Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "MoDisco/Components/J2SE5"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The J2SE5 | + | The J2SE5 metamodel : it is the reflect of Java language, as it has been defined in version 3 of "Java Language Specification" from Sun Microsystems ("JLS3" corresponds to JDK 5). |
| − | J2SE5 | + | J2SE5 metamodel contains 101 metaclasses. |
| − | To better understand it, this page will introduce main features ( | + | To better understand it, this page will introduce main features (metaclasses and links). |
You could also browse definition model, j2se5.ecore available in sources (see [[#Install| install section]]). | You could also browse definition model, j2se5.ecore available in sources (see [[#Install| install section]]). | ||
| − | A good tip is also to see [http://help.eclipse.org/help31/index.jsp javadoc] associated to | + | A good tip is also to see [http://help.eclipse.org/help31/index.jsp javadoc] associated to metamodel implemented by Eclipse team in project [[JDT| JDT (Java Development Tool)]]. This metamodel and J2SE5 are very similar. |
| − | == Main | + | == Main metaclasses == |
=== ASTNode === | === ASTNode === | ||
| − | Every | + | Every metaclasses (without metaclass '''Model''') inherit from ASTNode. |
As its name indicate it, ASTNode represent a graph node. | As its name indicate it, ASTNode represent a graph node. | ||
| − | ASTNode has a reference to Comment | + | ASTNode has a reference to Comment metaclass because almost every java element could be associated to a comment (bloc or line comment and Javadoc). More details in [[#Zoom on comments| "Comment" section]]. |
| − | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass ASTNode.jpg|frame|center|ASTNode | + | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass ASTNode.jpg|frame|center|ASTNode metaclass]] |
=== Model, Package, AbstractTypeDeclaration === | === Model, Package, AbstractTypeDeclaration === | ||
| − | Root element of each J2SE5 model in an instance of "Model" | + | Root element of each J2SE5 model in an instance of "Model" metaclass. It is a translation of java application concept, so it contains package declarations (instances of PackageDeclaration metaclass). And package declarations contain type declarations (instances compatible with AbstractTypeDeclaration metaclass), and so on ... |
| − | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass Model PackageDeclaration.jpg|frame|center|Model, Package & type declaration | + | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass Model PackageDeclaration.jpg|frame|center|Model, Package & type declaration superclass]] |
=== NamedElement & notion of Proxy === | === NamedElement & notion of Proxy === | ||
A lot of java elements are "named", and this name could be considered as an identifier : methods, packages, types, variables, fields, ... | A lot of java elements are "named", and this name could be considered as an identifier : methods, packages, types, variables, fields, ... | ||
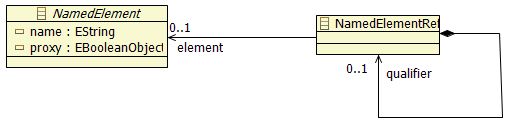
| − | So all of corresponding | + | So all of corresponding metaclasses inherit from NamedElement metaclass. It will be usefull to resolve references in binding, see [[#NamedElementRef|NamedElementRef]] metaclass. |
| − | And an other goal of this | + | And an other goal of this metaclass is to indicate which element is a part of the current java application or not (element from an external library of from JDK). Then external elements are tagged as proxy through dedicated attribute and could be easily filtered. |
For example, instruction "System.out.println" has been decomposed in three named elements (one class, one variable and one method) which defintion are not part of current java application. So attribute "proxy" of these elements has been initialized as true. | For example, instruction "System.out.println" has been decomposed in three named elements (one class, one variable and one method) which defintion are not part of current java application. So attribute "proxy" of these elements has been initialized as true. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
