Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Orion/Documentation/User Guide/Reference/Repositories page
Contents
Repositories page
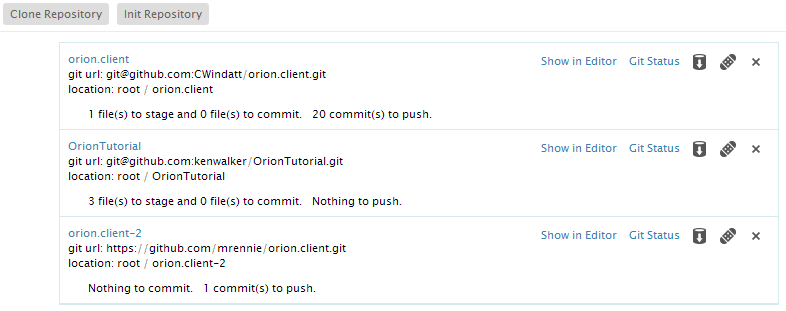
The Repositories page allows you to view and manage the Git repositories associated with your Orion account. When you visit this page you will see a list of all Git repositories you currently have cloned.
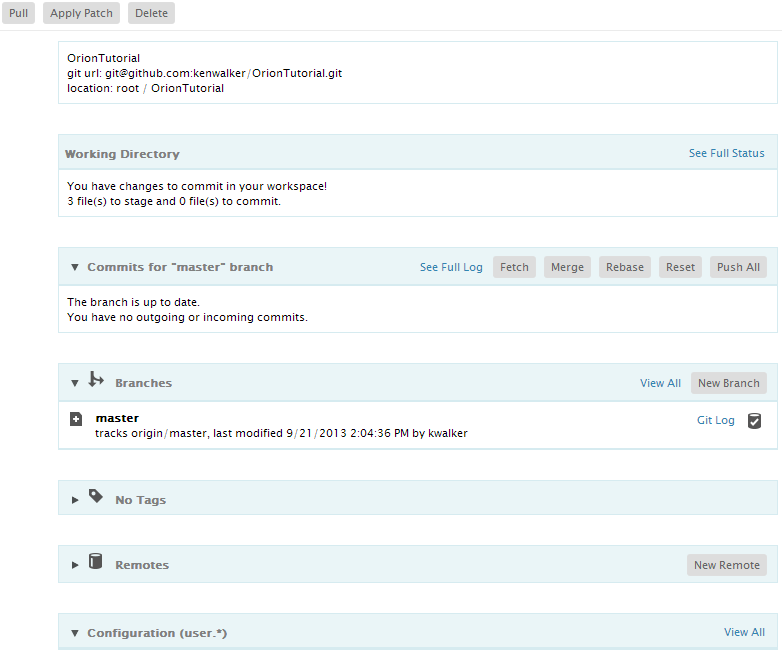
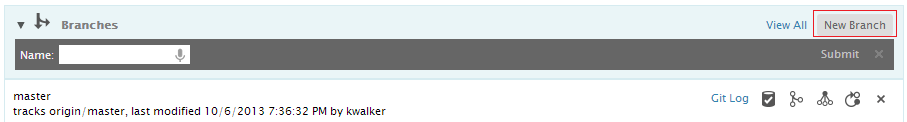
To see detailed information about a repository, click its name. The detailed view includes all the usual Git repository details such as name and url. Additional sections on the page enumerate things like index state, incoming and outgoing commits, branches, and tags. You can open and close most sections on the page using the twistie icon adjacent to the section name. The branches and tags sections show you the most recently used items, but you can click the associated View All links to see full lists of anything.
Repository configuration
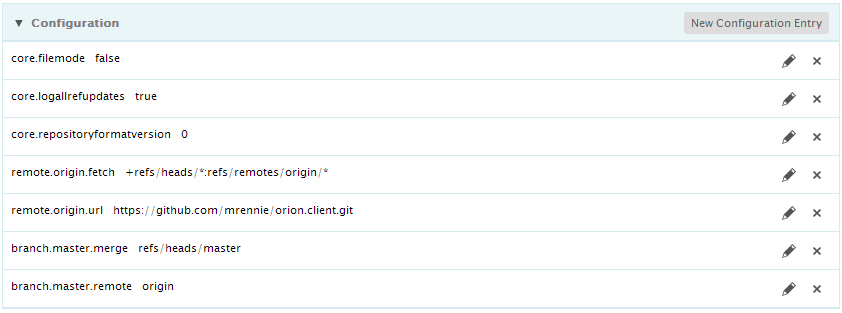
The bottom of the repository page shows the configuration of the repository. On the main page you will see just user.*. To see the full list, click View All. From here you can add additional configuration properties to the repository, and change or delete properties.
Adding repositories
Create a new empty repository by clicking Init Repository on the tool bar, or click Clone Repository to clone an existing Git repository. Cloning will produce a dialog where you enter the Git repository URL, and optionally any credentials required to access or modify the repository.
Actions on a repository
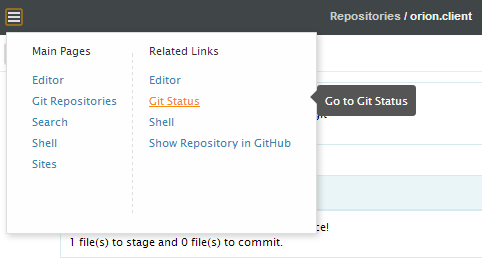
You can pull the latest content, apply a patch, or delete an existing repository from the main toolbar on the page. The Related menu allows you to navigate to other views on the repository, such as viewing the repository content on the Navigator page or working with the repository changes on the Git Status page.
Adding branches
Once a repository is created or cloned, the master branch is set as the current branch. You can create your own branch, work on it and merge it back to master. To create a new branch, click the New Branch button, type in the new branch name, and press the 'Enter' key or click the Submit button.
Actions on a local branch
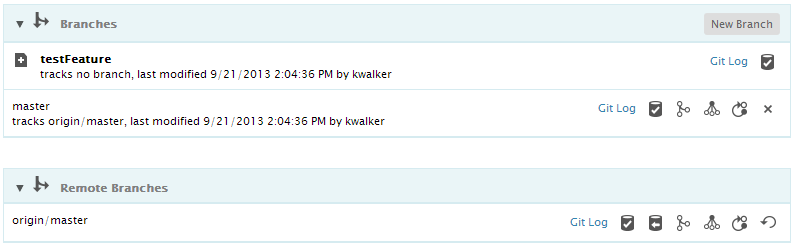
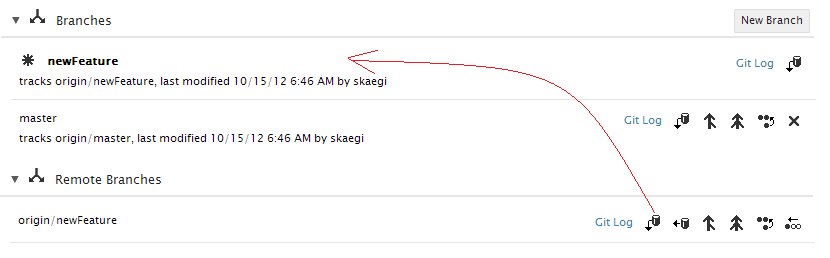
Once a new branch is created, it is in the local repository but not in the remote yet. Next to each branch is a row of buttons as below. You can manage the branches using these actions.
Deleting a local branch
From the branch actions, click the delete icon to delete a local branch. A confirmation dialog will pop up, providing you a chance to confirm your decision.
You can navigate to the Log page to see details on the branch. From the actions next to the branch, the link Git Log will take you to the Git log page.
Merging branches
Merging branches involves two branches: the branch whose actions you are working with, and your active branch. For example, clicking the Merge icon for your newly created branch will merge its content to your active branch. You can also merge from remote branches.
 You can also merge branches in the Log page or Status page.
You can also merge branches in the Log page or Status page.
Setting the active branch
The active branch is the branch that contains your working copy. When you create a new branch, it is not automatically set as the active branch. Suppose you created this branch to start work on a new feature. From the actions next to the branch, click on the checkout icon to make the branch active.
Once a branch is checked out, it is shown as bold and highlighted with a star.
The active branch represents your working directory, and therefore the Git Status page will always reflect the status of the active branch.
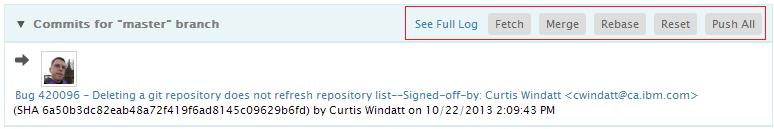
Pushing a local branch
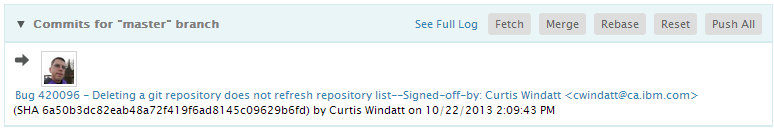
Once a branch is checked out, a list of the commits for that branch will appear. Arrows next to the commits will indicate if the commits are incoming or outgoing. Clicking on the Push All action will push all the commits to a remote tracking branch.
For a newly created branch, you can choose an existing remote branch, or more likely, create a new remote tracking branch for your work.
You can also push changes and create remote branchs from the Log page or Status page.
Viewing remote branches
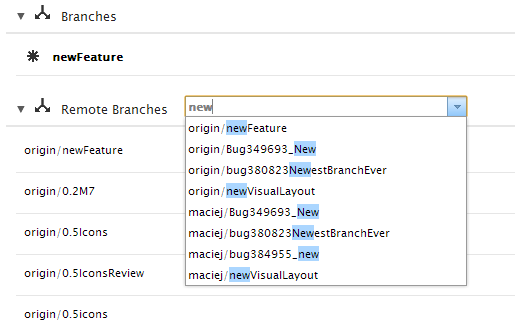
Clicking the View All link in the branches section of the page will show all of the branches for a repository, including the remote branches.
If you have trouble finding a particular branch in the list, you can type in the filter box to find the branch.
Updating the list of remote branches
When someone creates a new remote branch in a repository, the branch will not appear in the branch list for other users until the repository is fetched or pulled. For example, if you ask another developer to check out your "newFeature" branch, the branch will not appear if the repository hasn't been fetched or pulled since you created the branch.
You can click Pull in the main toolbar, and enter your credentials if required to access the repository. The remote branches will be updated.
Actions on a remote branch
The main page for a repository only shows some of your recently used local branches. To view remote branches, click View All in the toolbar at the top of the Branches section.
Many of the actions on a remote branch are different from those on a local branch, but the Git Log and Merge actions are the same. The Git Log action will navigate to the same log page but with the remote branch content. You can also switch to the local branch content there. Next to the remote branch name row in the Remote table, you will find the actions for managing that remote branch.
Checking out a remote branch
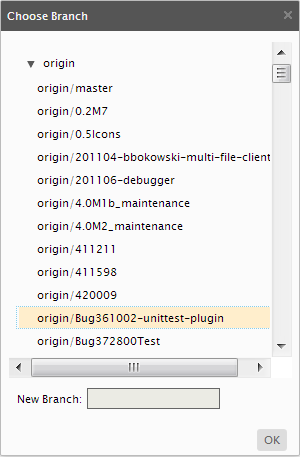
Normally a newly fetched remote branch is not in your local branches yet. You have to checkout in order to work on it. From the actions next to the branch, click the Checkout icon.
The remote branch is checked out as the current local branch.
Please note that if you try to check out a remote branch that already has a local branch in your repository, you will get a warning message : "the local branch already exists".
Fetching and merging content of a remote branch
You can fetch a remote branch and merge it to your active local branch. First, click View All in the Branches section of the page. This will show all local and remote (tracking) branches associated with the repository. From the actions next to a remote branch, there is a button to Fetch the latest contents from the remote into your personal remote tracking branch. Then, you can Merge or Rebase those changes into your active local branch.
If you want to fetch and merge changes for your active branch, you can also use actions in Commits section.
Please note that you can achieve the same result by performing the same actions in Log page or Status page.
Resetting local index from a remote branch
You can also reset a local branch to replace with the contents of the remote tracking branch.
From the actions next to the remote branch, click the Reset icon to reset the local branch content. A dialog will pop up asking for confirmation.