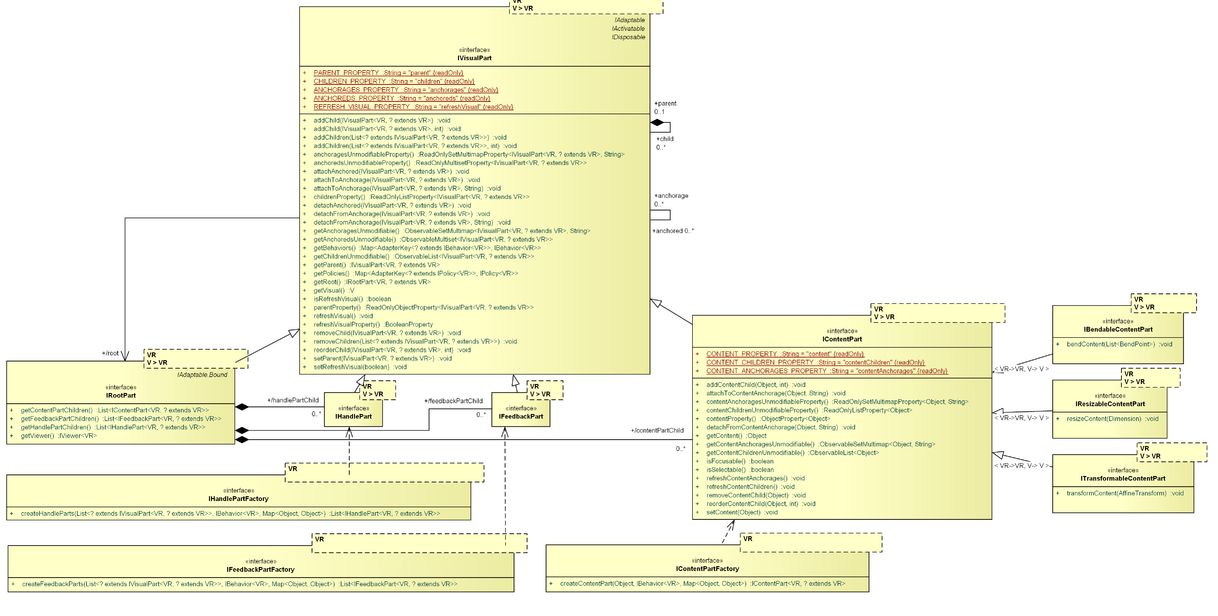
Parts
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.parts
The Parts package contains all abstractions related to controllers (aka parts) in a model-view-controller architecture. For each abstraction, a corresponding (abstract) realization is provided, from which specific controllers can be sub-classed.
IVisualPart, AbstractVisualPart
The IVisualPart interface is the main MVC abstraction for controller objects, and therefore, controls a visual and handles user interaction. Visual parts are organized in a hierarchy, i.e. every part (except the root part) is associated with a parent part, and can control a number of children parts. Additional to the parent-child relations, visual parts can be part of anchored-anchorage relations, which are independent to the hierarchy, i.e. anchoreds and anchorages can be located at arbitrary places within the hierarchy.
Visual parts are adaptable, so that you can adapt policies and behaviors to them (as well as anything else if needed). This is an integral part of user interaction, because the tools will delegate input events to corresponding policies of the visual part which controls the event target (visual). Visual parts are also activatable. During activation/deactivation they will activate/deactivate their adapters.
Moreover, an IVisualPart exposes observable properties for:
-
"active": This visual part was activated/deactivated. -
"adapters": The adapters (policies, behaviors, etc.) of this visual part changed. -
"parent": The parent of this visual part changed. -
"children": The children of this visual part changed. -
"anchorages": The anchorages of this visual part changed. -
"anchoreds": The anchoreds of this visual part changed.
IRootPart, AbstractRootPart
The IRootPart interface is a specialization of the IVisualPart interface. There is exactly one IRootPart per IViewer. It contains all IContentParts, IFeedbackParts, and IHandleParts as children and manages the root visuals.
IContentPart, AbstractContentPart
The IContentPart interface is a specialization of the IVisualPart interface. Content parts are bound to content model elements, i.e. they provide a link to the model, and allow manipulations of the model via addContentChild(), removeContentChild(), attachToContentAnchorage(), and detachFromContentAnchorage().
IFeedbackPart, AbstractFeedbackPart
The IFeedbackPart interface is a specialization of the IVisualPart interface. Feedback parts are used to give visual feedback to the user during interactions. They are usually rendered on top of the content parts.
IHandlePart, AbstractHandlePart
The IHandlePart interface is a specialization of the IVisualPart interface. Handle parts are used for visual handles, which can be used for interaction, i.e. to manipulate elements. They are usually rendered on top of the feedback parts.
IContentPartFactory
The IContentPartFactory interface is part of a default mechanic in MVC: It is used during the content synchronization within the ContentBehavior to create new content parts. Therefore, if you want to use this default mechanic, you have to supply an IContentPartFactory suitable to your content model.
ITransformableContentPart
The ITransformableContentPart interface is to be implemented by IContentParts, which support transformations of their content. This is e.g. used to persist a translate operation.
IResizableContentPart
The IResizableContentPart interface is to be implemented by IContentParts, which support resize of their content. This is e.g. used to persist a resize operation.
IBendableContentPart
The IBendableContentPart interface is to be implemented by IContentParts, which support bending of their content (i.e. manipulation throw inserting or moving of bend points). This is e.g. used to persist a bend operation.
IFeedbackPartFactory
The IFeedbackPartFactory interface is part of a default mechanic in MVC: It is used for creating feedback parts within the default behaviors, i.e. in response to mouse hover or selection changes.
IHandlePartFactory
The IHandlePartFactory interface is part of a default mechanic in MVC: It is used for creating handle parts within the default behaviors, i.e. in response to mouse hover or selection changes.
PartUtils
The PartUtils class is a collection of utility methods when working with visual parts.
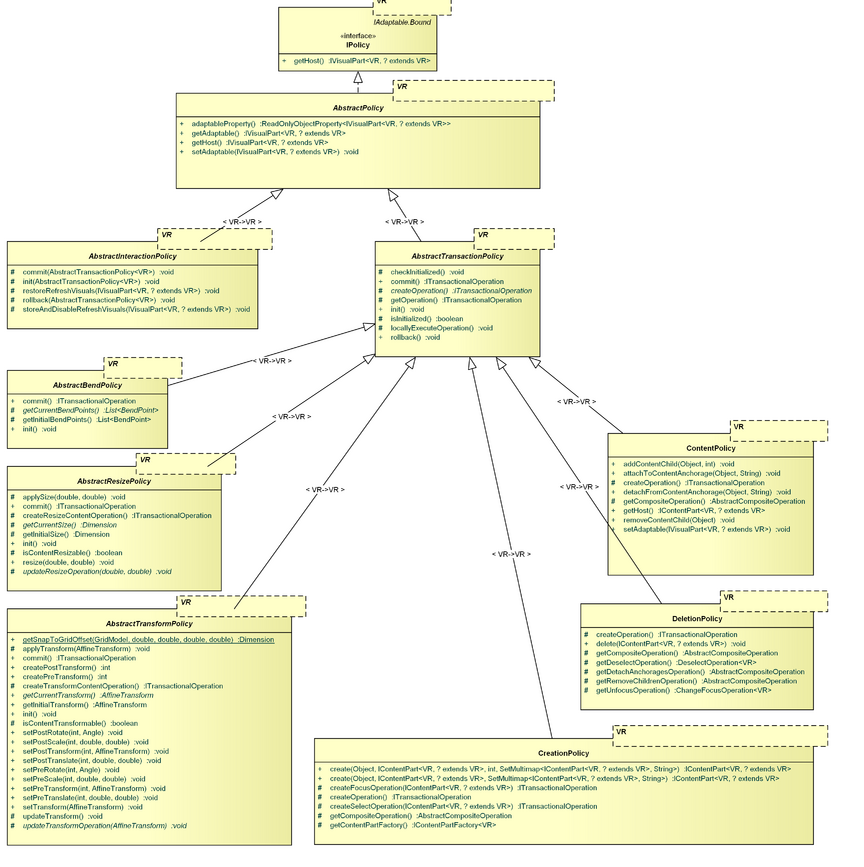
Policies
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.policies
The Policies package contains the IPolicy abstraction, a related abstract base implementation (AbstractPolicy), and concrete implementations for the manipulation of the ContentModel, namely ContentPolicy, CreationPolicy, and DeletionPolicy.
IPolicy, AbstractPolicy
An IPolicy is bound to an IVisualPart, referred to as the host of the policy. There are basically two kinds of policies, interaction and transaction policies. An interaction policy is called by a ITool to handle part of an interaction (e.g. click, drag). A transaction policy is one that may be used by other (interaction or transaction) policies to actually perform a visual or semantic operation (e.g. create model element). It has to encapsulate the to be performed operation as an ITransactionalOperation.
An IPolicy is similar to an IBehavior in that it is bound to an IVisualPart. However, behaviors are active by themselves (they actively listen to changes), while policies are always called from the outside (they are passive). Further, the response of an IPolicy is meant to be undoable, whereas the response of an IBehavior is not.
AbstractTransactionPolicy
The AbstractTransactionPolicy is the base class for all policies that perform undoable changes. The offer init(), commit(), and rollback(), which enclose an undoable transaction.
AbstractInteractionPolicy
The AbstractInteractionPolicy is the base class for all policies that response to an interaction gesture. They usually delegate to some transactional policies to perform a visual or content relevant reaction.
ContentPolicy
The ContentPolicy is an AbstractTransactionPolicy to handle content changes, i.e. adding/removing of content children, as well as attaching/detaching to/from content anchorages. Therefore, it can be used to retrieve an operation which performs the desired content changes.
CreationPolicy
The CreationPolicy is an AbstractTransactionPolicy that handles the creation of new content objects using the ContentPolicy. Therefore, it can be used to retrieve an operation which performs the desired creations.
DeletionPolicy
The DeletionPolicy is an AbstractTransactionPolicy that handles the deletion of existing content objects using the ContentPolicy. Therefore, it can be used to retrieve an operation which performs the desired deletions.
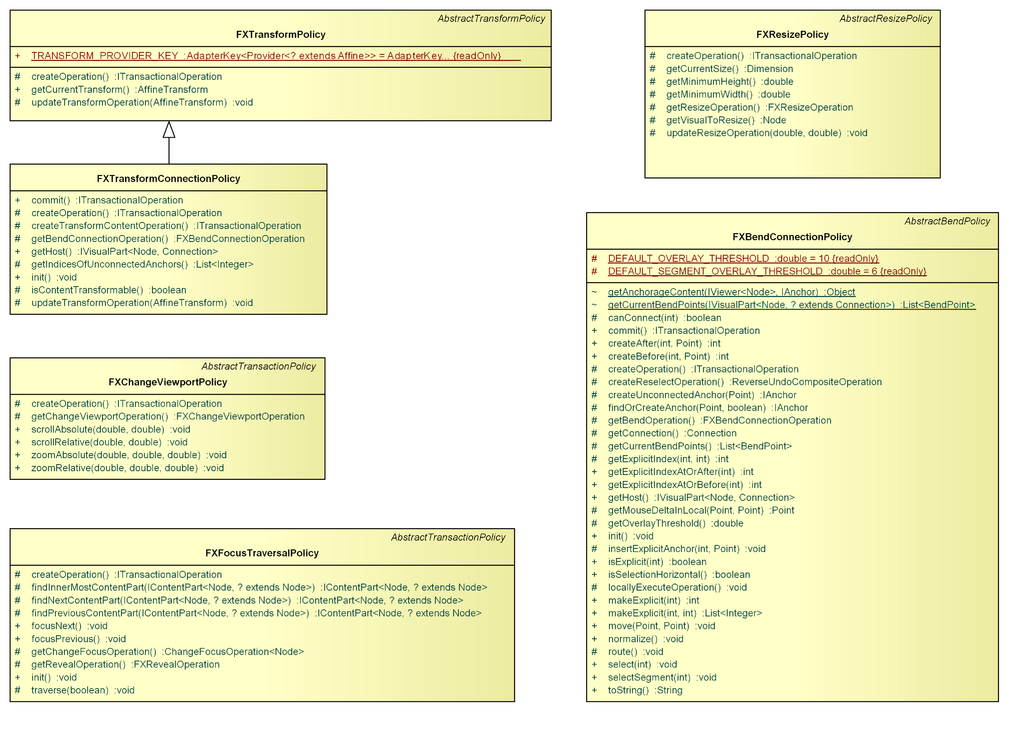
AbstractTransformPolicy
The AbstractTransformPolicy is an AbstractTransactionPolicy that supports content transformation of ITransformableContentParts.
AbstractResizePolicy
The AbstractResizePolicy is an AbstractTransactionPolicy that supports content resizing of IResizableContentParts.
AbstractBendPolicy
The AbstractBendPolicy is an AbstractTransactionPolicy that supports content bending of IBendableContentParts.
