Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Java11/Examples"
m |
(Undo revision 431060 by Lshanmug.in.ibm.com (talk)) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
This is an informal page listing examples of features that are implemented by the Java 11 Support. You are welcome to try out these examples. If you find bugs, please file a bug after checking for a duplicate entry [https://bugs.eclipse.org/bugs/buglist.cgi?cmdtype=dorem&remaction=run&namedcmd=J11.Open&sharer_id=152344 here]. | This is an informal page listing examples of features that are implemented by the Java 11 Support. You are welcome to try out these examples. If you find bugs, please file a bug after checking for a duplicate entry [https://bugs.eclipse.org/bugs/buglist.cgi?cmdtype=dorem&remaction=run&namedcmd=J11.Open&sharer_id=152344 here]. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 16: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
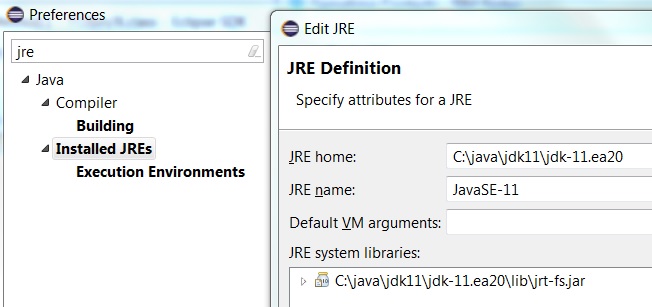
[note: Eclipse -> Preferences in Mac / Window -> Preferences in Windows] | [note: Eclipse -> Preferences in Mac / Window -> Preferences in Windows] | ||
| − | | | + | | Java 11 JRE recognized as a valid JRE |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Project JRE | ! scope="row" | Project JRE | ||
| Line 24: | Line 22: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Package Explorer | ! scope="row" | Package Explorer | ||
| − | | Go to Package Explorer and expand the Java 11 JRE || | + | | Go to Package Explorer and expand the Java 11 JRE || Modules (eg java.base etc) are listed in the package explorer view |
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="3" | The First Step: Java 11 Compliance | ! colspan="3" | The First Step: Java 11 Compliance | ||
| Line 33: | Line 31: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
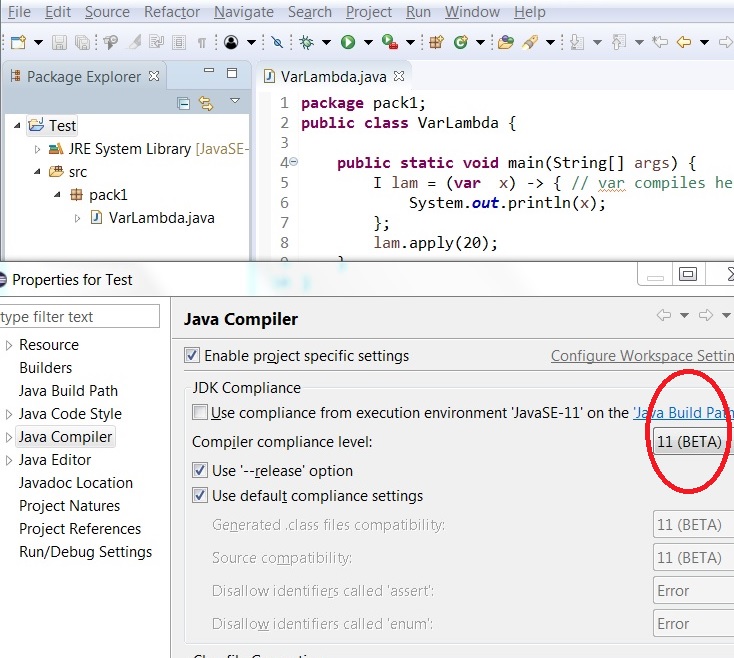
[[File:j11.compliance.jpg]] | [[File:j11.compliance.jpg]] | ||
| − | | | + | |11 is shown in the drop down list |
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="3" | Basic Necessity : Compilation and Error Reporting | ! colspan="3" | Basic Necessity : Compilation and Error Reporting | ||
| Line 101: | Line 99: | ||
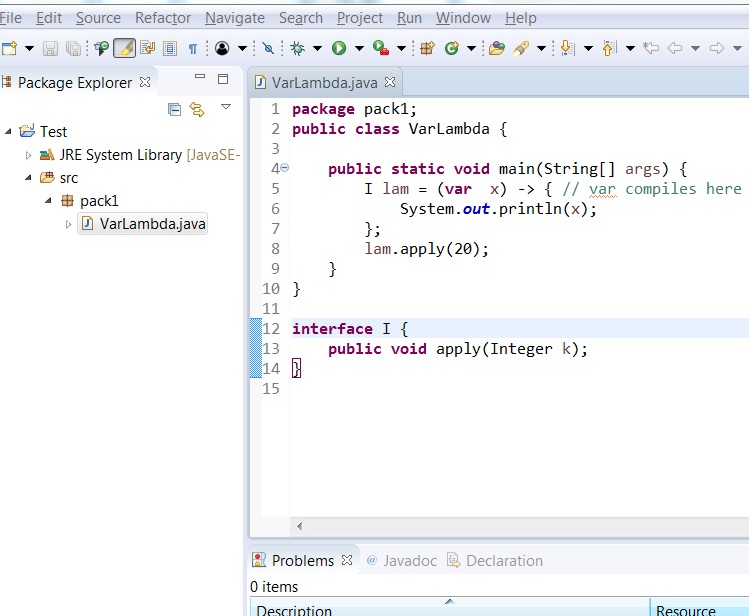
| | | | ||
Compiler errors shown | Compiler errors shown | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! colspan="3" | Hover and Navigation | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Hover | ||
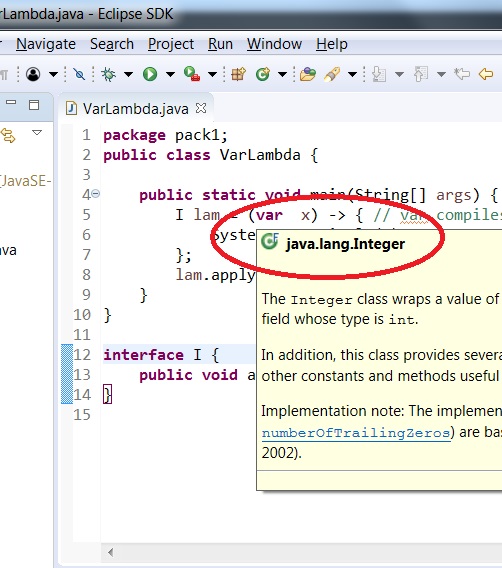
| + | | Use the following code: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | package pack1; | ||
| + | public class VarLambda { | ||
| + | |||
| + | public static void main(String[] args) { | ||
