Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "SMILA/Documentation/2011.Simplification/Search"
m (→Search Service API) |
m (→Query Parameters) |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
=== Query Parameters === | === Query Parameters === | ||
| − | The query record mainly consists of parameters. The Search API defines the | + | The query record mainly consists of parameters. The Search API defines the names of these parameters, the allowed values as well as the default values for a set of commonly used parameters. All implementations should use these properties if possible, i.e. they should not introduce additional parameters for the same purpose, but it may be possible that certain parameters are not supported because it is not feasible with the underlying technology. For some parameters we also defined default values. All parameters are single-valued unless otherwise specified. |
| − | * query: | + | * ''query'': Either a search string using a query syntax or a query record describing the query by setting values for application attributes. The index implementor can define a query syntax to be able to build complex search criteria in a single string. However, SMILA currently does not define an own query syntax. |
| − | ** using query string: | + | **Example using a query string: |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Record> | <Record> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
</Record> | </Record> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | ** using query object: | + | **Example using a query object: |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Record> | <Record> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
</Record> | </Record> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * maxcount: number of records | + | * ''maxcount'': The maximum number of records which should be returned to the search client. Default value is 10. Example: |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
<Val key="maxcount" type="long">3</Val> | <Val key="maxcount" type="long">3</Val> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * offset: number | + | * ''offset'': The number of hits which, starting from the top, should be skipped in the search result. Default value is 0. Use this parameter to implement result list paging and to provide the user a means to navigate through the result pages: If resultSize=10, the "next page" queries can be identical to the initial query, but with resultOffset=10, 20, ... Example: |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
<Val key="offset" type="long">3</Val> | <Val key="offset" type="long">3</Val> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * threshold: minimal relevance score that a result must have | + | * ''threshold'': The minimal value of the relevance score that a result must have to be returned to the search client. Default is 0.0. |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
<Val key="threshold" type="double">0.5</Val> | <Val key="threshold" type="double">0.5</Val> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * language: language of the query | + | * ''language'': The natural language of the query. No default value. This parameter may be required for language-specific pipelets/services that need to know in which language the user is expressing his or her query to be able to deliver feasible results. Example: |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">sinn des lebens</Val> | <Val key="query">sinn des lebens</Val> | ||
<Val key="language">de</Val> | <Val key="language">de</Val> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * index: | + | * ''index'': Some index services (like our LuceneIndexService) can manage multiple indices at once. When doing so, they can use this parameter to select the index which is to be searched with the current request. However, when using such a scenario, it is recommended to configure a default index name, so that search requests will succeed without having this parameter set explicitly. Example: |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
<Val key="index">wikipedia</Val> | <Val key="index">wikipedia</Val> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * resultAttributes: multi-valued parameter | + | * ''resultAttributes'': A multi-valued parameter containing the names of the attributes which the search engine should add to the result records. Since including too many attributes will decrease performance, the list should contain only those attributes that are needed by some pipelets for further processing after the search has taken place or for displaying the results in the end. Omitting the parameter results in getting all available attributes. Example: |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
</Seq> | </Seq> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * highlight: sequence of string values specifying attribute names for which highlighting should be | + | * ''highlight'': A sequence of string values specifying the attribute names for which highlighting should be returned. |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
