Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "JWT Transformations (up to JWT 1.2.0 included)"
(→Export) |
(→Import) |
||
| Line 225: | Line 225: | ||
=== Export & Import === | === Export & Import === | ||
We have two different transformations: one from JWT to BPMN and one the other way round (from BPMN to JWT). | We have two different transformations: one from JWT to BPMN and one the other way round (from BPMN to JWT). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 07:13, 26 May 2009
Contents
Terminology
In this page, transformation will stand for a transformation of a workflow from one standard to another.
Since JWT workflow file type is the core of this project, the term import will stand for transformations that produce a JWT workflow file, and the term export will stand for transformations that produce a description of a workflow into another format, from JWT.
Aim
The aim of transformations is to make possible to use workflows designed with JWT in another contexts. While JWT workflow file format is not a standard used by other workflow editors, engines, etc..., it is necessary to give to JWT the ability to export workflows to use them elsewhere, and to import other workflow description file types not to discourage users that would migrate from external workflow editor to JWT.
Transformations are the basis of compatibility.
Transformations will be used when we will implement a function that will deploy the JWT workflow on a workflow engine only with a few clicks...
How to use it
You need a JWT WE with the jwt-transformations-base plugin installed as well as any transformation plugin you want to use, for example jwt-bpmn or jwt-xpdl.
This makes available "Export" and "Import" buttons in the JWT WE toolbar, and under those any transformations provided by the installed plugins. To use for example the XPDL transformation, choose Export, and there choose JWT2XPDL in the dialog box ; fill in the output file name, and start the transformation by clicking on OK.
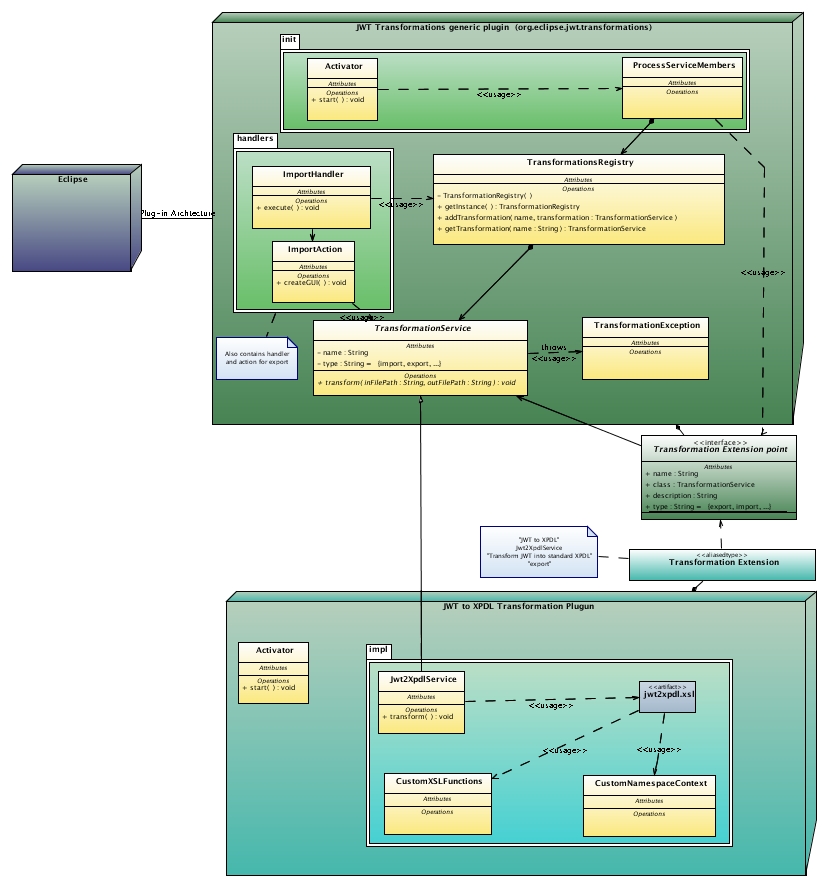
Architecture
To facilitate the add of a transformation, we chose to use the extensions-based Eclipse plug-in architecture, as described by the picture:
When the plugin is started
Activator is called on the generic transformation plug-in. This activation calls the ProcessServiceMember.process method, which will get all informations to get informations from the extension point and add it to a registry that will be use later. (This mechanism is done as explained at http://www.eclipse.org/articles/Article-Plug-in-architecture/plugin_architecture.html) This part of the code is used only once, at activation.
