Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
REST support in STP
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Exposing a database to RESTfull service directly
- 3 Starting from importing and creating some POJO classes
- 4 Resource View
- 5 Deploy REST Project
Introduction
This page aims to define the basic processes on how to support REST in stp, there is sample to simplifies how to create a RESTfull service from a database directly.
There are two ways to support to create RESTfull service:
* Exposing a database to RESTfull service directly * Starting from importing some POJO class into a rest project
Exposing a database to RESTfull service directly
We can create a RESTfull service by starting from a database with the following steps:
Create a REST project using STP.Service Creation Wizard
add project nature "org.eclipse.jem.workbench.JavaEMFNature" which defined in WTP DALI subproject and Java Persistence Facet, once the project has the nature and JP Facet, some DALI function will be available in the subsequent steps.
Generate Entity classes from database
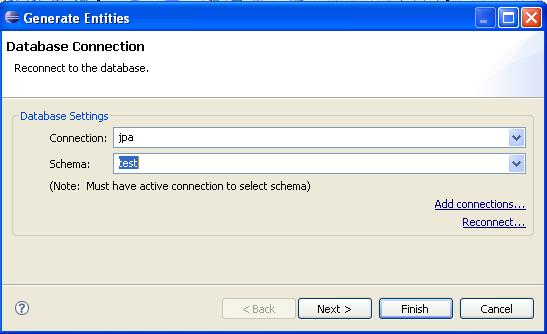
select a database to connect
select tables that want to be exposed as REST resource from the databse
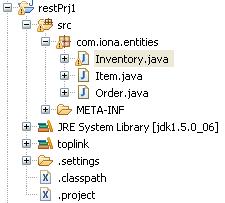
the following classes will be generated:
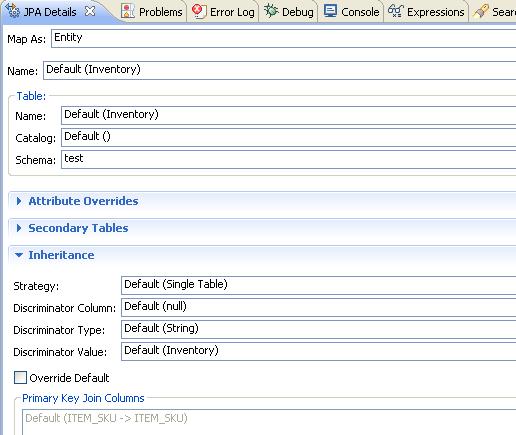
three entities class will be generated, these classes are annotated with JPA annotations(by the way, the used JPA implementation library is Oracle TopLink), users can modify the annotations in the generated classes through JPA detail view, it looks like:
add all entity classes into a persistence unit by configuring persistence.xml
Generate Resources class for each entity class
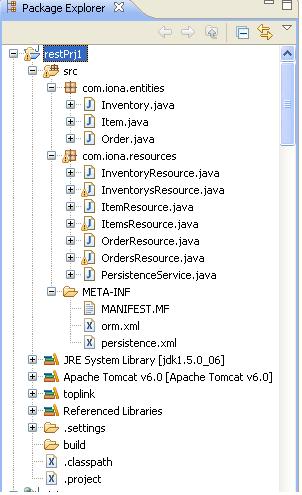
In this step, we will provide a tool for generating Resource class from entity classes. User select the entity classes that generated from database to generate resource classes ,all these resource classes are annotated with annotations defined in jsr311 specification. each entity class maps to two Resource classes, for example, Item class has ItemResource class and ItemsResource class, ItemResource class responsible for getting detail info of a specific item, updating and deleting the item, ItemsResource class is responsible for returning item list and adding a new item. After resource classes are generated, the project package view looks like:
Entity class com.iona.entities.Item looks like:
//Item.java
@Entity
@Table(schema="test")
public class Item implements Serializable {
@Id
private long sku;
private String description;
private String name;
private int version;
private String category;
@OneToMany(mappedBy="item")
private Set<Order> orderTableCollection;
@OneToMany(mappedBy="item")
private Set<Inventory> inventoryCollection;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public Item() {
super();
}
public long getSku() {
return this.sku;
}
public void setSku(long sku) {
this.sku = sku;
}
....
Resource com.iona.resources.ItemsResource :
//ItemsResource.java
@UriTemplate("/items/")
public class ItemsResource {
@HttpContext
private UriInfo context;
public ItemsResource() {
}
public ItemsResource(UriInfo context) {
this.context = context;
}
@HttpMethod("GET")
@ProduceMime({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public Collection<Item> get(@QueryParam("start")
@DefaultValue("0")
int start, @QueryParam("max")
@DefaultValue("10")
int max) {
.......