</Seq> | </Seq> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * sortby: sequence of maps each containing a key "attribute" (any string) and "order" ("ascending"/"descending") specifying that the search result should be be sorted by the named attributes in the given direction. Omitting this parameter | + | * ''sortby'': A sequence of maps each containing a key "attribute" (any string) and "order" ("ascending"/"descending") specifying that the search result should be be sorted by the named attributes in the given direction. Omitting this parameter results in search result sorting by relevance (score, similarity, ranking, ....). Multiple maps can be added and should be evaluated in the order of their appearance. |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
</Seq> | </Seq> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * groupby: sequence of maps each containing a key "attribute" (any string) and "maxcount" (long). This tells the search to produce a grouping of the search results by these attributes, returning "maxcount" groups for each attribute. Optionally each groupby map may contain a map under key "sortby" with keys "order" ("ascending"/"descending") and "criterion" (any string, e.g. "count" or "value") specifying in which order to return these groups (e.g. "count" by number of this per group or "value" by attribute value name). | + | * ''groupby'': A sequence of maps each containing a key "attribute" (any string) and "maxcount" (long). This tells the search to produce a grouping of the search results by these attributes, returning "maxcount" groups for each attribute. Optionally each groupby map may contain a map under key "sortby" with keys "order" ("ascending"/"descending") and "criterion" (any string, e.g. "count" or "value") specifying in which order to return these groups (e.g. "count" by number of this per group or "value" by attribute value name). |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> | ||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
</Seq> | </Seq> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * filter: sequence of maps describing for certain attributes which values they are required to have in valid result records. Each of the maps contains a key "attribute" and one or more value descriptions: | + | * ''filter'': sequence of maps describing for certain attributes which values they are required to have in valid result records. Each of the maps contains a key "attribute" and one or more value descriptions: |
** "oneOf", "allOf", "noneOf": sequences of values describing required or forbidden attribute values. | ** "oneOf", "allOf", "noneOf": sequences of values describing required or forbidden attribute values. | ||
** "atLeast", "atMost", "greaterThan", "lessThan": single values describing lower and upper bounds (including or excluding the bound values) for the attribute value. | ** "atLeast", "atMost", "greaterThan", "lessThan": single values describing lower and upper bounds (including or excluding the bound values) for the attribute value. | ||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
</Seq> | </Seq> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * ranking: | + | * ''ranking'': A configuration of how to rank the search results. This is highly depending on the used search engine, so we don't specify this further in SMILA. |
=== Result Annotations === | === Result Annotations === | ||
Revision as of 06:42, 11 March 2011
This page describes the search service and related parts of SMILA. This includes the query and result helpers, the processing of search requests in BPEL workflows, and the sample servlet used to create a simple web-based GUI for search.
Contents
Introduction
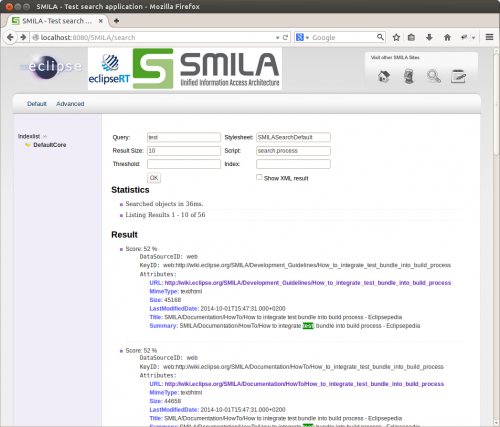
Let's start right at the top: Provided that you installed SMILA and created an index by starting a crawler as described in 5 Minutes to Success, you can now use you web browser to go to http://localhost:8080/SMILA/search and search on the index:
What happens behind the scenes when you enter a query string and submit the form, is that a servlet creates a SMILA record from the HTTP parameters, uses the search service to execute a BPEL workflow on this record, receives an enriched version of the query record and also a list of result records in XML form, and uses an XSLT stylesheet to create a result page in HTML format.
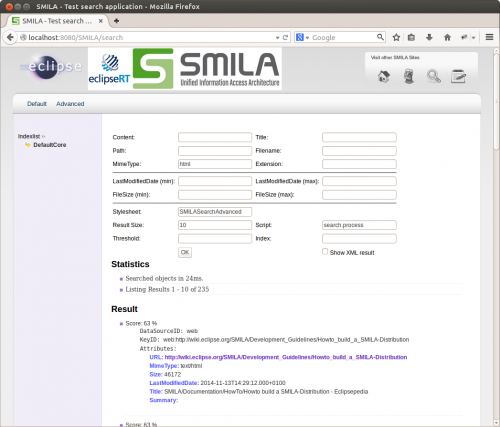
By clicking the Advanced link at the top of the search page (or by entering the URL http://localhost:8080/SMILA/search?style=SMILASearchAdvanced, you can switch to a more detailed search form page, which allows you to construct more specific search queries:
If you want to use the default search servlet for your own search page, you are encouraged to use the two XSLT files creating these HTML pages as a reference or basis when building your pages.