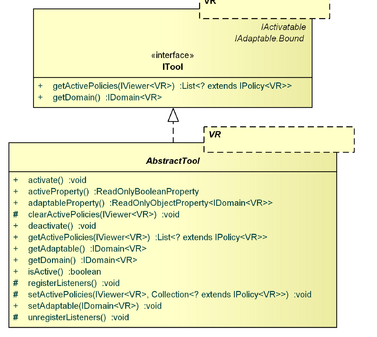
Tools
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.tools
The Tools package contains the ITool abstraction and its related AbstractTool realization.
ITool, AbstractTool
An ITool delegates input events to corresponding (interaction) IPolicies, which are responsible of handling the interaction.
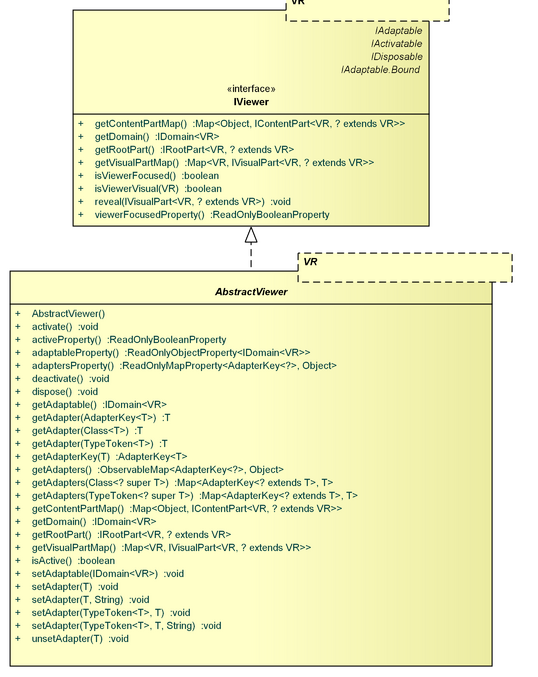
Viewer
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.viewer
The Viewer package contains the IViewer abstraction and the related AbstractViewer realization.
IViewer, AbstractViewer
An IViewer is the container for an IVisualPart hierarchy and provides a link to the IDomain.
MVC.FX
- feature: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx
- bundle: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx
The MVC.FX module of GEF4 MVC provides specializations of the abstractions and implementations provided by MVC, which are bound to JavaFX-based visualizations.
{Root}
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx
The {Root} package contains a Guice Module with default bindings for MVC.FX.
MvcFxModule
The MvcFxModule extends MvcModule. It defines methods to register bindings for the JavaFX-specific extensions to MVC and adds respective default bindings.
Behaviors
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.behaviors
The Behaviors package contains JavaFX/MVC.FX-specific IBehavior implementations.
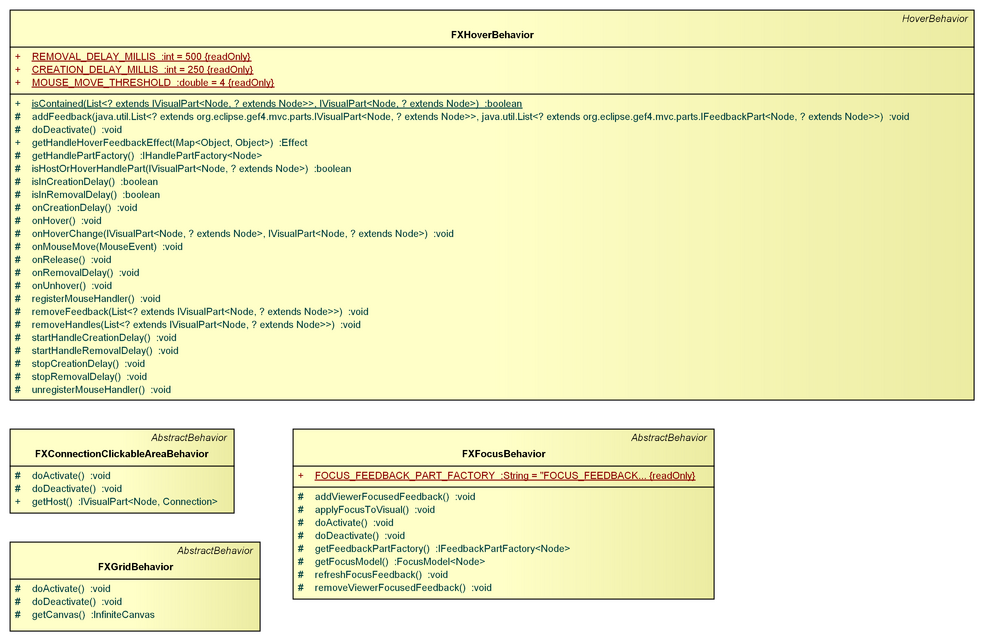
FXConnectionClickableAreaBehavior
The FXConnectionClickableAreaBehavior controls the size of the connection's curve node visible area dependent on the zoom level.
FXFocusBehavior
The FXFocusBehavior is listening for FocusModel changes and transfers them over to JavaFX.
FXGridBehavior
The FXGridBehavior is listening for GridModel changes in order to apply those changes to the GridLayout of the IViewer.
FXHoverBehavior
The FXHoverBehavior is listening for HoverModel changes in order to generate feedback/handles when hovering a part.
Domain
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.domain
The Domain package contains a JavaFX-specific IDomain implementation, which does not provide own logic but is used as a target for adapter map bindings within MVC.FX.
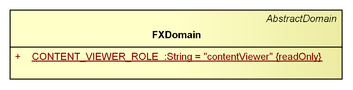
FXDomain
The FXDomain parameterizes the AbstractDomain with javafx.scene.Node, but does not extend it further. It is basically intended to provide a target for adapter bindings and adapter scoping (see GEF4 Common).
Operations
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.operations
The Operations package contains all IUndoableOperation implementations contributed by MVC.FX.
FXBendConnectionOperation
The FXBendConnectionOperation can be used to manipulate the points constituting an Connection, i.e. its start point, way points, and end point. When manipulating the start or end point, it does also connect it to the IVisualPart under mouse when applicable.
FXChangeViewportOperation
The FXChangeViewportOperation can be used to manipulate the InfiniteCanvas of the content FXViewer, i.e. the scroll offset and content transformation.
FXResizeOperation
The FXResizeOperation can be used to resize a javafx.scene.Node.
FXRevealOperation
The FXRevealOperation can be used to reveal an IVisualPart in its IViewer.
FXTransformOperation
The FXTransformOperation can be used to manipulate the transformation associated with an IVisualPart due to FXTransformProvider.
Parts
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.parts
The Parts package contains all IContentPart, IVisualPart, IFeedbackPart, and IHandlePart implementations and related classes.
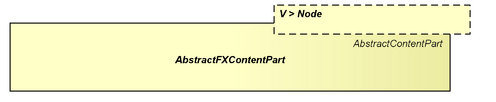
AbstractFXContentPart
The AbstractFXContentPart is a specialization of the AbstractContentPart which establishes javafx.scene.Node as the visual root type. It does also register its whole visual hierarchy at the visual-part-map.
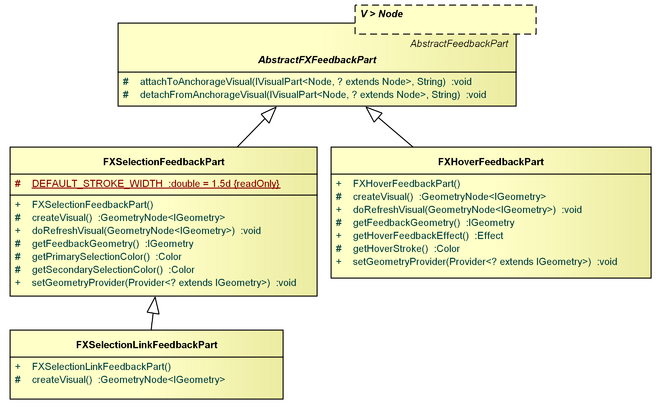
AbstractFXFeedbackPart, FXHoverFeedbackPart, FXSelectionFeedbackPart, FXSelectionLinkFeedbackPart
The AbstractFXFeedbackPart is a specialization of the AbstractFeedbackPart which establishes javafx.scene.Node as the visual root type. It does also register a org.eclipse.gef4.fx.listeners.VisualChangeListener upon attachment to an anchorage which refreshes the feedback visual upon anchorage visual changes.
The FXHoverFeedbackPart displays a feedback geometry in response to HoverModel changes.
The FXSelectionFeedbackPart displays a feedback geometry in response to SelectionModel changes and FocusModel changes.
The FXSelectionLinkFeedbackPart is a specialization of the FXSelectionFeedbackPart which displays a dashed feedback geometry in response to SelectionModel changes and FocusModel changes.
FXDefaultFocusFeedbackPartFactory, FXDefaultHoverFeebackPartFactory, FXDefaultSelectionFeedbackPartFactory
The FXDefaultFocusFeedbackPartFactory , FXDefaultHoverFeebackPartFactory and FXDefaultSelectionFeedbackPartFactory use FXHoverFeedbackPart, FXSelectionFeedbackPart, and FXSelectionLinkFeedbackPart for generating feedback if the associated geometry provider is bound as an adapter on the hovered/selected part.
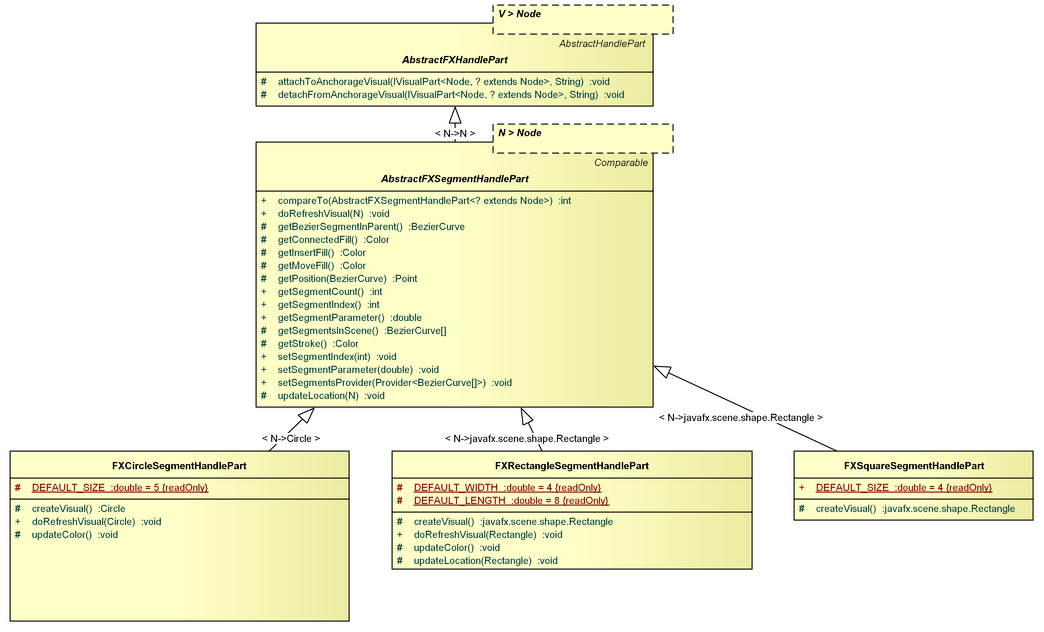
AbstractFXHandlePart, AbstractFXSegmentHandlePart, FXCircleSegmentHandlePart, FXRectangleSegmentHandlePart, FXSquareSegmentHandlePart
The AbstractFXHandlePart is a specialization of the AbstractHandlePart which establishes javafx.scene.Node as the visual root type. It does also register a org.eclipse.gef4.fx.listeners.VisualChangeListener upon attachment to an anchorage which refreshes the handle visual upon anchorage visual changes.
The AbstractFXSegmentHandlePart is a specialization of the AbstractFXHandlePart which is bound to a segment of a poly-bezier handle geometry, represented by an array of BezierCurves. A segment index identifies that segment (0, 1, 2, ...). A segment parameter specifies the position of this handle part on the segment (0 = start, 0.5 = mid, 1 = end).
The FXCircleSegmentHandlePart is a specialization of the AbstractFXSegmentHandlePart which uses a javafx.scene.shape.Circle for the handle visualization.
The FXRectangleSegmentHandlePart is a specialization of the AbstractFXSegmentHandlePart which uses a javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle for the handle visualization.
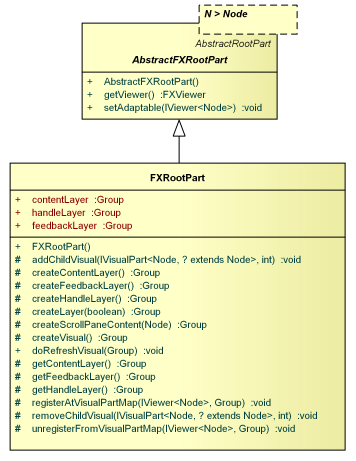
The AbstractFXRootPart is a specialization of the AbstractRootPart which establishes javafx.scene.Node as the visual root type. It does also register the part as soon as a link to the IViewer is obtained.
FXDefaultHoverHandlePartFactory, FXDefaultSelectionHandlePartFactory
The FXDefaultHoverHandlePartFactory and FXDefaultSelectionHandlePartFactory use FXCircleSegmentHandlePart, FXRectangleSegmentHandlePart, and FXSquareSegmentHandlePart for generating handles if the associated geometry provider is bound as an adapter on the hovered/selected part.
FXRootPart
The FXRootPart provides a content layer, a feedback layer, and a handle layer in which the visuals of the corresponding parts are displayed. The feedback layer is above the content layer, and the handle layer is above the feedback layer.
FXPartUtils
Policies
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.policies
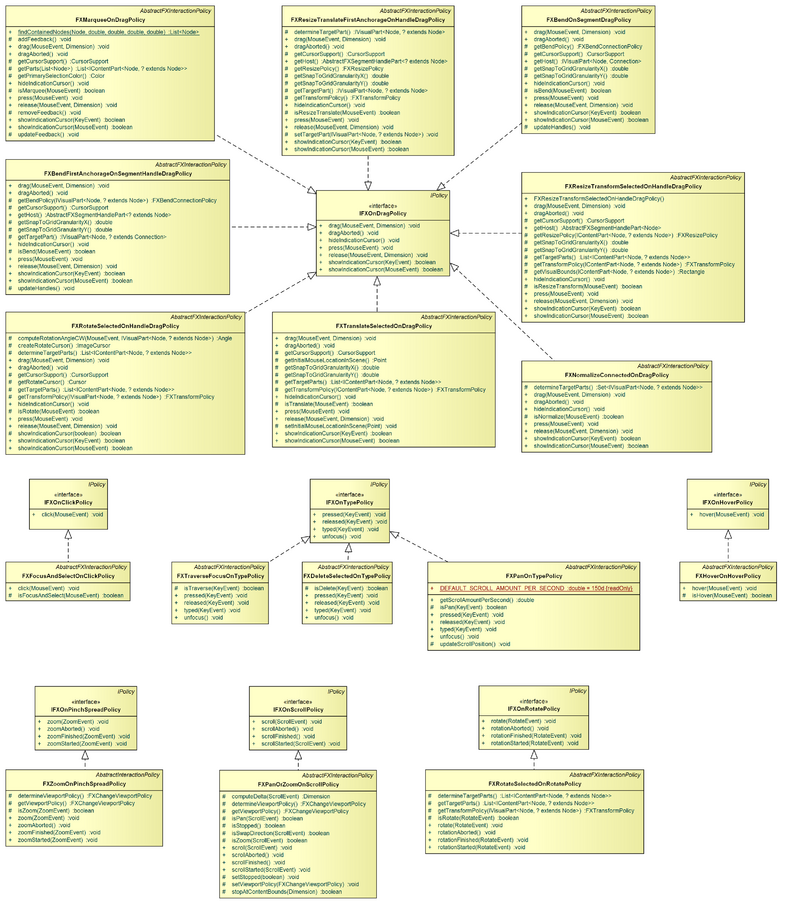
The Policies package contains all IPolicy implementations contributed by MVC.FX. These can be divided into transactional policies, which can be used to generate an operation that performs certain changes, and interaction policies, which are associated with certain user interactions (mouse click/drag, touch pinch/spread, etc.).
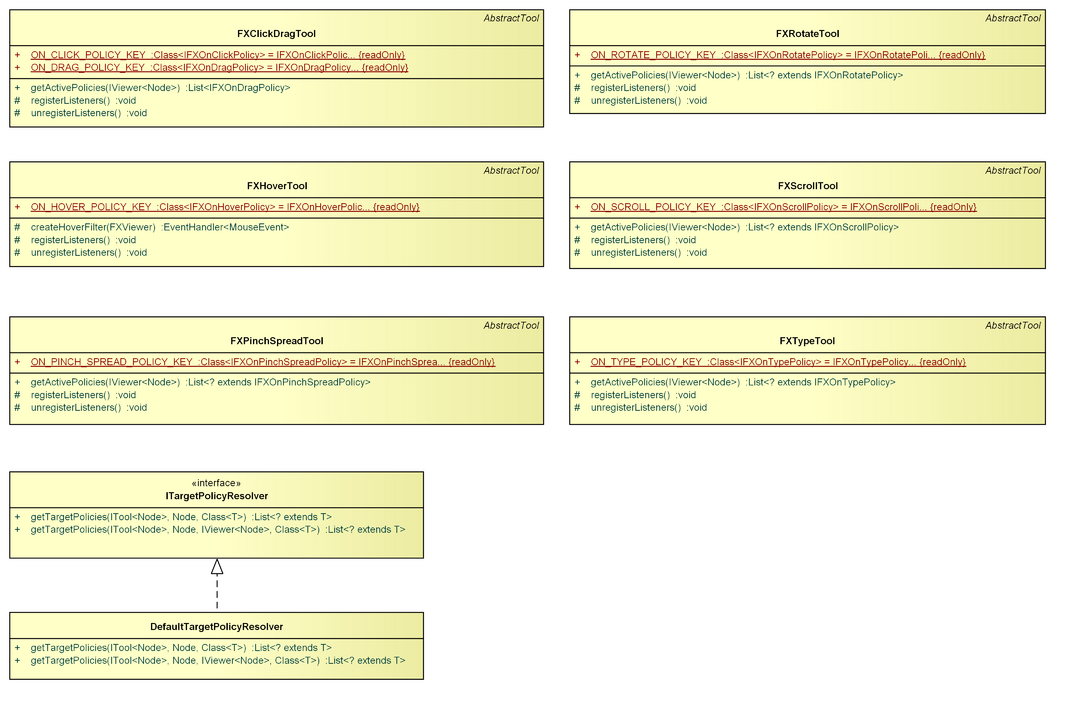
IFXOnClickPolicy
An IFXOnClickPolicy is called upon mouse click events by the FXClickDragTool. You can use it as an adapter on any IVisualPart for which mouse click interaction is desired, and you can also register multiple instances of IFXOnClickPolicy on the same IVisualPart (with different adapter roles).
IFXOnDragPolicy
An IFXOnDragPolicy is called during a mouse press-drag-release gesture by the FXClickDragTool. You can use it as an adapter on any IVisualPart for which mouse drag interaction is desired, and you can also register multiple instances of IFXOnDragPolicy on the same IVisualPart (with different adapter roles).
IFXOnHoverPolicy
An IFXOnHoverPolicy is called upon mouse hover by the FXHoverTool. You can use it as an adapter on any IVisualPart for which mouse hover interaction is desired, and you can also register multiple instances of IFXOnHoverPolicy on the same IVisualPart (with different adapter roles).
IFXOnPinchSpreadPolicy
An IFXOnPinchSpreadPolicy is called during a pinch/spread touch gesture by the FXPinchSpreadTool. You can use it as an adapter on any IVisualPart for which pinch/spread touch interaction is desired, and you can also register multiple instances of IFXOnPinchSpreadPolicy on the same IVisualPart (with different adapter roles).
IFXOnRotatePolicy
An IFXOnRotatePolicy is called during a rotate touch gesture by the FXRotateTool. You can use it as an adapter on any IVisualPart for which rotate touch interaction is desired, and you can also register multiple instances of IFXOnRotatePolicy on the same IVisualPart (with different adapter roles).
IFXOnScrollPolicy
An IFXOnScrollPolicy is called upon mouse wheel scrolling or during a touch scroll gesture by the FXScrollTool. You can use it as an adapter on any IVisualPart for which scroll interaction is desired, and you can also register multiple instances of IFXOnScrollPolicy on the same IVisualPart (with different adapter roles).
IFXOnTypePolicy
An IFXOnTypePolicy is called upon key presses and releases by the FXTypeTool. You can use it as an adapter on any IVisualPart for which keyboard interaction is desired, and you can also register multiple instances of IFXOnTypePolicy on the same IVisualPart (with different adapter roles).
FXFocusAndSelectOnClickPolicy
The FXFocusAndSelectOnClickPolicy is an IFXOnClickPolicy that focusses and selects the host part upon mouse click. It manipulates the FocusModel and SelectionModel.
FXMarqueeOnDragPolicy
The FXMarqueeOnDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy that can be used to span a marquee selection area covering multiple parts using mouse drag. It manipulates the SelectionModel.
FXTranslateSelectedOnDragPolicy
The FXTranslateSelectedOnDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy that relocates the host visual when dragging with the mouse. It is based on the FXTransformPolicy of its host.
FXBendOnSegmentDragPolicy
The FXBendOnSegmentDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy that can be used to drag individual segments of a Connection with an orthogonal org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.OrthogonalRouter. It is based on the FXBendConnectionPolicy of its host.
FXNormalizeConnectedOnDragPolicy
The FXNormalizeConnectedOnDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy used to remove superfluous segments of outgoing or incoming org.eclipse.gef4.fx.connection.Connections with an orthogonal OrthogonalRouter when dragging the source or target element. It is based on the FXBendConnectionPolicy of the connected parts.
FXBendFirstAnchorageOnSegmentHandleDragPolicy
The FXBendOnSegmentHandleDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy which can be applied to FXSegmentHandlePart to bend the host's first anchorage, i.e. manipulate the org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.Connection visual of the first anchorage of the host FXSegmentHandlePart. It uses the FXBendConnectionPolicy of the first anchorage.
FXResizeTransformSelectedOnHandleDragPolicy
The FXResizeRelocateOnHandleDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy that can be applied to FXSegmentHandlePart to resize and relocate the first anchorage of its host on mouse drag. It is based on FXResizePolicy and FXTransformPolicy of the selected parts.
FXRotateSelectedOnHandleDragPolicy
The FXRotateSelectedOnHandleDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy that that can be applied to FXSegmentHandlePart to rotate the selected parts on mouse drag. It is based on the FXTransformPolicy of the selected parts.
FXResizeTransformFirstAnchorageOnHandleDragPolicy
The FXResizeTransformFirstAnchorageOnHandleDragPolicy is an IFXOnDragPolicy that that can be applied to FXSegmentHandlePart to resize and transform the visual of its host's first anchorage on mouse drag. It is based on the FXResizePolicy and FXTransformPolicy of the host's first anchorage.
FXHoverOnHoverPolicy
The FXHoverOnHoverPolicy is an IFXOnHoverPolicy that hovers the host part upon mouse hover. It manipulates the HoverModel.
FXZoomOnPinchSpreadPolicy
The FXZoomOnPinchSpreadPolicy is an is an IFXOnPinchSpreadPolicyzooms the InfiniteCanvas of the content FXViewer with a touch pinch/spread gesture. It is based on the FXChangeViewportPolicy of its host.
FXRotateSelectedOnRotatePolicy
The FXRotateSelectedOnRotatePolicy is an is an IFXOnRotatePolicy that rotates the selected parts with a touch rotate gesture. It is based on the FXTransformPolicy of the selected parts.
FXPanOrZoomOnScrollPolicy
The FXPanOrZoomOnScrollPolicy changes the scroll offset or zoom level of the org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.InfiniteCanvas of the content FXViewer upon mouse/touch scroll events. It is based on the FXChangeViewportPolicy of the FXRootPart.
FXDeleteSelectedOnTypePolicy
The FXDeleteSelectedOnTypePolicy is an IFXOnTypePolicy that deletes the selected parts when pressing the <Delete> key. It manipulates the ContentModel.
FXPanOnTypePolicy
The FXPanOnTypePolicy is an IFXOnTypePolicy that changes the scroll offset of the org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.InfiniteCanvas of the content FXViewer upon arrow key presses. It is based on the FXChangeViewportPolicy of the FXRootPart.
FXSelectFocusedOnTypePolicy
The FXSelectFocusedOnTypePolicy is an IFXOnTypePolicy that selects/deselects the focus element on (select) key type. It manipulates the FocusModel.
FXTraverseFocusOnTypePolicy
The FXTraverseFocusOnTypePolicy is an IFXOnTypePolicy that traverses the focus element on (tab) key type. It manipulates the FocusModel.
FXChangeViewportPolicy
The FXChangeViewportPolicy is a transaction policy that can be used to manipulate org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.InfiniteCanvas of the content FXViewer.
FXTransformPolicy
The FXTransformPolicy is a transaction policy that can be used to transform the visual of its host.
FXResizePolicy
The FXResizePolicy is a transaction policy that can be used to resize the visual of its host.
FXBendConnectionPolicy
The FXBendConnectionPolicy is a transaction policy that can be used to manipulate the points constituting an org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.Connection, i.e. its start point, way points, and end point. When moving a point the policy takes care of:
- Removing overlaid neighbor points.
- Re-adding temporarily removed neighbor points.
- Reconnecting points to the IVisualPart under mouse when applicable.
Per default, the FXBendConnectionPolicy can only be applied to those IVisualParts which use org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.Connection as their visual. This can be adjusted by sub-classing and overriding the corresponding #getConnection() method.
FXTransformConnectionPolicy
The FXTransformConnectionPolicy is a specialization of #FXTransformPolicy that can be applied to IVisualParts which use org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.Connection as their visual. Per default, it transforms only those points of a connection that are not bound to an anchorage.