=== NamedElementRef === | === NamedElementRef === | ||
| − | To represent links between java elements, as java AST defines only string references, | + | To represent links between java elements, as java AST defines only string references, metaclass NamedElementRef initially contained only this information. |
But an important addition was to resolve binding between elements, so is is actually possible to navigate directly in elements graph. It has been represented through a relationship from a NamedElementRef to a NamedElement (proxy or not). | But an important addition was to resolve binding between elements, so is is actually possible to navigate directly in elements graph. It has been represented through a relationship from a NamedElementRef to a NamedElement (proxy or not). | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
=== BodyDeclaration === | === BodyDeclaration === | ||
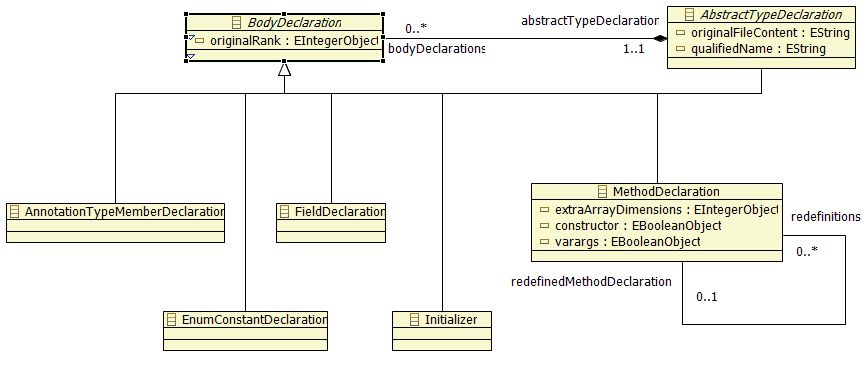
| − | A type declaration has different kinds of contents : fields, methods, static block, initialization block or other type declarations. All of these elements are of type BodyDeclaration | + | A type declaration has different kinds of contents : fields, methods, static block, initialization block or other type declarations. All of these elements are of type BodyDeclaration metaclass. |
[[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass BodyDeclaration and its hierarchy.jpg|frame|center|BodyDeclaration and its hierarchy]] | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass BodyDeclaration and its hierarchy.jpg|frame|center|BodyDeclaration and its hierarchy]] | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
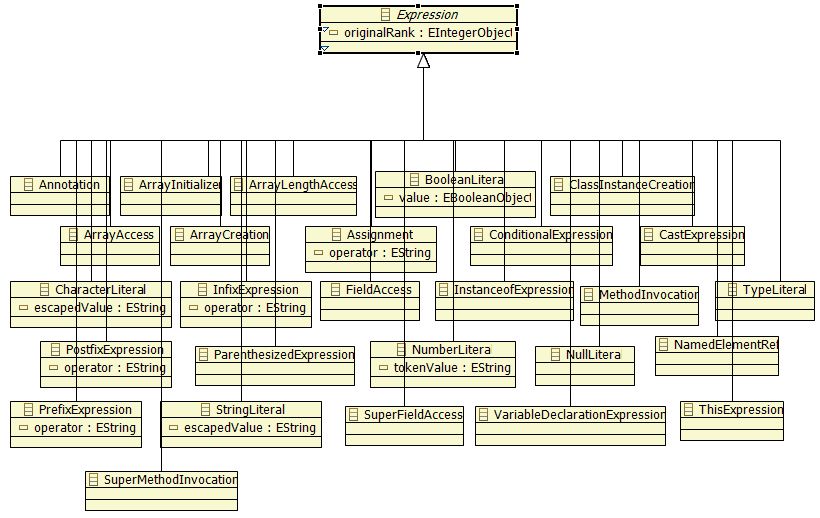
Like in many languages, concept of expression exists in Java : it is a portion of code, without declarations, and its evaluation returns a value, numerical or boolean or other ... | Like in many languages, concept of expression exists in Java : it is a portion of code, without declarations, and its evaluation returns a value, numerical or boolean or other ... | ||
| − | For example, <source lang="java">++i</source> is an expression and will be translated in concept of PrefixExpression | + | For example, <source lang="java">++i</source> is an expression and will be translated in concept of PrefixExpression metaclass. |
| − | All types of expressions shall inherit from Expression | + | All types of expressions shall inherit from Expression metaclass. |
[[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass Expression and its hierarchy.jpg|frame|center|Expression and its hierarchy]] | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass Expression and its hierarchy.jpg|frame|center|Expression and its hierarchy]] | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
=== Statements === | === Statements === | ||
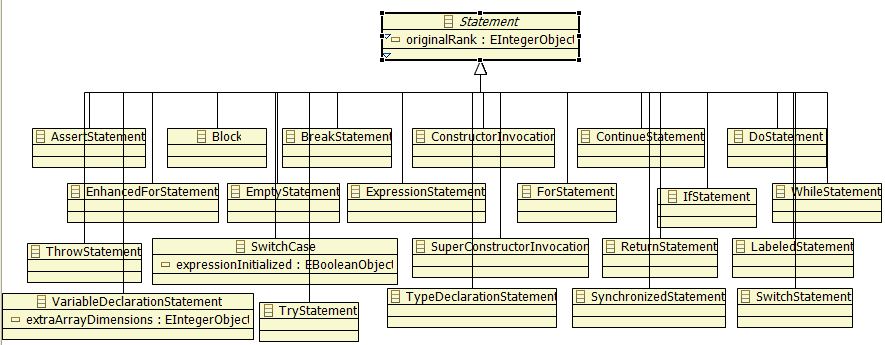
| − | An "instruction" in Java is represented by Statement | + | An "instruction" in Java is represented by Statement metaclass. A block of code (Block metaclass) contains a collection of statements, an a block of code may be contained by a method. |
Some example of statements in java : <source lang="java">if, while, for, do, ...</source> | Some example of statements in java : <source lang="java">if, while, for, do, ...</source> | ||
All of their definitions use concept of expression to separate value from instruction keyword. | All of their definitions use concept of expression to separate value from instruction keyword. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
There is three kinds of comments : line comments (//), block comments (/* */) and javadoc (/** */). | There is three kinds of comments : line comments (//), block comments (/* */) and javadoc (/** */). | ||