Search Processing
Having seen the tip of the iceberg, we dive down to the very bottom of SMILA search: the actual processing of search requests in SMILA BPEL pipelines. We assume that you are accustomed to the basic SMILA workflow processing features used in indexing workflows. You may want to refer to SMILA/Documentation/BPEL_Workflow_Processor for details.
Search Pipelines
Search workflows (or pipelines) look just like indexing pipelines, they are only used a bit differently: Instead of pushing lists of records corresponding to data source objects through them, they are invoked with a single record representing the search request. This record contains the values of the parameters which were defined by the Search API (see below). The request object can be analyzed and enriched with additional information during the workflow before the actual search on the index takes place. The results of this search are not added to the blackboard as records of their own, but are added to the request record under the key "records". Further pipelets may then do further processing based on the request data and the result record list (e.g. highlighting). Finally, the request record including the search results is returned to the client and can be presented.
Pipelet invocations look the same as in indexing pipelines. See SMILA.application/configuration/org.eclipse.smila.processing.bpel/pipelines/searchpipeline.bpel for a complete example search pipeline (the one used in the above sample).
Search Service API
The actual Search API is quite simple: SMILA registers an OSGi service with the interface org.eclipse.smila.search.api.SearchService. It provides a few methods that take a SMILA query record and the name of a search workflow as input, execute the workflow on the record, and return the result in different formats:
- Record search(String workflowName, Record query) throws ProcessingException: This is the basic method of the search service, returning the result records as native SMILA data structures. The other methods call this method for the actual search execution, too, and then just convert the result.
- org.w3c.dom.Document searchAsXml(String workflowName, Record query) throws ProcessingException: Returns the search result as an XML DOM document. See below for the schema of the result.
- String searchAsXmlString(String workflowName, Record query) throws ProcessingException: Returns the search result as an XML string. See below for the schema of the result.
The schema of XML search results is basically as follows (target namespace is http://www.eclipse.org/smila/search, see org.eclipse.smila.search.api/xml/search.xsd for the full definition):
<element name="SearchResult"> <complexType> <sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"> <element name="Workflow" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" /> <element ref="rec:Record" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" /> </sequence> </complexType> </element>
You can view the result XML when using the sample SMILA search page http://localhost:8080/SMILA/search if you enable the Show XML result option before submitting the query.
The content of the query record basically depends a lot on the used search services. However, the Search API also includes a recommendation where to put some basic commonly used search parameters which all index integrations should honor (of course they may specify extensions that are not covered by the generic Search API). The following sections describes these recommendations.
Query Parameters
The query record mainly consists of parameters. The Search API defines the names of these parameters, the allowed values as well as the default values for a set of commonly used parameters. All implementations should use these properties if possible, i.e. they should not introduce additional parameters for the same purpose, but it may be possible that certain parameters are not supported because it is not feasible with the underlying technology. For some parameters we also defined default values. All parameters are single-valued unless otherwise specified.
- query: Either a search string using a query syntax or a query record describing the query by setting values for application attributes. The index implementor can define a query syntax to be able to build complex search criteria in a single string. However, SMILA currently does not define an own query syntax.
- Example using a query string:
<Record> <Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> </Record>
- Example using a query object:
<Record> <Map key="query"> <Val key="author">shakespeare</Val> <Val key="title">hamlet</Val> </Map> </Record>
- maxcount: The maximum number of records which should be returned to the search client. Default value is 10. Example:
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Val key="maxcount" type="long">3</Val>
- offset: The number of hits which, starting from the top, should be skipped in the search result. Default value is 0. Use this parameter to implement result list paging and to provide the user a means to navigate through the result pages: If resultSize=10, the "next page" queries can be identical to the initial query, but with resultOffset=10, 20, ... Example:
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Val key="maxcount" type="long">3</Val> <Val key="offset" type="long">3</Val>
- threshold: The minimal value of the relevance score that a result must have to be returned to the search client. Default is 0.0.
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Val key="threshold" type="double">0.5</Val>
- language: The natural language of the query. No default value. This parameter may be required for language-specific pipelets/services that need to know in which language the user is expressing his or her query to be able to deliver feasible results. Example:
<Val key="query">sinn des lebens</Val> <Val key="language">de</Val>
- index: Some index services (like our LuceneIndexService) can manage multiple indices at once. When doing so, they can use this parameter to select the index which is to be searched with the current request. However, when using such a scenario, it is recommended to configure a default index name, so that search requests will succeed without having this parameter set explicitly. Example:
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Val key="index">wikipedia</Val>
- resultAttributes: A multi-valued parameter containing the names of the attributes which the search engine should add to the result records. Since including too many attributes will decrease performance, the list should contain only those attributes that are needed by some pipelets for further processing after the search has taken place or for displaying the results in the end. Omitting the parameter results in getting all available attributes. Example:
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Seq key="resultAttributes"> <Val>author</Val> <Val>title</Val> </Seq>
- highlight: A sequence of string values specifying the attribute names for which highlighting should be returned.
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Seq key="highlight"> <Val>content</Val> </Seq>
- sortby: A sequence of maps each containing a key "attribute" (any string) and "order" ("ascending"/"descending") specifying that the search result should be be sorted by the named attributes in the given direction. Omitting this parameter results in search result sorting by relevance (score, similarity, ranking, ....). Multiple maps can be added and should be evaluated in the order of their appearance.
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Seq key="sortby"> <Map> <Val key="attribute">year</Val> <Val key="order">descending</Val> </Map> <Map> <Val key="attribute">author</Val> <Val key="order">ascending</Val> </Map> </Seq>
- groupby: A sequence of maps each containing a key "attribute" (any string) and "maxcount" (long). This tells the search to produce a grouping of the search results by these attributes, returning "maxcount" groups for each attribute. Optionally each groupby map may contain a map under key "sortby" with keys "order" ("ascending"/"descending") and "criterion" (any string, e.g. "count" or "value") specifying in which order to return these groups (e.g. "count" by number of this per group or "value" by attribute value name).
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Seq key="groupby"> <Map> <Val key="attribute">year</Val> <Val key="maxcount" type="long">10</Val> </Map> <Map> <Val key="attribute">author</Val> <Map key="sortby"> <Val key="criterion">value</Val> <Val key="order">ascending</Val> </Map> <Val key="maxcount" type="long">5</Val> </Map> </Seq>
- filter: sequence of maps describing for certain attributes which values they are required to have in valid result records. Each of the maps contains a key "attribute" and one or more value descriptions:
- "oneOf", "allOf", "noneOf": sequences of values describing required or forbidden attribute values.
- "atLeast", "atMost", "greaterThan", "lessThan": single values describing lower and upper bounds (including or excluding the bound values) for the attribute value.
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Seq key="filter"> <Map> <Val key="attribute">author</Val> <Seq key="oneOf"> <Val>pratchett</Val> <Val>adams</Val> </Seq> </Map> <Map> <Val key="attribute">year</Val> <Val key="atLeast">1990</Val> <Val key="lessThan">2000</Val> </Map> </Seq>
- ranking: A configuration of how to rank the search results. This is highly depending on the used search engine, so we don't specify this further in SMILA.
Result Annotations
The search result is usually the request record, enriched by result data.