When a transformation is called
The method that handle the call just has to call TransformationsRegister.getInstance.getTransformation(transformationName_defined_in_extension).transform It is aimed to have one or several generic handlers that would be defined in generic plug-in, to unify transformations that have the same goal (export to model, export to execution platform compliant type...)
Extensibility
If necessary, it is easy to add some metadata to a transformation. To do it, just add an attribute to the extension point, add it as an attribute to the transformationService class, and set it when you load the extension is ProcessServieRegistry.
How do I add a transformation to JWT?
Nothing is easier!
Of course, it requires org.eclipse.jwt.transformation.base plug-in.
You just have to implement a class that extends TransformationService, with its method transform (that will be called to apply the transformation). Then, you create an extension for the extension point org.eclipse.jwt.transformations that defines a name for your transformation and the class that implements the transformation (extending TransformationService), and more other optional fields.
Take a look at the extension of StubTransformation from JWT repository to give you a concrete example.
Transformations Gallery
Here are the file types that are already compatible, or that will soon be, with JWT
XSLT based Transformation
- For XSL transformations, there is a tool plugin called jwt-transformations-xslt-tools which contains some stuff to call XSL transformations and some extenstion classes that can be used to "introspect" the JWT XML model file.
- These transformations use Xalan 2.7.1 (for XSLT) and (Xerces 2.9) for XPath processors
- Important: Any plugin that wishes to add an extension class have to add in its MANIFEST.MF this line Eclipse-RegisterBundle: org.apache.xalan
XPDL
Only export JWT to XPDL is available. But there are some limitations.
This transformation uses XSLT.
See the JWT2XPDL documentation.
jPDL
Thoughts
Since jPDL is not an EMF-based metamodel, there are 3 main ways to process this transformation:
- Use XSLT
- pros: XSLT is standard, not IP issue, easy to integrate
- cons: XSLT not really extensible, customizable, maintainable...
- Use JWT model API and a DOM/SAX API for output
- pros: DOM or SAX API are embedded in Java, no IP issue
- cons: DOM/SAX not so fun to use
- Use JWT model API and jpdl Java API (package org.jbpm.jpdl)
- pros: full Java, maybe easier to use
- cons: code from jBpm API => IP issues for integration into JWT, a lot of deps...
Here are some mappings:
- jwt:Activity(Name) -> process-definition(name)
- InitialNode -> start-state
- (automatic) Action (without role) -> node
- Application -> action (same a Bonita hook)
- (human) Action (with role) -> task
- role -> swimlane
BPMN
These transformations use ATL.
About ATL
Then the plugin requires org.eclipse.m2m.atl.engine. Here is a piece of code that can be used to run ATL transformations in Java. To be moved to ATL Howtos?
/** * This sample is shared under WTFPL * http://sam.zoy.org/wtfpl/ */ package org.eclipse.jwt.transformations.bpmn; import java.net.URL; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.eclipse.emf.common.util.URI; import org.eclipse.m2m.atl.drivers.emf4atl.ASMEMFModel; import org.eclipse.m2m.atl.engine.AtlEMFModelHandler; import org.eclipse.m2m.atl.engine.AtlLauncher; import org.eclipse.m2m.atl.engine.AtlModelHandler; /** * Should implement a template method pattern... */ class ATLTransformation { private static ATLTransformation instance = null; private final static String resourcePath = "/org.eclipse.jwt.transformations.bpmn/src/org/eclipse/jwt/transformations/bpmn/resources/"; private AtlEMFModelHandler modelHandler; private URI XML_ModelResource; private URI JWT_ModelResource; private URI BPMN_ModelResource; private URL JWT2BPMN_TransfoResource; private URL BPMN2JWT_TransfoResource; private ASMEMFModel xmlMetamodel; private ASMEMFModel jwtMetamodel; private ASMEMFModel