Providers
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.providers
The Providers package provides a number of com.google.inject.Provider, which are used by several mechanisms:
- FXBendConnectionPolicy uses a
Provider<IAnchor>to find an org.eclipse.gef4.fx.anchors.IAnchor for an IVisualPart at which a point of an org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.Connection can be attached. - FXTransformPolicy uses a
Provider<Affine>to transform the visual of an IVisualPart. - FXDefaultFocusFeedbackPartFactory, FXDefaultHoverFeebackPartFactory, FXDefaultSelectionFeedbackPartFactory and FXDefaultHoverHandlePartFactory, FXDefaultSelectionHandlePartFactory use a
Provider<IGeometry>to determine the position and shape of feedback and handle visuals.
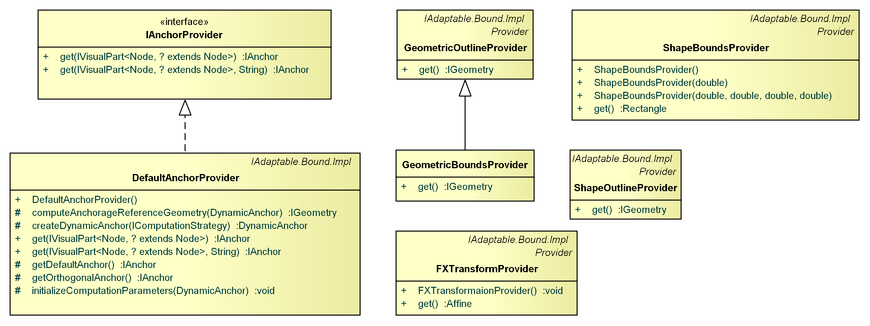
DefaultAnchorProvider
The DefaultAnchorProvider provides an anchor for a given (anchorage) IVisualPart.
FXTransformProvider
The FXTransformProvider adds an javafx.scene.transform.Affine to the transforms list of the visual of the part at which it is bound as an adapter. It does also allow access to that javafx.scene.transform.Affine, which is used by several (transaction) policies to perform transformations.
GeometricOutlineProvider, GeometricBoundsProvider, ShapeOutlineProvider, ShapeBoundsProvider
The GeometricOutlineProvider and GeometricBoundsProvider return the core geometry and related bounds of the visual of the part to which they are bound as an adapter.
The ShapeOutlineProvider and ShapeBoundsProvider do likewise for the visual (shape) outline and bounds.
Tools
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.tools
The Tools package contains JavaFX-specific ITool implementations for different interactions (e.g. mouse drag).
FXClickDragTool
The FXClickDragTool registers listeners for mouse click and drag interactions. The target IVisualPart is determined by searching the visual part hierarchy, beginning at the part that controls the visual, which was pressed, until a part is found that supports at least one IFXOnClickPolicy or IFXOnDragPolicy, respectively.
FXHoverTool
The FXHoverTool registers listeners for mouse hover interaction, i.e. mouse enter and mouse exit events for visuals. The target IVisualPart is determined by searching the visual part hierarchy, beginning at the part that controls the visual, which was hovered, until a part is found that supports at least one IFXOnHoverPolicy.
FXPinchSpreadTool
The FXPinchSpreadTool registers listeners for touch pinch/spread gesture interaction, i.e. moving two fingers apart or bringing them together (the default zoom gesture on many touch displays). The target IVisualPart is determined by searching the visual part hierarchy, beginning at the part that controls the visual, which was touched, until a part is found that supports at least one IFXOnPinchSpreadPolicy.
FXRotateTool
The FXRotateTool registers listeners for touch rotate gesture interaction, i.e. moving two fingers around each other (or moving one finger around another). The target IVisualPart is determined by searching the visual part hierarchy, beginning at the part that controls the visual, which was touched, until a part is found that supports at least one IFXOnRotatePolicy.
FXScrollTool
The FXScrollTool registers listeners for scroll interaction, which may either be mouse wheel scrolling, or touch scrolling, i.e. dragging two fingers up or down. The target IVisualPart is determined by searching the visual part hierarchy, beginning at the part that controls the visual, which was scrolled or touched, until a part is found that supports at least one IFXOnScrollPolicy.
FXTypeTool
The FXTypeTool registers listeners for keyboard interaction. The currently focused (see FocusModel) IVisualPart is used as the target part for keyboard interaction if it supports at least one IFXOnTypePolicy.
Viewer
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.viewer
The Viewer package contains a JavaFX-specific IViewer implementation.
FXViewer
The FXViewer is a JavaFX-specific IViewer implementation. It provides an org.eclipse.gef4.fx.nodes.InfiniteCanvas as its visual control, to which the FXRootPart adds respective top-level children.
MVC.UI
- feature: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.ui
- bundle: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.ui
The MVC.UI module of GEF4 MVC provides aspects for an integration into the Eclipse UI:
- Binding the operation history from the Eclipse Workbench.
- An UndoablePropertySheetPage for contribution to the Eclipse 'Properties' view.
{Root}
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.ui
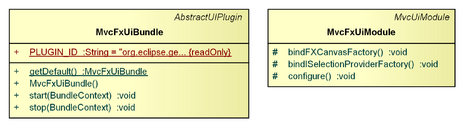
MvcUiModule
The MvcUiModule contains bindings for the Eclipse integration. Currently, only a binding for the org.eclipse.core.commands.operations.IOperationHistory of the Eclipse workbench is provided, so that operations executed in the context of an IDomain are undoable/redoable from the Eclipse UI.
Parts
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.ui.parts
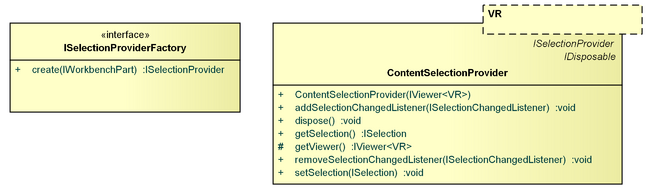
ISelectionProviderFactory
The ISelectionProviderFactory interface can be used to implement a factory that creates an org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ISelectionProvider for a given org.eclipse.ui.IWorkbenchPart.
ContentSelectionProvider
The ContentSelectionProvider is an implementation of the org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ISelectionProvider interface that provides the content elements of the currently selected IContentParts, and can select IContentParts based on their content elements.
Properties
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.ui.properties
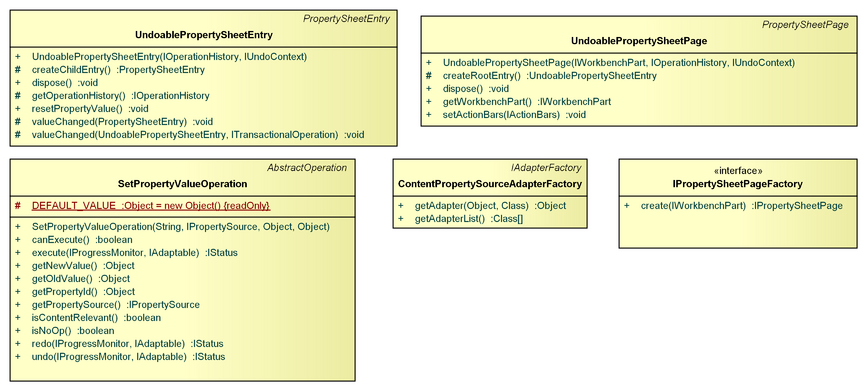
IPropertySheetPageFactory
The IPropertySheetPageFactory interface allows to implement a factory to create an org.eclipse.ui.views.properties.IPropertySheetPage for an org.eclipse.ui.IWorkbenchPart.