- records: A seq of maps describing the actual search result, i.e. the records retrieved from the index. Each record should have an additional attribute "_weight" describing the relevance score of this record with respect to the query. The "records" sequence's size is limited by the "maxcount" parameter.
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <!-- other query parameters --> <Seq key="records"> <Map> <Val key="_weight" type="double">0.95</Val> <Val key="_recordid">file:hamlet</Val> <Val key="title">Hamlet</Val> <Val key="author">Shakespeare</Val> ... </Map> <Map> <Val key="_weight" type="double">0.90</Val> <Val key="_recordid">file:hitchhiker</Val> <Val key="title">Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy</Val> <Val key="author">Adams</Val> ... </Map> </Seq>
- count: Total number of records in the index that have any relevance to the query
- indexSize (optional): Total number of records in the searched index.
- runtime: execution time of request in ms, added by the search service.
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Val key="count" type="long">123456</Val> <Val key="indexSize" type="long">987654321</Val> <Val key="runtime" type="long">42</Val> <!-- other query parameters --> <Seq key="records"> <!-- contains returned records --> </Seq>
- groups: grouping result according to the groupby parameters: number of relevant records grouped by their values in the grouping attribute:
<Val key="query">meaning of life</Val> <Map key="groups"> <Seq key="year"> <Map> <Val key="value">2000</Val> <Val key="count" type="long">42</Val> </Map> <Map> <Val key="value">2001</Val> <Val key="count" type="long">21</Val> </Map> ... </Seq> <Seq key="author"> <Map> <Val key="value">adams</Val> <Val key="count" type="long">13</Val> </Map> <Map> <Val key="value">shakespear</Val> <Val key="count" type="long">17</Val> </Map> ... </Seq> </Map> </Val>
- _highlight: annotation of the result record, usually used to highlight relevant sections from the result documents to give the user an impression if it could be what he searched for. What is returned here exactly will probably depend on the used search engine. For example, the Lucene integration in SMILA returns the raw form of the text to highlight and information about the parts to highlight:
<Seq key="records"> <Map> ... <Map key="_highlight"> <Map key="content"> <Val key="text">... To be or not to be ...</Val> <Seq key="positions"> <Map> <Val key="start" type="long">7</Val> <Val key="end" type="long">9</Val> <Val key="quality" type="long">100</Val> </Map> <Map> <Val key="start" type="long">20</Val> <Val key="end" type="long">22</Val> <Val key="quality" type="long">95</Val> </Map> </Seq> </Map> <Map> ... </Map>
Using the HighlightingPipelet this can be transformed into a highlighted text fragment (here using * as the highlight):
<Seq key="records"> <Map> <Val key="_weight" type="double">0.95</Val> <Val key="_recordid">file:hamlet</Val> <Val key="title">Hamlet</Val> <Val key="author">Shakespeare</Val> <Map key="_highlight"> <Map key="content"> <Val key="text">... To *be* or not to *be* ...</Val> </Map> <Map> ... </Map>
Helper Classes
There are some classes that help a client to create query records with their annotations and to read out result records and their annotation. You can find them in package org.eclipse.smila.search.api.helper:
- QueryBuilder: helper class for building queries and sending the query to search service. Returns a result in the form of the next class:
- ResultAccessor: wrapper for the complete search result. Provides methods to access the basic top-level result annotations and to access each search result record wrapped by a:
- ResultRecordAccessor: Defines methods for accessing some of the result record annotations.
See the source code or javadocs for more details of the provided methods.
Servlet
Additionally to this "search backend", SMILA contains a simple servlet that creates a query record from HTTP parameters and displays the result as an HTML page by converting the XML search result using an XSLT stylesheet. This servlet is intended for quick demos, not for productive use. It is usually deployed in the Tomcat instance that comes with SMILA at "/SMILA/search". On first invocation it currently creates a quite empty query record (it sets some default parameters like resultSize etc) and processes it with the default pipeline "SearchPipeline". The pipeline should be able to process such a query and return an empty result list, not an error. The XML representation of this empty result is then transformed using the default stylesheet ("SMILASearchDefault") to present an initial search page.
