Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Scout/Tutorial/3.8/Jython Integration"
(→Add Logic for Jython Interpreter and Interaction with Scout Form) |
(→Add Logic for Jython Interpreter and Interaction with Scout Form) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Add Logic for Jython Interpreter and Interaction with Scout Form == | == Add Logic for Jython Interpreter and Interaction with Scout Form == | ||
| − | + | # In the Scout Explorer select the ''RunButton'' element of the ''DesktopForm'' | |
| + | # In the Scout Object Properties click on the green plus-icon next to the link ''Exec Click Action'' to add the corresponding method | ||
| + | # Replace the proposed implementation with the code provided below | ||
@Override | @Override | ||
| Line 46: | Line 48: | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remarks: | ||
| + | * Updating the sys.path should conceptually go to a place where it's calles once per client startup. | ||
| + | * There might be more elegant ways to ensure Jython is able to access the Python modules provided in the Lib subfolder of the jythonlib.jar. | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 1 June 2012
Contents
Introduction
With Release 3.8 the Scout SDK offers support to integrate external JAR files into a Scout application with a few clicks. In this tutorial we use this capability to demonstrate how Jython may be integrated in your Scout application.
According to the Wiki "Jython is a Java implementation of Python" and Python itself claims "You can learn to use Python and see almost immediate gains in productivity and lower maintenance costs." In any case, we need an example library here and combining Java with a powerful scripting language can help to solve a significant variety of problems.
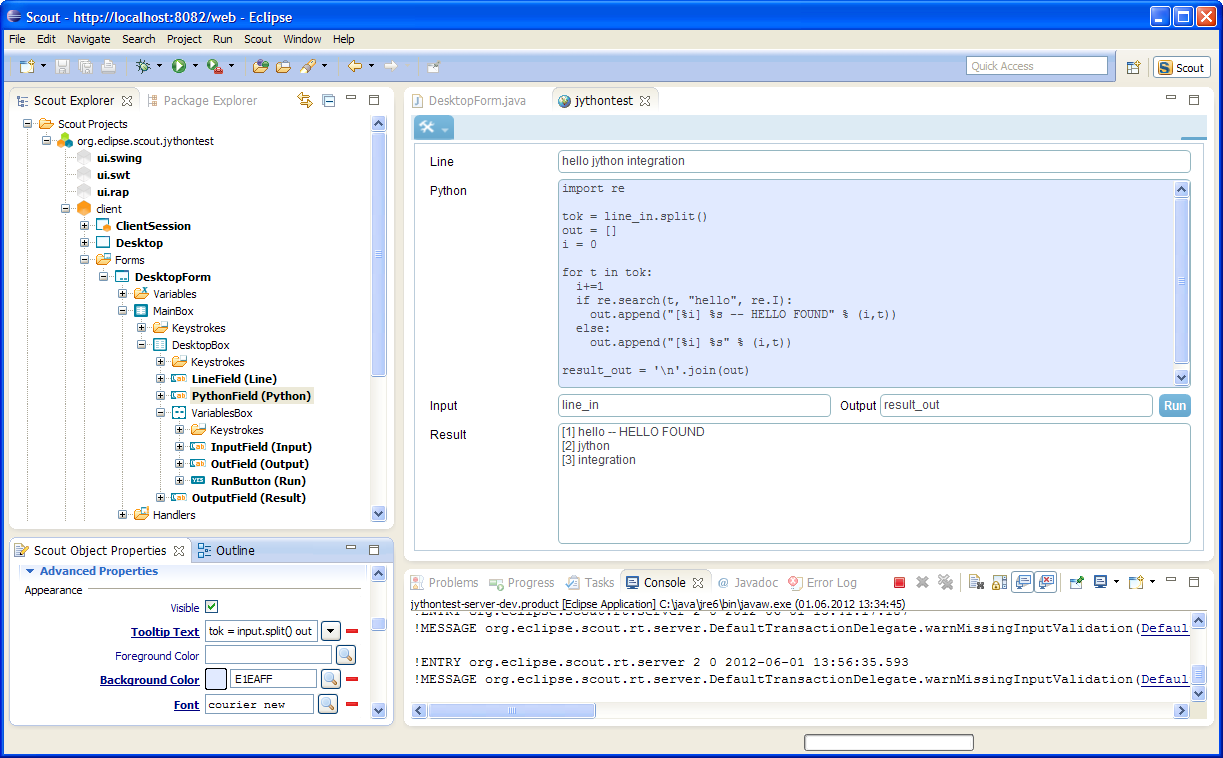
The result at the end of this tutorial will look similar to the screenshot below:
Building the Jythonlib.jar =
bla
Create New Scout Project and add the Library bundle
bla
Add and Configure the Form Fields on the Desktop Form
bla
Add Logic for Jython Interpreter and Interaction with Scout Form
- In the Scout Explorer select the RunButton element of the DesktopForm
- In the Scout Object Properties click on the green plus-icon next to the link Exec Click Action to add the corresponding method
- Replace the proposed implementation with the code provided below
@Override
protected void execClickAction() throws ProcessingException {
getResultField().clearErrorStatus();
try {
// make sure Lib is visible to access python modules
PySystemState sys = Py.getSystemState();
PyString pyLibPath = new PyString("__pyclasspath__/Lib");
if (!sys.path.contains(pyLibPath)) {
sys.path.append(pyLibPath);
}
// get interpreter, read input variable from input field
PythonInterpreter pi = new PythonInterpreter();
pi.set(getInputField().getValue(), new PyString(getLineField().getValue()));
// run script, transfer output to result field
pi.exec(getPythonField().getValue());
getResultField().setValue(pi.get(getOutputField().getValue()).asString());
}
catch (Exception e) {
getResultField().setValue(null);
getResultField().setErrorStatus(e.toString());
}
}
Remarks:
- Updating the sys.path should conceptually go to a place where it's calles once per client startup.
- There might be more elegant ways to ensure Jython is able to access the Python modules provided in the Lib subfolder of the jythonlib.jar.