| + | I lam = (var x) -> { // hover over var | ||
| + | System.out.println(x); | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | lam.apply(20); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | interface I { | ||
| + | public void apply(Integer k); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:var11.hover.jpg]] | ||
| + | | Hover and Navigation | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="3" | Nestmates | ! colspan="3" | Nestmates | ||
| Line 106: | Line 130: | ||
! scope="row" | Basic Nesting Principles | ! scope="row" | Basic Nesting Principles | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | <b>Description: Nest Based Access - A JVM Concept.</b> | |
| − | + | A top level class and all inner classes form a single unit for access, a "nest".JVM | |
| − | + | specification added two attributes in the classfile NestHost and NestMember. The top | |
| − | The top most class will have the NestMember attribute listing all the members while | + | most class will have the NestMember attribute listing all the members while each of |
| − | each of the inner classes will have a NestHost attribute listing the top level class. | + | the inner classes will have a NestHost attribute listing the top level class. Using |
| − | Using this, some of the synthetic bridge methods are elided transparent to the programmer. | + | this, some of the synthetic bridge methods are elided transparent to the programmer. |
| − | Note that this feature is relevant only for tools that process byte code and hence, in general, | + | Note that this feature is relevant only for tools that process byte code and hence, |
| − | this feature would be "transparent" to a "normal" programmer. This feature is applicable for byte | + | in general, this feature would be "transparent" to a "normal" programmer. This feature |
| − | code processors, for eg our Disassembler has been enhanced to show these attributes. | + | is applicable for byte code processors, for eg our Disassembler has been enhanced to |
| − | + | show these attributes. For further info please read JEP 181. | |
| − | + | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<source lang="java"> | <source lang="java"> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 159: | ||
In each of X$A, X$A$B, X$Y the attribute: | In each of X$A, X$A$B, X$Y the attribute: | ||
Nest Host: #22 X | Nest Host: #22 X | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 02:43, 13 March 2019
This is an informal page listing examples of features that are implemented by the Java 11 Support. You are welcome to try out these examples. If you find bugs, please file a bug after checking for a duplicate entry here.