bpmnMetamodel; private URL JWT2BPMN_Pool_TransfoResource; private URL JWT2BPMN_Sub_TransfoResource; static public ATLTransformation getInstance() { if (instance == null) instance = new ATLTransformation(); return instance; } private void createResources() { modelHandler = (AtlEMFModelHandler) AtlModelHandler .getDefault(AtlModelHandler.AMH_EMF); XML_ModelResource = URI.createPlatformPluginURI(resourcePath + "XML.ecore", false); JWT_ModelResource = URI.createPlatformPluginURI(resourcePath + "jwt.ecore", false); BPMN_ModelResource = URI.createPlatformPluginURI(resourcePath + "bpmn.ecore", false); JWT2BPMN_TransfoResource = ATLTransformation.class.getResource("resources/JWT2BPMN.asm"); JWT2BPMN_Pool_TransfoResource = ATLTransformation.class.getResource("resources/Jwt2BpmnAllInPool.asm"); JWT2BPMN_Sub_TransfoResource = ATLTransformation.class.getResource("resources/Jwt2BpmnAllInSub.asm"); BPMN2JWT_TransfoResource = ATLTransformation.class.getResource("resources/BPMN2JWT.asm"); } private void initMetamodels(Map<String, Object> models) { xmlMetamodel = (ASMEMFModel) modelHandler.loadModel( "XML", modelHandler.getMof(), XML_ModelResource); jwtMetamodel = (ASMEMFModel) modelHandler.loadModel( "jwt", modelHandler.getMof(), JWT_ModelResource); bpmnMetamodel = (ASMEMFModel) modelHandler.loadModel( "bpmn", modelHandler.getMof(), BPMN_ModelResource); models.put("XML", xmlMetamodel); models.put("jwt", jwtMetamodel); models.put("bpmn", bpmnMetamodel); } public void jwt2bpmn(String inFilePath, String outFilePath) { try { Map<String, Object> models = new HashMap<String, Object>(); createResources(); initMetamodels(models); // get/create models ASMEMFModel jwtInputModel = (ASMEMFModel) modelHandler.loadModel("IN", jwtMetamodel, URI.createFileURI(inFilePath)); ASMEMFModel bpmnOutputModel = (ASMEMFModel) modelHandler.newModel("OUT", URI.createFileURI(outFilePath).toFileString(), bpmnMetamodel); // load models models.put("IN", jwtInputModel); models.put("OUT", bpmnOutputModel); // launch AtlLauncher.getDefault().launch(this.JWT2BPMN_Pool_TransfoResource, Collections.EMPTY_MAP, models, Collections.EMPTY_MAP, Collections.EMPTY_LIST, Collections.EMPTY_MAP); modelHandler.saveModel(bpmnOutputModel, outFilePath, false); dispose(models); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void bpmn2jwt(String inFilePath, String outFilePath) { try { Map<String, Object> models = new HashMap<String, Object>(); createResources(); initMetamodels(models); // get/create models ASMEMFModel bpmnInputModel = (ASMEMFModel) modelHandler.loadModel("IN", bpmnMetamodel, URI.createFileURI(inFilePath)); ASMEMFModel jwtOutputModel = (ASMEMFModel) modelHandler.newModel("OUT", URI.createFileURI(outFilePath).toString(), jwtMetamodel); // load models models.put("IN", bpmnInputModel); models.put("OUT", jwtOutputModel); // launch AtlLauncher.getDefault().launch(this.BPMN2JWT_TransfoResource, Collections.EMPTY_MAP, models, Collections.EMPTY_MAP, Collections.EMPTY_LIST, Collections.EMPTY_MAP); modelHandler.saveModel(jwtOutputModel, outFilePath, false); dispose(models); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void dispose(Map<String, Object> models) { for (Object model : models.values()) ((ASMEMFModel)model).dispose(); } }
As you can see, ATL transformations can be called in 4 steps:
- Add metamodel derscription to ATL
- Add models to ATL (specifying the metamodel that is used to describe them)
- Call the transformation (specifying the resource that describes the transformation and input and output files)
Remark: You can see that this piece of code loads directly ATL compiled files (*.asm) instead of ATL files. We could easily generate asm files from ATL at runtime using ATLCompiler class; however, it is better to assume that we have the compiled version of transformations. This way, we avoid compiling each time we call a transformation, and make the transformation faster.
Export & Import
We have two different transformations: one from JWT to BPMN and one the other way round (from BPMN to JWT).