| − | Every comments contains text fragments, but we could have more informations on javadoc (Javadoc | + | Every comments contains text fragments, but we could have more informations on javadoc (Javadoc metaclass), it could contain javadoc tags that are identified and collected through instances of TagElement metaclass. |
[[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass Comment and its hierarchy.jpg|frame|center|Comment and its hierarchy]] | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass Comment and its hierarchy.jpg|frame|center|Comment and its hierarchy]] | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
Official usage of annotations has been introduced in version 5 of JDK. | Official usage of annotations has been introduced in version 5 of JDK. | ||
| − | To handle it, annotation declarations are managed as type declarations (AnnotationTypeDeclaration | + | To handle it, annotation declarations are managed as type declarations (AnnotationTypeDeclaration metaclass) with specific attributes (AnnotationTypeMemberDeclaration metaclass). |
| − | And annotation usages are translated in instances of Annotation | + | And annotation usages are translated in instances of Annotation metaclass, which reference corresponding annotation declarations. And parameters are translated in instances of MemberValuePair metaclass. |
[[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass AnnotationTypeDeclaration and Annotation.jpg|frame|center|Annotation]] | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 metaclass AnnotationTypeDeclaration and Annotation.jpg|frame|center|Annotation]] | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
Version 5 of JDK introduces also concept of "generics". | Version 5 of JDK introduces also concept of "generics". | ||
| − | Generic types of methods declarations are translated respectively in instances of TypeDeclaration of MethodDeclaration | + | Generic types of methods declarations are translated respectively in instances of TypeDeclaration of MethodDeclaration metaclass with arguments as instances of TypeParameter metaclass. |
| − | Usage of these generics are translated in instances of ParameterizedType | + | Usage of these generics are translated in instances of ParameterizedType metaclass which reference concret elements (type and types arguments). |
| − | Specific case of type argument is "wildcard" (for example <? extends X>. There is a specific | + | Specific case of type argument is "wildcard" (for example <? extends X>. There is a specific metaclass to handle it : WildCardType. |
[[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 generics declarations and usages.jpg|frame|center|Generics]] | [[Image:MoDisco-J2SE5 generics declarations and usages.jpg|frame|center|Generics]] | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
== Associated Discoverers == | == Associated Discoverers == | ||
| − | The main discoverer available for this | + | The main discoverer available for this metamodel : [[MoDisco/JavaDiscoverer|JavaDiscoverer]] |
It also exists an other project which produces a very similar model of Java applications : [http://www.eclipse.org/gmt/modisco/toolBox/JavaAbstractSyntax JavaAST] | It also exists an other project which produces a very similar model of Java applications : [http://www.eclipse.org/gmt/modisco/toolBox/JavaAbstractSyntax JavaAST] | ||
I hope these two discoverers will be merged in futur. | I hope these two discoverers will be merged in futur. | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 4 March 2009
The J2SE5 metamodel : it is the reflect of Java language, as it has been defined in version 3 of "Java Language Specification" from Sun Microsystems ("JLS3" corresponds to JDK 5).
J2SE5 metamodel contains 101 metaclasses. To better understand it, this page will introduce main features (metaclasses and links).