UndoablePropertySheetPage, UndoablePropertySheetEntry
The UndoablePropertySheetPage is a org.eclipse.ui.views.properties.PropertySheetPage extension that allows to perform undo/redo of property value changes also in case the viewer/editor is not active.
The UndoablePropertySheetEntry provides undo support for changes made to org.eclipse.ui.views.properties.IPropertySource by the Eclipse 'Properties' view. Clients can construct a org.eclipse.ui.views.properties.PropertySheetPage and use this class as the root entry. All changes made to property sources displayed on that page will be done using the provided org.eclipse.core.commands.operations.IOperationHistory.
SetPropertyValueOperation
The SetPropertyValueOperation can be used to set or reset the value of a property. It is used by the UndoablePropertySheetEntry.
ContentPropertySourceAdapterFactory
The ContentPropertySourceAdapterFactory adapts the content model objects of IContentPart to org.eclipse.ui.views.properties.IPropertySource.
MVC.FX.UI
- feature: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.ui
- bundle: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.ui
The MVC.FX.UI module of GEF4 MVC provides JavaFX-specific aspects for an integration into the Eclipse UI.
{Root}
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.ui
The {Root} package contains a Guice Module which binds an org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ISelectionProvider and handles the construction of an FXCanvas to render the JavaFX scene graph.
MvcFxUiModule
The MvcFxUiModule contains bindings for the JavaFX/Eclipse integration.
Parts
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.ui.parts
The Parts package contains spcific org.eclipse.ui.part.ViewPart and org.eclipse.ui.part.EditorPart implementations which wrap an FXCanvas.
The JavaFX-unrelated classes in this package will be moved to the MVC.UI module as outlined in Bugzilla #469478.
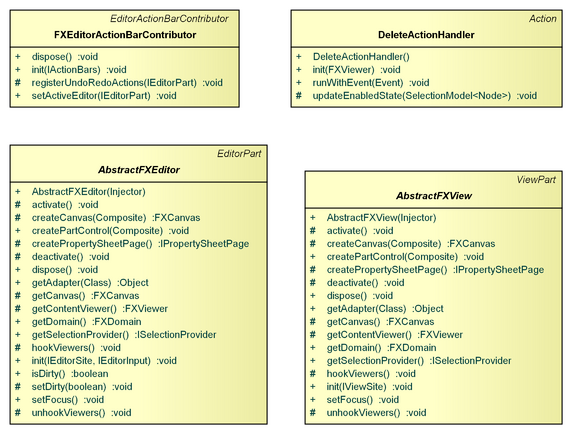
FXEditor
The AbstractFXEditor is a org.eclipse.ui.part.EditorPart extension, which can be used to embed an editor, based on MVC.FX, into the Eclipse UI.
FXEditorActionBarContributor
The FXEditorActionBarContributor is an org.eclipse.ui.part.EditorActionBarContributor extension, which lets the undo/redo action group of the corresponding org.eclipse.ui.part.IEditorPart contribute to the action bars.
FXView
The AbstractFXView is a org.eclipse.ui.part.ViewPart extension, which can be used to embed a viewer, based on MVC.FX, into the Eclipse UI.
DeleteActionHandler
The DeleteActionHandler handles deletion based on the selected IContentParts.
MVC.FX.UI
The MVC.FX.UI module of GEF4 FX provides enhanced support for integrating with the Eclipse UI.
Properties
- package: org.eclipse.gef4.mvc.fx.ui.properties
The Properties package provides support for integrating JavaFX-related cell editors into the Eclipse 'Properties' view.
FXPaintPropertyDescriptor
An FXPaintPropertyDescriptor is a property descriptor that integrates an org.eclipse.gef4.fx.jface.FXPaintLabelProvider and org.eclipse.gef4.fx.jface.FXPaintCellEditor.
Migration from GEF (MVC) 3.x to MVC, MVC.FX, MVC.UI, MVC.FX.UI
GEF4 MVC was written completely from scratch. While some proven concepts have been transferred from GEF (MVC) 3.x, central concepts and mechanisms have been reworked. The most notable differences are:
- More modularity, separating out Eclipse Workbench UI dependencies: While GEF (MVC) 3.x provided a single bundle (with Eclipse UI dependencies), GEF4 MVC clearly separates out those dependencies into the MVC.UI and MVC.FX.UI bundles, so that standalone graphical applications can be realized based on MVC and MVC.FX alone. Furthermore, rendering toolkit independent abstractions (provided by MVC) are now clearly separated from rendering toolkit (i.e. JavaFX) specific concretizations (provided by MVC.FX.
- Usage of JavaFX instead of SWT/Draw2d.
- Usage of adapter pattern throughout: While GEF (MVC) 3.x only used the Eclipse Platform provided adaptable pattern for Eclipse Workbench UI integration tasks (e.g. integration with properties view), this mechanism is used intensively within GEF4 MVC to configure the complete graphical application. That is, tools and viewers are adapted to the domain, viewer models and the root part are adapted to the viewer, policies and behaviors are adapted to visual parts.
- Usage of dependency injection
- Own visual parts for feedback and handles (compared to 'lightweight' feedback)
- Separation of policies (passive, invoked by tools) and behaviors (active, listening for changes)
- Separation of interaction policies (directly invoked by tools, related to interaction) and transaction policies (called by interaction policies, realize the content manipulation)
- Pure interaction-gesture-based tools without own transactional logic (compared to monolithic 'selection tool'): In contrast to GEF (MVC) 3.x, where tools were dedicated to certain semantic operations (creation, selection, etc.), tools are now pretty dumb and dedicated to interaction gestures (click/drag, scroll, etc.), and forward all interactions to respective interaction policies. While the tools provides the transactional context (i.e. it opens and closes a respective operation via the domain, so that all operations that are executed as a result of the interaction can be undone together) they do not translate the gesture-based interaction into semantical operations themselves. This responsibility lies with the interaction policies alone. Where a GEF (MVC) 3.x application had thus to specialize one of the default tools to add different semantic behavior, this can now be achieved by registering different interaction policies, which is much more lightweight.