}
@HttpMethod("POST")
@ConsumeMime({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public Response post(Item data) {
.......
}
@UriTemplate("{itemId}/")
public ItemResource getItemResource() {
return new ItemResource(context);
}
}
Resource com.iona.resources.ItemResource :
//ItemResource.java
public class ItemResource {
private UriInfo context;
/** Creates a new instance of ItemResource */
public ItemResource() {
}
public ItemResource(UriInfo context) {
this.context = context;
}
@HttpMethod("GET")
@ProduceMime({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public Item get(@UriParam("itemId")Integer ItemId) {
.......
}
@HttpMethod("PUT")
@ConsumeMime({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public void put(@UriParam("ItemId")
Integer id, Item data) {
.......
}
@HttpMethod("DELETE")
public void delete(@UriParam("ItemId")
Integer id) {
.......
}
@UriTemplate("orders/")
public OrdersResource getOrdersResource(@UriParam("itemId")
Integer id) {
final Item parent = getEntity(id);
return new OrdersResource(context) {
protected Collection<Order> getEntities(int start, int max){
Set<Order> entities = parent.getOrderTableCollection();
if (entities == null) {
}
return entities;
}
};
}
}
There also should be some EntityProvider generated for converting ProduceMime and ConsumeMime types to Java object?
Starting from importing and creating some POJO classes
Users also can create a empty rest project, and then import some POJO java object, add REST annotations in the class using STP Resource View.
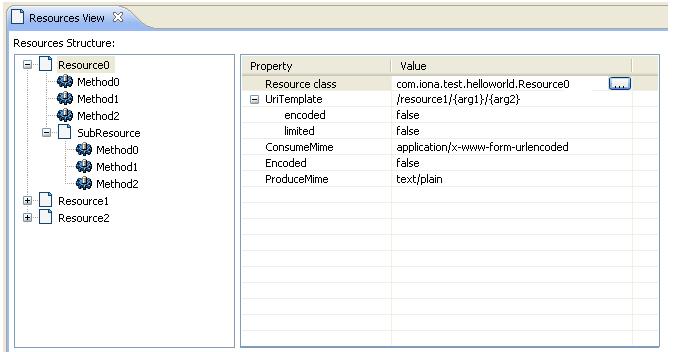
Resource View
In this view, a selected project is the input of the view, all java class which annotated with REST annotation will be displayed as resources in left tree viewer.
Users can do following operations in the Resource view:
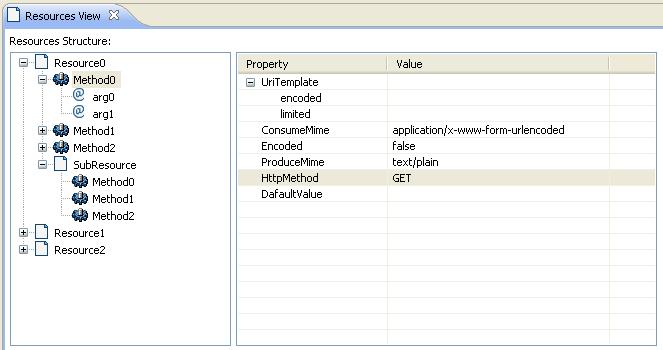
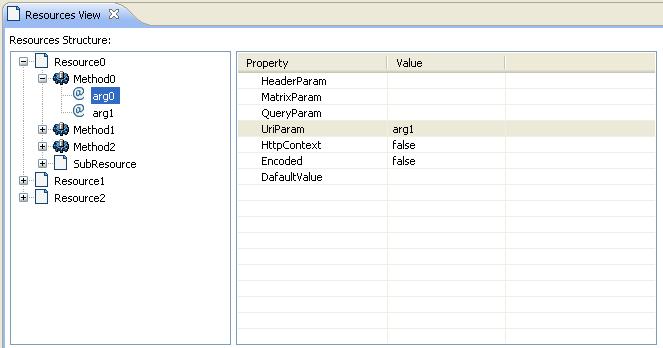
* Open resource by double clicking on the any node of the tree, the corresponding Java file will be open with Java file editor * Add new resource. * Edit resource by change annotations in the attribute editor, once a annotation is changed, it will be saved in Java file as annoation
Update Resource annotation:
Update Method annotation:
Update Parameter annotaion: