Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EclipseLink/UserGuide/MOXy/Type Level/Mapping to a Type or Element/Default Root Element"
< EclipseLink | UserGuide | MOXy | Type Level
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
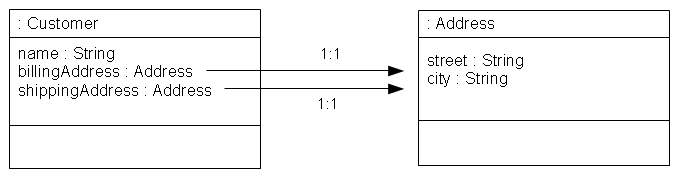
At least one of your mapped classes must have a default root element defined. This tells EclipseLink what the top-level root of your XML document will be. Consider the <tt>Customer</tt> and <tt>Address</tt> classes shown in this example: | At least one of your mapped classes must have a default root element defined. This tells EclipseLink what the top-level root of your XML document will be. Consider the <tt>Customer</tt> and <tt>Address</tt> classes shown in this example: | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Defaultrootelement.png]]<br><br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
These classes correspond to the XML schema, shown in this example. | These classes correspond to the XML schema, shown in this example. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| − | + | <xsd:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> | |
| − | + | <xsd:complexType name="address-type"> | |
| − | + | <xsd:sequence> | |
| − | + | <element name="street" type="xsd:string"/> | |
| − | + | <element name="city" type="xsd:string"/> | |
| − | + | </xsd:sequence> | |
| − | + | </xsd:complexType> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> | |
| − | + | <xsd:sequence> | |
| − | + | <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string"/> | |
| − | + | <xsd:element name="billing-address" type="address-type"/> | |
| − | + | <xsd:element name="shipping-address" type="address-type"/> | |
| − | + | </xsd:sequence> | |
| − | + | </xsd:complexType> | |
| − | + | </xsd:schema> | |
| − | + | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 6 January 2011
EclipseLink MOXy
| EclipseLink | |
| Website | |
| Download | |
| Community | |
| Mailing List • Forums • IRC • mattermost | |
| Issues | |
| Open • Help Wanted • Bug Day | |
| Contribute | |
| Browse Source |
![]() Key API
Key API
Contents
Default Root Element
At least one of your mapped classes must have a default root element defined. This tells EclipseLink what the top-level root of your XML document will be. Consider the Customer and Address classes shown in this example:
These classes correspond to the XML schema, shown in this example.
<xsd:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:complexType name="address-type"> <xsd:sequence> <element name="street" type="xsd:string"/> <element name="city" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:element name="billing-address" type="address-type"/> <xsd:element name="shipping-address" type="address-type"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
When an instance of the Customer class is persisted to XML, the EclipseLink runtime performs the following:
- Gets the default root element.The Customer class instance corresponds to the root of the XML document. The EclipseLink runtime uses the default root element specified on the descriptor (customer) to start the XML document. EclipseLink then uses the mappings on the descriptor to marshal the object's attributes:
<customer> <name>…</name> </customer> - When the EclipseLink runtime encounters an object attribute such as billingAddress, it checks the mapping associated with it to determine with what element (billing-address) to continue:
<customer> <name>…</name> <billing-address/> </customer>
The EclipseLink runtime checks the mapping's reference descriptor (Address) to determine what attributes to persist:<customer> <name>…</name> <billing-address> <street>…</street> <city>…</city> </billing-address> </customer>
![]()
Note: The undefined document root element of a referenced object is ignored during marshalling with an any collection mapping and object mapping.