Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Scout/Concepts/CodeType"
Dev.jmini.fr (Talk | contribs) (First version) |
m (Category changed) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ScoutPage|cat= | + | {{ScoutPage|cat=Shared}} |
A CodeType is a structure to represent a tree key-{{ScoutLink|Concepts|Code|code}} association. They are used in {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartField|SmartField}} and {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartColumn|SmartColumn}}. | A CodeType is a structure to represent a tree key-{{ScoutLink|Concepts|Code|code}} association. They are used in {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartField|SmartField}} and {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartColumn|SmartColumn}}. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Description== |
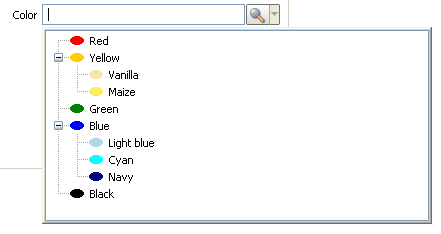
| + | CodeType are used in {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartField|SmartField}} to let the user choose between a finish list of values. The value stored by the field correspond to the key of the selected code. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Scout_SmartField_Hierarchy_SWT.png]] | |
| − | {{ | + | A CodeType can be seen as a tree of {{ScoutLink|Concepts|Code|Codes}}. Each code associate to the key (the {{ScoutProp|Id}}) other properties: among others a {{ScoutProp|Text}} and an {{ScoutProp|IconId}}. |
| − | + | In order to have the same resolving mechanism (getting the display text of a key) CodeType are also used in {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartColumn|SmartColumn}}. To chose multiple value of the list, the fields {{ScoutLink|Concepts|ListBox|ListBox}} (flat CodeType) and {{ScoutLink|Concepts|TreeBox|TreeBox}} (hierarchical CodeType) can be used. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| + | === Organisation of the codes === | ||
The codes are organized in a tree. Therefore a CodeType can have one or more child codes at the root level, and each code can have other child codes. In lot of cases a list of codes (meaning a tree containing only leafs at the first level) is sufficient to cover most of the need. | The codes are organized in a tree. Therefore a CodeType can have one or more child codes at the root level, and each code can have other child codes. In lot of cases a list of codes (meaning a tree containing only leafs at the first level) is sufficient to cover most of the need. | ||
Child codes are ordered in their parent code. This is realized with the {{ScoutLink|Concepts|Order Annotation|order annotation}}. | Child codes are ordered in their parent code. This is realized with the {{ScoutLink|Concepts|Order Annotation|order annotation}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Type of the key === | ||
| + | The type of the key is defined by its generic parameter <code><T></code>. It is very common to use a type from the <code>java.lang.*</code> package (like <code>Integer</code> or <code>String</code>) but any Java Object is suitable. It must: | ||
| + | * implements <code>Serializable</code> | ||
| + | * have correctly implemented <code>equals()</code> and <code>hashCode()</code> functions | ||
| + | * present in the server and the client | ||
There is no obligation to have the same type for the {{ScoutProp|Id}} between the codes of a CodeType (meaning the same generic type parameter for the codes inner-class). However it is a good practice to have the same type between the codes of a CodeType, because the Id are used as value of {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartField|SmartFields}}. Therefore the generic parameter describing the type of value of a SmartField must be compatible with the type of the codes contained in the CodeType. | There is no obligation to have the same type for the {{ScoutProp|Id}} between the codes of a CodeType (meaning the same generic type parameter for the codes inner-class). However it is a good practice to have the same type between the codes of a CodeType, because the Id are used as value of {{ScoutLink|Concepts|SmartField|SmartFields}}. Therefore the generic parameter describing the type of value of a SmartField must be compatible with the type of the codes contained in the CodeType. | ||
| − | |||
| + | ==Using a CodeType== | ||
| + | === SmartField or SmartColumn === | ||
| + | {{ScoutProp|CodeType}} in a SmartField (or SmartColumn). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | public class YesOrNoSmartField extends AbstractSmartField<Boolean> { | ||
| + | // other configuration of properties. | ||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | protected Class<? extends ICodeType<?>> getConfiguredCodeType(){ | ||
| + | return YesOrNoCodeType.class; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the SmartField (or SmartColumn) works with a CodeType, a specific LookupCall is instantiated to get the LookupRows based on the Codes contained in a CodeType. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Accessing a code directly === | ||
| + | Scout-runtime will handle the instantiation and the caching of CodeTypes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This function returns the text corresponding to the key using a CodeType: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | public String getColorName(String key){ | ||
| + | ICode c = CODES.getCodeType(ColorCodeType.class).getCode(key); | ||
| + | if(c != null) { | ||
| + | return c.getText(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return null; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Static CodeType == | ||
| + | === Java Code and structure === | ||
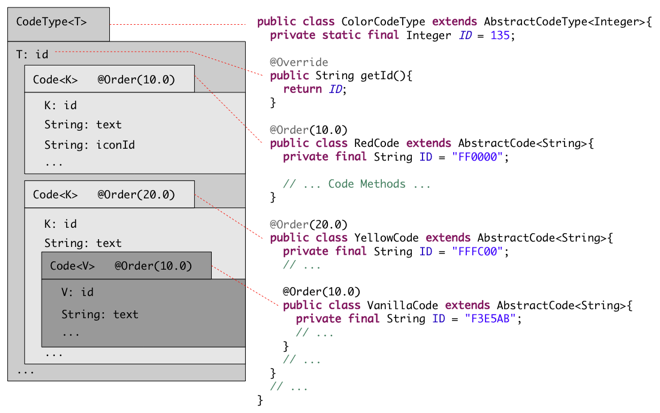
| + | [[Image:Scout_CodeType_Structure.png]] | ||
| − | |||
The common way to define a CodeType is to extend AbstractCodeType. Each code is an inner-class extending AbstractCode. Like usual the properties of Codes and CodeTypes can be set with {{ScoutLink|Concepts|GetConfigured Methods|getConfiguredXxxxxx()}} methods. | The common way to define a CodeType is to extend AbstractCodeType. Each code is an inner-class extending AbstractCode. Like usual the properties of Codes and CodeTypes can be set with {{ScoutLink|Concepts|GetConfigured Methods|getConfiguredXxxxxx()}} methods. | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{ScoutLink|Concepts|CodeType/Example|See the Java Code}} of a simple <code>YesOrNoCodeType</code> having just two codes: |
| + | * <code>YesOrNoCodeType.YesCode</code> | ||
| + | * <code>YesOrNoCodeType.NoCode</code> | ||
| − | The SDK provides some help to generate CodeTypes and Codes. The CodeType appears in the {{ScoutLink|SDK|Explorer View|Explorer View}} in the '''Enumerations''' folder under shared | + | === With the SDK === |
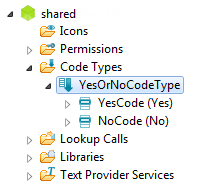
| + | The SDK provides some help to generate CodeTypes and Codes. The CodeType appears in the {{ScoutLink|SDK|Explorer View|Explorer View}} in the '''Enumerations''' folder under {{ScoutLink|Concepts|Shared Plug-In|shared}}. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:ScoutSDK_CodeType.png]] | |
| − | + | It is possible to add a new CodeType using a wizard. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Dynamic CodeType == |
| + | Code types are not necessary hardcoded. It is possible to implement other mechanisms to load CodeType dynamically. | ||
| − | + | The description of the Codes can come from a database or from an XML files. If you want to do so, you just need to implement the method corresponding to the event {{ScoutEvent|LoadCodes}}. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | {{ | + | |
| − | + | {{note|TODO| Describe good organization of classes to load codeType from an XML File or a Database. With small UML graph}} | |
| − | + | It is possible to use the static and the dynamic approach together. In this case, if there is a conflict (2 codes for the same id) the event {{ScoutEvent|OverwriteCode}} is triggered. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 12:21, 3 November 2011
The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.
A CodeType is a structure to represent a tree key-The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. association. They are used in The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. and The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/..
- implements: The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.
- extends: The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.
Contents
Description
CodeType are used in The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. to let the user choose between a finish list of values. The value stored by the field correspond to the key of the selected code.
A CodeType can be seen as a tree of The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.. Each code associate to the key (the The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.) other properties: among others a The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. and an The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/..
In order to have the same resolving mechanism (getting the display text of a key) CodeType are also used in The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.. To chose multiple value of the list, the fields The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. (flat CodeType) and The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. (hierarchical CodeType) can be used.
Organisation of the codes
The codes are organized in a tree. Therefore a CodeType can have one or more child codes at the root level, and each code can have other child codes. In lot of cases a list of codes (meaning a tree containing only leafs at the first level) is sufficient to cover most of the need.
Child codes are ordered in their parent code. This is realized with the The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/..
Type of the key
The type of the key is defined by its generic parameter <T>. It is very common to use a type from the java.lang.* package (like Integer or String) but any Java Object is suitable. It must:
- implements
Serializable - have correctly implemented
equals()andhashCode()functions - present in the server and the client
There is no obligation to have the same type for the The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. between the codes of a CodeType (meaning the same generic type parameter for the codes inner-class). However it is a good practice to have the same type between the codes of a CodeType, because the Id are used as value of The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.. Therefore the generic parameter describing the type of value of a SmartField must be compatible with the type of the codes contained in the CodeType.
Using a CodeType
SmartField or SmartColumn
The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. in a SmartField (or SmartColumn).
public class YesOrNoSmartField extends AbstractSmartField<Boolean> { // other configuration of properties. @Override protected Class<? extends ICodeType<?>> getConfiguredCodeType(){ return YesOrNoCodeType.class; } }
If the SmartField (or SmartColumn) works with a CodeType, a specific LookupCall is instantiated to get the LookupRows based on the Codes contained in a CodeType.
Accessing a code directly
Scout-runtime will handle the instantiation and the caching of CodeTypes.
This function returns the text corresponding to the key using a CodeType:
public String getColorName(String key){ ICode c = CODES.getCodeType(ColorCodeType.class).getCode(key); if(c != null) { return c.getText(); } return null; } }
Static CodeType
Java Code and structure
The common way to define a CodeType is to extend AbstractCodeType. Each code is an inner-class extending AbstractCode. Like usual the properties of Codes and CodeTypes can be set with The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. methods.
The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. of a simple YesOrNoCodeType having just two codes:
-
YesOrNoCodeType.YesCode -
YesOrNoCodeType.NoCode
With the SDK
The SDK provides some help to generate CodeTypes and Codes. The CodeType appears in the The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. in the Enumerations folder under The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/..
It is possible to add a new CodeType using a wizard.
Dynamic CodeType
Code types are not necessary hardcoded. It is possible to implement other mechanisms to load CodeType dynamically.
The description of the Codes can come from a database or from an XML files. If you want to do so, you just need to implement the method corresponding to the event The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/..
It is possible to use the static and the dynamic approach together. In this case, if there is a conflict (2 codes for the same id) the event The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. is triggered.
Note for advanced users:
Each CodeType is instantiated for
- each language
- each partition
Note: A drawback that the CodeType Class is not aware of the language and the partition it is instantiate for. Only the The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/. that manage the CodeType instances knows for which language and which partition they have been instantiated.
See Also
- The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.
- The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.
- The Scout documentation has been moved to https://eclipsescout.github.io/.