You could also browse definition model, j2se5.ecore available in sources (see install section).
A good tip is also to see javadoc associated to metamodel implemented by Eclipse team in project JDT (Java Development Tool). This metamodel and J2SE5 are very similar.
Contents
Main metaclasses
ASTNode
Every metaclasses (without metaclass Model) inherit from ASTNode. As its name indicate it, ASTNode represent a graph node. ASTNode has a reference to Comment metaclass because almost every java element could be associated to a comment (bloc or line comment and Javadoc). More details in "Comment" section.
Model, Package, AbstractTypeDeclaration
Root element of each J2SE5 model in an instance of "Model" metaclass. It is a translation of java application concept, so it contains package declarations (instances of PackageDeclaration metaclass). And package declarations contain type declarations (instances compatible with AbstractTypeDeclaration metaclass), and so on ...
NamedElement & notion of Proxy
A lot of java elements are "named", and this name could be considered as an identifier : methods, packages, types, variables, fields, ... So all of corresponding metaclasses inherit from NamedElement metaclass. It will be usefull to resolve references in binding, see NamedElementRef metaclass.
And an other goal of this metaclass is to indicate which element is a part of the current java application or not (element from an external library of from JDK). Then external elements are tagged as proxy through dedicated attribute and could be easily filtered. For example, instruction "System.out.println" has been decomposed in three named elements (one class, one variable and one method) which defintion are not part of current java application. So attribute "proxy" of these elements has been initialized as true.
NamedElementRef
To represent links between java elements, as java AST defines only string references, metaclass NamedElementRef initially contained only this information. But an important addition was to resolve binding between elements, so is is actually possible to navigate directly in elements graph. It has been represented through a relationship from a NamedElementRef to a NamedElement (proxy or not).
BodyDeclaration
A type declaration has different kinds of contents : fields, methods, static block, initialization block or other type declarations. All of these elements are of type BodyDeclaration metaclass.
Expressions
Like in many languages, concept of expression exists in Java : it is a portion of code, without declarations, and its evaluation returns a value, numerical or boolean or other ...
For example,++iAll types of expressions shall inherit from Expression metaclass.
Statements
An "instruction" in Java is represented by Statement metaclass. A block of code (Block metaclass) contains a collection of statements, an a block of code may be contained by a method.
Some example of statements in java :if, while, for, do, ...
All of their definitions use concept of expression to separate value from instruction keyword.
Zoom on comments
There is three kinds of comments : line comments (//), block comments (/* */) and javadoc (/** */). Every comments contains text fragments, but we could have more informations on javadoc (Javadoc metaclass), it could contain javadoc tags that are identified and collected through instances of TagElement metaclass.
Zoom on annotations
Official usage of annotations has been introduced in version 5 of JDK. To handle it, annotation declarations are managed as type declarations (AnnotationTypeDeclaration metaclass) with specific attributes (AnnotationTypeMemberDeclaration metaclass). And annotation usages are translated in instances of Annotation metaclass, which reference corresponding annotation declarations. And parameters are translated in instances of MemberValuePair metaclass.
Zoom on generics
Version 5 of JDK introduces also concept of "generics". Generic types of methods declarations are translated respectively in instances of TypeDeclaration of MethodDeclaration metaclass with arguments as instances of TypeParameter metaclass. Usage of these generics are translated in instances of ParameterizedType metaclass which reference concret elements (type and types arguments).
Specific case of type argument is "wildcard" (for example <? extends X>. There is a specific metaclass to handle it : WildCardType.
Requirements
To use the plug-in you need:
- JDK 1.5 or above
- a version of Eclipse 3.3 or above with the following set of plugins installed
- EMF 2.3.0 or higher
Install
You will find a version of this plug-in attached in following bug.
As IP review of this plugin is not finished, here is installation instructions :
- Extract archive file in your Eclipse workspace, then use "import" menu to import this project.
- Use "export" menu to export this project as a plugin (Deployable plugins and fragments) in your Eclipse installation. Don't forget to choose "Package plug-ins as individual jar archives" option.
- re-start your Eclipse to take in account this plug-in
Associated Discoverers
The main discoverer available for this metamodel : JavaDiscoverer
It also exists an other project which produces a very similar model of Java applications : JavaAST I hope these two discoverers will be merged in futur.