Note that the servlet actually enriches the XML search result a bit, so the input for the XSLT stylsheet does not completely conform to the defined XML schema. Currently, it adds a section containing the names of indexes available in the LuceneSearchService so that the search page can display the names for selection on the left side:
<SearchResult xmlns="http://www.eclipse.org/smila/search"> <Workflow>searchpipeline</Workflow> <Record xmlns="http://www.eclipse.org/smila/record"> <!-- effective query and embedded result records ---> </Record> <!-- part added by SearchServlet --> <IndexNames> <IndexName>test_index</IndexName> </IndexNames> </SearchResult>
You can use the same mechanism to add other information to the XML that is necessary to display the search form but not contained in the search service result, you just have to implement your own servlet or extend the default servlet. Please refer to the source code for details.
XSLT Stylesheets for SMILA search and result pages
The stylesheets are loaded from the configuration directory "org.eclipse.smila.search.servlet" and select using the HTTP parameter "style". The value of this parameter must be the stylesheet filename without suffix, the suffix must bei .xsl. The servlet currently uses the hardcoded default name "SMILASearchDefault" if no other value is set.
In the default application, three stylesheets are avaiable:
- SMILASearchDefault: the default search page. Use this as a reference for how to describe simple queries and to present result lists, including paging through bigger results.
- SMILASearchAdvanced: same layout for the result list, but demostrates how to create more complex query records with attribute values and filters.
- SMILASearchTest: primitive layout, no paging, but demonstrates the setting of even more query features.
To start with another than the default stylesheet, you can add a "style" parameter to the initial URL. E.g., to start with the "advanced" stylesheet, use: http://localhost:8080/SMILA/search?style=SMILASearchAdvanced.
In the following we will describe how to set query record features using the servlet. Please have a look at those sample stylesheets for complete examples of how to apply them, as we will not present something like a full tutorial here (-;
Setting parameters
To set a parameter, just use the parameter name as the HTTP parameter name. All values for this HTTP parameter are added to the "parameters" annotation of the query record. E.g., to set the "resultSize" parameter to 7 using an HTML hidden input field, use:
<input type="hidden" name="resultSize" value="7" />See below for naming rules for the HTTP parameter names to set attribute literals and annotations. Note that you cannot set a parameter with a name that matches one of these rules.
Setting attributes
You can add literal string values to attributes using "A.<AttributeName>" as the HTTP parameter name. E.g., to set a value from a HTML text input field as an literal in attribute "Title", use:
<input type="text" name="A.Title" />
Setting other parameters
To add a "sortby" parameter for an attribute, use "sortBy.<AttributeName>=<order>", e.g.
<input type="hidden" name="sortby.FileSize" value="descending" />To create a filter for an attribute, use HTTP params:
- "F.val.<AttributeName>" to add filter values to an "oneOf" filter.
- "F.min.<AttributeName>" and "F.max.<AttributeName>" to set the lower/upper bounds of an "atLeast"/"atMost" filter.
If both "F.val" and "F.min/F.max" paramaters are set, the servlet will create both an enumeration filter and a range filter with the same filter mode. It depends on the used search engine integration what happens in this case. E.g.
- to set a filter for attribute "MimeType" restricting the result to HTML documents, use:
<input type="hidden" name="F.val.MimeType" value="text/html" />- to set a filter for attribute "FileSize" restricting the result to document sizes between 1000 and 10000 bytes, use:
<input type="hidden" name="F.min.FileSize" value="1000" /> <input type="hidden" name="F.max.FileSize" value="10000" />
To set a value in the Ranking parameter for the complete record or an attribute, use "R[.<AttributeName>].<ValueName>". E.g., the following input field sets add a parameter "Operator=OR" to attribute "Content":
<input type="hidden" name="R.Operator.Content" value="OR" />