Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "User:Rick.barkhouse.oracle.com/VTD"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
VTD-XML ([http://vtd-xml.sourceforge.net/ http://vtd-xml.sourceforge.net/]) is a high-performance XML processing model that deals with XML in a binary form, instead of the traditional text form. VTD stands for '''V'''irtual '''T'''oken '''D'''escriptor. | VTD-XML ([http://vtd-xml.sourceforge.net/ http://vtd-xml.sourceforge.net/]) is a high-performance XML processing model that deals with XML in a binary form, instead of the traditional text form. VTD stands for '''V'''irtual '''T'''oken '''D'''escriptor. | ||
| − | VTD-XML parses an XML document and builds an internal data structure representing the entire XML document in <tt>byte[]</tt> form. Each "token" of the XML document is represented as | + | VTD-XML parses an XML document and builds an internal data structure representing the entire XML document in <tt>byte[]</tt> form. Each "token" of the XML document is represented as a 64-bit integer. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==VTD-XML Core Concepts== | ==VTD-XML Core Concepts== | ||
| − | |||
===Generating a VTD-XML Representation of the XML Document (Unmarshal)=== | ===Generating a VTD-XML Representation of the XML Document (Unmarshal)=== | ||
| Line 160: | Line 148: | ||
===Generating a VTD-XML Index File for Faster Parsing=== | ===Generating a VTD-XML Index File for Faster Parsing=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Appendix== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===VTD-XML Binary Format=== | ||
| + | |||
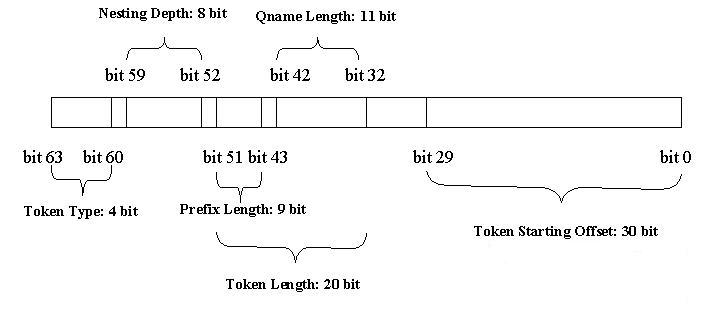
| + | With VTD-XML, each "token" of the XML document is represented as the following 64-bit integer: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Vtd_layout.jpg]] | ||
| + | * Big endian | ||
| + | * Starting offset: 30 bits (b29 ~ b0) maximum value is 2^30 -1 = 1G -1 | ||
| + | * Length: 20 bits (b51 ~ b32) maximum value is 2^20-1 = 1M -1 | ||
| + | ** For some token type | ||
| + | *** Prefix length: 9 bits (b51~ b43) max value 511 | ||
| + | *** Q-name length: 11 bits (b42 ~ b 32) max value 1023 | ||
| + | * Depth: 8 bits (b59~b52) max value is 2^8-1 = 255 | ||
| + | * Token type: 4 bits (b63~b60) | ||
| + | * Reserved bit: 2 bits (b31: b30) | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 14 December 2012
VTD-XML Investigation
VTD-XML (http://vtd-xml.sourceforge.net/) is a high-performance XML processing model that deals with XML in a binary form, instead of the traditional text form. VTD stands for Virtual Token Descriptor.
VTD-XML parses an XML document and builds an internal data structure representing the entire XML document in byte[] form. Each "token" of the XML document is represented as a 64-bit integer.
VTD-XML Core Concepts
Generating a VTD-XML Representation of the XML Document (Unmarshal)
Instantiate a new VTDGen object, and parse a byte[]:
VTDGen vg = new VTDGen(); // from existing byte[] // could be either VTD-XML bytes, or bytes from a regular File, etc. (?) // true indicates namespace aware byte[] bytes = ... vg.setDoc(bytes); vg.parse(true); // - or - // from file vg.parseFile("old.xml", false);
- Obtained from VTDGen instance
- Allows for basic "walking" through elements
- Maintains a single cursor into the byte[] representation of XML
XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ns0:Test xmlns:ns0="uri" xmlns:ns1="n"> <ns1:name>OBJ1</ns1:name> <sub-bean> <ns1:name>OBJ2</ns1:name> </sub-bean> <sub-bean> <ns1:name>OBJ3</ns1:name> </sub-bean> </ns0:Test>
VTDGen vg = new VTDGen(); vg.parseFile("old.xml", false); VTDNav vn = vg.getNav(); // Move cursor to ROOT if (vn.toElement(VTDNav.ROOT)) { System.out.println("Found Root: " + vn.getCurrentIndex()); // Move cursor to first occurrance of 'name', searching in forward direction (FIRST_CHILD) if (vn.toElementNS(VTDNav.FIRST_CHILD, "n", "name")) { System.out.println("Found 'name': " + vn.getCurrentIndex()); // Get the index of the text belonging to the current node int textIndex = vn.getText(); if (textIndex != -1) { System.out.println("Getting 'name' text: " + textIndex); System.out.println(vn.toNormalizedString(textIndex)); } } while (vn.toElementNS(VTDNav.NEXT_SIBLING, null, "sub-bean")) { int subBeanIndex = vn.getCurrentIndex(); System.out.println("Found 'sub-bean': " + subBeanIndex); if (vn.toElementNS(VTDNav.FIRST_CHILD, "n", "name")) { System.out.println("Found 'name': " + vn.getCurrentIndex()); // Get the index of the text belonging to the current node int textIndex = vn.getText(); if (textIndex != -1) { System.out.println("Getting 'name' text: " + textIndex); System.out.println(vn.toNormalizedString(textIndex)); } } // Rewind to top of "sub-bean", to get the next child; vn.toElement(VTDNav.PARENT); } }
Output:
Found Root: 5 Found 'name': 17 Getting 'name' text: 18 --> OBJ1 Found 'sub-bean': 28 Found 'name': 38 Getting 'name' text: 39 --> OBJ2 Found 'sub-bean': 49 Found 'name': 59 Getting 'name' text: 60 --> OBJ3
- Created from VTDNav instance
- Allows for XPath execution
- Allows for iterating over elements selected by XPath
VTDGen vg = new VTDGen(); vg.parseFile("old.xml", false); VTDNav vn = vg.getNav();
Writing a VTD-XML Document (Marshal)
VTDGen vg = new VTDGen(); vg.parseFile("old.xml", false); VTDNav vn = vg.getNav(); XMLModifier xm = new XMLModifier(); xm.bind(vn); // ... // Write to OutputStream xm.output(new FileOutputStream("new.xml"));
Generating a VTD-XML Index File for Faster Parsing
Appendix
VTD-XML Binary Format
With VTD-XML, each "token" of the XML document is represented as the following 64-bit integer:
- Big endian
- Starting offset: 30 bits (b29 ~ b0) maximum value is 2^30 -1 = 1G -1
- Length: 20 bits (b51 ~ b32) maximum value is 2^20-1 = 1M -1
- For some token type
- Prefix length: 9 bits (b51~ b43) max value 511
- Q-name length: 11 bits (b42 ~ b 32) max value 1023
- For some token type
- Depth: 8 bits (b59~b52) max value is 2^8-1 = 255
- Token type: 4 bits (b63~b60)
- Reserved bit: 2 bits (b31: b30)