Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Introduction to EclipseLink (ELUG)"
m (→Introduction to EclipseLink) |
m (testing images) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
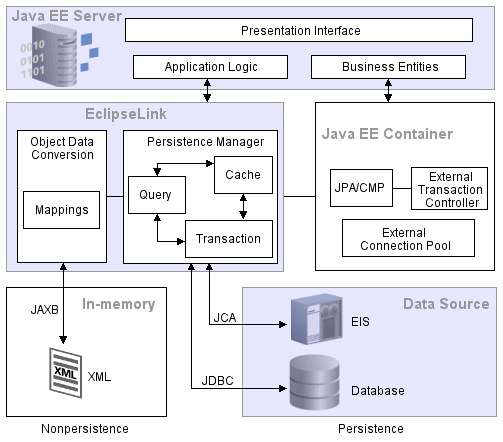
EclispeLink builds high-performance applications that store persistent object-oriented data in a relational database. It successfully transforms object-oriented data into either relational data or Extensible Markup Language (XML) elements. | EclispeLink builds high-performance applications that store persistent object-oriented data in a relational database. It successfully transforms object-oriented data into either relational data or Extensible Markup Language (XML) elements. | ||
| − | Figure 1-1 EclipseLink Runtime Architecture | + | ''Figure 1-1 EclipseLink Runtime Architecture'' |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Under02.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 08:53, 17 October 2007
Contents
Introduction to EclipseLink
EclipseLink is an advanced, object-persistence and object-transformation framework that provides development tools and run-time capabilities that reduce development and maintenance efforts, and increase enterprise application functionality.
What Is EclipseLink?
EclispeLink builds high-performance applications that store persistent object-oriented data in a relational database. It successfully transforms object-oriented data into either relational data or Extensible Markup Language (XML) elements.
Figure 1-1 EclipseLink Runtime Architecture
Using EclipseLink , you can integrate persistence and object-transformation into your application, while staying focused on your primary domain problem by taking advantage of an efficient, flexible, and field-proven solution (see Section 1.2, "What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch").
What Is the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch
EclipseLink Key Features
EclipseLink Application Architectures
This Page: