Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EclipseLink/Examples/Distributed"
< EclipseLink | Examples
m (→Analysis DI5:) |
m (→TypeConverter) |
||
| Line 390: | Line 390: | ||
====TypeConverter==== | ====TypeConverter==== | ||
*Use of a TypeConverter (not an ObjectTypeConverter) may be one option. We would map the '''BigInteger''' type to a '''String''' which could be stored in a column that is larger than the current 128 bit (16 byte) lenght of '''NUMERIC'''. This would eventually hit a maximum of 1-2K, where if we represented each bit as a 0 or 1 ''byte'' we could at least represent 1024 bits with this strategy. | *Use of a TypeConverter (not an ObjectTypeConverter) may be one option. We would map the '''BigInteger''' type to a '''String''' which could be stored in a column that is larger than the current 128 bit (16 byte) lenght of '''NUMERIC'''. This would eventually hit a maximum of 1-2K, where if we represented each bit as a 0 or 1 ''byte'' we could at least represent 1024 bits with this strategy. | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | @Entity | ||
| + | @TypeConverters({@TypeConverter(name="BigIntegerToString",dataType=String.class,objectType=BigInteger.class)}) | ||
| + | public class Parameters implements Serializable { | ||
| + | private static final long serialVersionUID = -1979843739878183696L; | ||
| + | @Column(name="maxValue", nullable=false, length=512) | ||
| + | @Convert("BigIntegerToString") | ||
| + | private BigInteger maxValue; | ||
| + | </source> | ||
==DI 6: EAR Redeploy should not affect remote clients== | ==DI 6: EAR Redeploy should not affect remote clients== | ||
Revision as of 11:51, 15 February 2011
Contents
- 1 Distributed Enterprise Case Study using JEE6 API - JPA 2.0, JSF 2.0, JAX-RS 1.1 and EJB 3.1
- 2 Requirements
- 2.1 R0: Unbounded Scalar Precision
- 2.2 R1: Increased Superscalar Performance
- 2.3 R1: Local Client Access
- 2.4 R2: Remote RMI Client Access Inside Firewall
- 2.5 R3: Remote WebService Client Access Outside Firewall
- 2.6 R4: Browser based Interface to Client Data on Server
- 2.7 R5: Separation of components and concerns
- 2.8 R6: Full abstraction of the database
- 2.9 R7: JEE6 API usage
- 2.10 R: Remote Update
- 2.11 R: Thread Modulation
- 2.12 R: Optimization by Truncation
- 3 Analysis
- 4 Use Cases
- 5 Design
- 5.1 DI 1: Distributed Communication Strategy
- 5.2 DI 2: Module Separation
- 5.3 DI 3: Remote RMI/EJB Communication type
- 5.4 DI 4: Type of client/server setup
- 5.5 DI 5: Limitations of BigInteger translation to BIGINT Database DataType
- 5.6 DI 6: EAR Redeploy should not affect remote clients
- 5.7 DI 7: Strategy for handling expected OptimisticLockException during high throughput concurrent traffic
- 5.8 DI 8: Variable Partition between Different Client Capabilities
- 5.9 DI9: Force binary compatibility with Model changes via the serialVersionUID
- 6 Data Model
- 7 Implementation
- 8 Hardware
- 9 Performance
- 10 Testing
- 10.1 WebLogic 10.3.4.0 Server Logs
- 10.2 GlassFish 3.1 Server Logs
- 10.3 TC1: Remote Session Bean Lookup on GlassFish 3.1 from SE Client on Same JVM
- 10.4 TC2:Remote Session Bean Lookup on GlassFish 3.1 from SE Client on Different JVM - Local Machine
- 10.5 TC3:Remote Session Bean Lookup on GlassFish 3.1 from SE Client on Different JVM - Remote Machine
- 10.6 TC13: Remote Session Bean Lookup on WebLogic 10.3.4.0 from SE Client on Different JVM - Remote Machine
- 11 Results
- 12 Status
- 13 Statistics
- 14 TODO
- 15 References
Distributed Enterprise Case Study using JEE6 API - JPA 2.0, JSF 2.0, JAX-RS 1.1 and EJB 3.1
- This case study describes the analysis, design, implementation and deployment of a distributed JEE6 application that makes use of the EJB 3.1, JPA 2.0, JSF 2.0, Servlet 3.0 and JAX-RS API implemented as part of the Oracle GlassFish Server 3.1 distribution. The Java IDE used for this tutorial is the tightly integrated SUN NetBeans 7.0 release that will be in beta until April 2011 but we are also able to use Eclipse Helios 3.6 as well.
- Why distributed? We need to investigate the concurrent behavior and exception handling of a near-real-world hammering of a server based JPA application from multiple clients. Specifically I am interested in how we implement 2-phase commit, handle OptimisticLockExceptions and design for a mix of transaction types involving REQUIRES(default)|REQUIRES_NEW|NOT_REQUIRED. We may also integrate different isolation levels.
- We will be concentrating on how to leverage the features of JPA 2.0 that are implemented by EclipseLink 2.x. These features should include...
Document History
| Date | Author | Version Description & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 20110209 | Michael O'Brien | 1.0 Initial draft starting |
Technology Summary
- Technology Statement: Develop a n:1 distributed application with many clients connected to one central persistence server
- Normally we do not decide on what APIs will be in use before we analyse the requirements. However, here is the list of technologies we are using - as we finalize the implementation.
- JPA 2.0 : All database interaction will be on the main server via a container managed @PersistenceContext on EJB session beans. The clients will modify detached entities and return them to the server for merging/persistence.
- JTA : We will continue to use container managed transactions via the dependency injected proxy so we do not have to manage transaction events ourselves
- EJB 3.1 : We will be using @Stateless @Remote beans but may be using @Singleton and/or container-managed JTA persistence units in the WAR for @Local beans
- JSF 2.0 : We will use the existing @ManagedBean and new .XHTML controller/view separation pattern
- JAX-RS 1.1 :
- JMS :
- JNI :(possible optimization via C++ using either IA32/64, SSE or even CUDA) - where the Java client is just the wrapper around the computation engine.
- We will not be using an L2 cache such as Coherence, ehCache or Terracotta at this point - we will be communicating using standard EJB beans such as session or message-driven beans.
- We will be presenting 2 identical implementations of this project
Problem
- Instead of the usual Employee demo or even the simple entity/jsp format of previous JPA tutorials - we will attempt at providing a usefull distributed java application that could be deployed to a live server that would be hosted outside our firewall.
- We require a real-world distributed app that can be used as a case study for the following issues.
- - performance (we need a way to hammer a JPA based server and change the client load at runtime)
- - management (test framework to try out central management of the server and clients)
- - analytics (how can we report JVM and persistence metrics with minimal thread overhead)
- - concurrency (how do we handle under-load forced OptimisticLockException conditions without resorting to synchronized blocks) - @Singleton SB for example
- - distributed memory (for clients that are not running persistence on their own - where they would benefit from an L2 cache like Coherence, ehCache or Terracotta - we need to prototype scenarios where the database or EclipseLink L1 in-memory cache can act as a distributed shared memory for the remote clients).
- Specifically, how do we propagate changes from some clients to others using both a
- 1) Star network of ManyToOne for clientsToServer
- 2) Mesh network of ManyToMany for clientsToClients
- Specifically, how do we propagate changes from some clients to others using both a
- We will develop a n:1 distributed application with many clients connected to
one central persistence server.
- Our selected real-world problem is how can we help prove the Collatz conjecture (or all integer paths lead to 1).
Collazt Numbers
- In the interest of advancing science - specifically the science of very large (and I mean very large) as in near googol class numbers and their sequences.
- The Collatz conjecture or (3n + 1) problem has not been proven yet. There have been attempts at verifying collatz up to 2^61 - however, massive amounts of scalar processing power is required to do this because the problem is non-linear and therefore must be brute force simulated even with optimizations.
- The algorithm is as follows for the set of positive integers to infinity.
odd numbers are transformed by 3n + 1 even numbers are divided by 2
- If you think in base 2, we see that for odd numbers we shift bits to the left, add the number to the result and set bit 0. For even numbers we shift bits to the right. We therefore have a simplified algorithm as follows.
odd: next binary = number << 1 + number + 1 even: next binary = number >> 1
- 'Observation 1: the maximum value remains at or around 2x the number of bits in the start number - at least so far in my own simulations up to 640 billion.
- We stop iteration and record the max path and max value when the sequence enters the 4-2-1 loop after the first 1 is reached. This sequence must be simulated for all positive integers up to the limit of the software being used. Fortunately, in Java (and .NET3) we can use BigInteger which supports unlimited length integers - as we would quickly overflow using a 64 bit long as soon as we started iterating numbers over 32 bits.
- Observation 2: I have determined - via a week of simulation distributed among 16 different machines in parallel - that we will need native computation.
Requirements
R0: Unbounded Scalar Precision
- Actually essentially unbounded integer precision is required - but if we are going to persist something we need a set column size.
- Java (and lately .NET and android). We could use the more efficient BitSet for binary operations but it won't help us because the bit length is fixed at 64 bits - we need at least 256. We will also need a conversion strategy for persisting unlimited numbers into limited length NUMERIC database fields.
R1: Increased Superscalar Performance
- We need to get better performance from a group of separate JVM's running in parallel on the same or different machines that we would get from a single instance of the client.
- The impact of distribution and processing of the client data packets should incur very little overhead on the central processing server.
R1: Local Client Access
- JSF browser based console will be developed
R2: Remote RMI Client Access Inside Firewall
- EJB 3.x remote session beans will be available
R3: Remote WebService Client Access Outside Firewall
- We will implement this by generating a WSDL from the JPA model and exposing a web service facade around the EJB 3.x session beans
R4: Browser based Interface to Client Data on Server
- We will implement this using JSF 2.0 to start.
R5: Separation of components and concerns
- The data model in the form of a JPA persistence context will be in a separate JAR project allowing us to share the model among the EJB beans, the WAR web project and the distributed clients of the business layer that includes the SE clients, the web services clients and any JMS client listeners.
R6: Full abstraction of the database
- We will use JPA 2.0 to manage the persistence of the model.
R7: JEE6 API usage
- Where available we will leverage any JEE6 features that help our implentation
R: Remote Update
- We need some sort of utility that will remote update all the client code (includes client classes and EJB session bean interfaces).
R: Thread Modulation
- A way to reduce the processor load of individual clients would be very usefull in allowing the overall distributed system to be throttled down (likely with wait states). We would perform a process very similar to PWM (pulse width modulation) - used for example in brightness control of LED systems by varying the on time square wave of a signal. In our case will could increase the thread wait/suspend time from 0=default to something like 60 sec.
R: Optimization by Truncation
- Assumption: This optimization depends on whether we need to actually compute the paths and maximums for a range of values 'below a higher range that jas just found new maximum value and maximum path attributes - rendering our current lower search kind of irrelevant. Except in the case where the sub-path is required for other types of optimization.
Analysis
AI1: Unidirectional or Bidirectional communication between clients and server
- At this point we will be implementing a protocol similar to stateless HTTP where each client requests from or posts resources to the server. The server does not initiate communication - it only responds to clients.
- Alternatively we will likely add JMS listener registration where the server will post messages to clients and the clients that subscribe to the JMS queue may choose to asynchronously respond to the message.
AI2: Synchronous or Asynchronous access to session beans from clients
- We have the choice of getting a reference to a remote session bean and holding that reference for the duration of the client work packet until we return results to the server. Or, we can perform separate calls to separate references to get and put the work unit. It will depend on the length of time to process the unit, the bean lifetime and how many beans are in the server pool.
AI3: JEE6 Technology State for major EE Servers
- As we will be deploying at least one implementation to one of the major EE servers - we need some selection criteria.
WebLogic 10.3.4.0
- Oracle WebLogic 10.3.4.0 was released on 15 Jan 2011, the following list of JEE6 APIs are implemented on top of its JEE5 certification.
WebLogic JEE6 Functionality
- Java Persistence 2.0 (JSR 317) - with patch
- CDI (Contexts and Dependency Injection) (JSR 299)
- DI (Dependency Injection) for Java (JSR 330)
- JAX-RS (RESTful Web Services) 1.1 (JSR 311)
- JSF (Java Server Faces) 2.0 (JSR 314)
WebSphere 8.0 Beta
https://www14.software.ibm.com/iwm/web/cc/earlyprograms/websphere/wsasoa/index.shtml
WebSphere JEE6 Functionality
- Java Persistence 2.0 (JSR 317)
- CDI (Contexts and Dependency Injection) (JSR 299)
- JSP 2.2 / Servlet 3.0 which includes @WebServlet
- JAX-RS (RESTful Web Services) 1.1 (JSR 311)
- partial JAX-WS 2.2
- JSF (Java Server Faces) 2.0 (JSR 314)
- EJB (Enterprise Java Beans) 3.1 (JSR 318)
- JCA 1.6
GlassFish 3.1
- Oracle GlassFish Server 3.1 is due for release this year. The IDE of choice is the tightly integrated Netbeans 7.0 Beta or
6.9.1
GlassFish JEE6 Functionality
- Java Persistence 2.0 (JSR 317) - with patch
- CDI (Contexts and Dependency Injection) (JSR 299)
- DI (Dependency Injection) for Java (JSR 330)
- JSP 2.2 / Servlet 3.0 which includes @WebServlet
- Bean Validation (JSR 303)
- JAX-RS (RESTful Web Services) 1.1 (JSR 311)
- JAX-WS 2.2
- JSF (Java Server Faces) 2.0 (JSR 314)
- EJB (Enterprise Java Beans) 3.1 (JSR 318)
- Web Profile
- Including EJB Lite
- JCA 1.6
JBoss 6
JBoss JEE6 Functionality
Use Cases
UC1: Request unit of work
UC2: Post completed unit of work
Variant Use Cases
UC101: Communication Errors
UC101.1: RMI Host not available
UC101.1: RMI Bean not available
UC101.1: RMI Host busy
UC102: Handle discarded unit of work
Design
DI 1: Distributed Communication Strategy
- How are we going to link the distributed clients? Are we linking the one-to-many or many-to-many where all clients communicate with each other (which would necessitate multiple EE servers).
- 1) Multiple SE clients linked to multiple SE clients - non EE
- 2) Multiple EE clients linked to multiple SE clients - overhead
- 3) Multiple SE clients linked to multiple EE clients - possible
- 4) Multiple EE clients linked to multiple EE clients - complex
- 5) Multiple SE clients linked to single SE server - non EE
- 6) Multiple SE clients linked to single EE server - in use
- This model is the most promising and offers the least overhead. The SE clients will get and post work packets. If any user or admin needs to check the data they can do so via a browser based interface to the server.
- 7) Multiple EE clients linked to single SE server - invalid
- 8) Multiple EE clients linked to single EE server - possible
DI 2: Module Separation
- All code should be separated by functionality
- Model layer: JPA persistence Entitities/MappedSuperclasses/Embeddables should be in a separate model jar (with no persistence.xml)
- The model layer ideally has 2 jars (one with entity interfaces), the other with the actual entities and their possible mapped superclasses and embeddables.
- Business layer: The business objects (Stateless Session Beans) should be in a separate ejb jar and their interfaces (only) need to exported to clients (not the SSB implementation class). Why? because clients will only be interacting with the instrumented $proxy of the session bean - not the bean itself (which is a field of the server proxy)
- The business layer ideally has 2 jars (one with the business interface classes) and one with the business implementation classes.
- Presentation layer: The JSF managed and backing beans should be separate from both the model (entities) and the implementation (session beans) - these are delegates of the controller servlet (FacesServlet) - which implements the FrontController design pattern.
- Model layer: JPA persistence Entitities/MappedSuperclasses/Embeddables should be in a separate model jar (with no persistence.xml)
DI 3: Remote RMI/EJB Communication type
Remote Session Beans on WebLogic 10.3.4.0
Remote Session Beans on GlassFish 3.1
DI 4: Type of client/server setup
- 1) multiple SE clients communicate to a single EE server
- 2) multiple EE clients communicate to a single EE server
Decision DI4:
- We will be using 1) and only run a single EE server with multiple SE clients
DI 5: Limitations of BigInteger translation to BIGINT Database DataType
- The core of this application is the use of BigInteger Math package library which allows us to use arbitrary length integers during scalar computation. The underlying implementation of BigInteger is not the native long 64-bit datatype which would cause overflow. The ArrayList is used to represent the BigInteger digits.
- There is an issue that occurs when an BigInteger is persisted to a database. Depending on the database (in this case Derby XA) and the JPA persistence provider (in this case EclipseLink - but we tested Hibernate as well) - the BigInteger will get truncated into a fixed size numeric field.
Results DI5:
- If we use JPA out of the box to persist a BigInteger that is larger than 64 bits like the maximum value for collatz path #88 with start 1,980,976,057,694,848,447 @61 bits and maximum 64,024,667,322,193,133,530,165,877,294,264,738,020 @125 bits - found by Tomás Oliveira e Silva and verified by Eric Roosendaal (which just happens to be the first maximum where the max bits is more than twice the start bits).
public static final BigInteger COLLATZ88 = BigInteger.valueOf(1980976057694848447L);
- Client Logs:
C:\_experiment\org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.CollatzSE\bin>c:\jdk1.6.0\bin\java -cp .;../resource/wlfullclient.jar org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.presentation.SEClient xps435
_collatz: Context for xps435 : javax.naming.InitialContext@199f91c
_collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/563])/563
_collatz: Narrowed Session Bean: ClusterableRemoteRef(-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/563])/563
_collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@454( id: 454) ID#454 1980976057694848448-1980976057694913983 from: xps435
_collatz: Proc cores: 2
_collatz: Interval: 65535
_collatz: Range: 1980976057694848448 to: 1980976057694913983
PM,65535,0,1980976057694848448,441 ,990488028847424224 ,15 ,
PM,65535,0,1980976057694848449,472 ,5942928173084545348 ,15 ,
PM,65535,0,1980976057694848450,578 ,18072027346986144304 ,31 2^63+,8848655310131368497
M,65535,0,1980976057694848462,578 ,19038843624808448404 ,31 2^63+,9815471587953672597
M,65535,0,1980976057694848463,578 ,20057382584160340696 ,47 2^63+,10834010547305564889
M,65535,0,1980976057694848478,578 ,28558265437212672832 ,47 2^63+,19334893400357897025
M,65535,0,1980976057694848479,578 ,30086073876240511288 ,47 2^63+,20862701839385735481
M,65535,0,1980976057694848487,578 ,274468915332352071232 ,62 2^63+,265245543295497295425
M,65535,0,1980976057694848671,578 ,564018617557005468928 ,78 2^63+,554795245520150693121
P,65535,0,1980976057694848795,653 ,385536583402371144736 ,109 2^63+,376313211365516368929
M,65535,0,1980976057694849106,653 ,594192453064170502480 ,140 2^63+,584969081027315726673
M,65535,0,1980976057694849199,653 ,1042124162902524644920 ,156 2^63+,1032900790865669869113
P,65535,0,1980976057694849826,808 ,9914389761744244528 ,234 2^63+,691017724889468721
M,65535,0,1980976057694849980,808 ,2967611385765393620872 ,265 2^63+,2958388013728538845065
M,65535,0,1980976057694850687,808 ,3008099293637365553848 ,344 2^63+,2998875921600510778041
M,65535,0,1980976057694850913,808 ,4512148940456048849092 ,375 2^63+,4502925568419194073285
M,65535,0,1980976057694851180,808 ,11421377005529375204776 ,406 2^63+,11412153633492520428969
M,65535,0,1980976057694854027,808 ,30457005348078377627776 ,703 2^63+,30447781976041522851969
M,65535,0,1980976057694870015,808 ,85563713241241454980420 ,2375 2^63+,85554489869204600204613
P,65535,0,1980976057694880475,883 ,1145817468019535170408 ,3500 2^63+,1136594095982680394601
P,65535,0,1980976057694891964,958 ,146548710408170692240 ,4734 2^63+,137325338371315916433
javax.ejb.EJBException: BEA1-040954FF03873057A4BD: Local Exception Stack:
Exception [EclipseLink-4002] (Eclipse Persistence Services - 2.1.2.v20101206-r8635): org.eclipse.persistence.exceptions.DatabaseException
Internal Exception: java.sql.SQLDataException: The resulting value is outside the range for the data type BIGINT.
Error Code: -1
Call: UPDATE PARAMETERS SET MAXPATH = ?, MAXVALUE = ?, NEXTNUMBERTOSEARCH = ?, VERSION = ? WHERE ((ID = ?) AND (VERSION = ?))
bind => [958, 85563713241241454980420, 1980976057694913983, 2, 451, 1]
Query: UpdateObjectQuery(org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.Parameters@451( id: 451))
at org.eclipse.persistence.exceptions.DatabaseException.sqlException(DatabaseException.java:324)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.databaseaccess.DatabaseAccessor.executeDirectNoSelect(DatabaseAccessor.java:797)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.databaseaccess.DatabaseAccessor.executeNoSelect(DatabaseAccessor.java:863)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.databaseaccess.DatabaseAccessor.basicExecuteCall(DatabaseAccessor.java:583)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.databaseaccess.DatabaseAccessor.executeCall(DatabaseAccessor.java:526)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.AbstractSession.executeCall(AbstractSession.java:980)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.IsolatedClientSession.executeCall(IsolatedClientSession.java:131)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.queries.DatasourceCallQueryMechanism.executeCall(DatasourceCallQueryMechanism.java:206)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.queries.DatasourceCallQueryMechanism.executeCall
(DatasourceCallQueryMechanism.java:192)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.queries.DatasourceCallQueryMechanism.updateObject(DatasourceCallQueryMechanism.java:747)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.queries.StatementQueryMechanism.updateObject(StatementQueryMechanism.java:430)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.queries.DatabaseQueryMechanism.updateObjectForWriteWithChangeSet(DatabaseQueryMechanism.java:1144)
at org.eclipse.persistence.queries.UpdateObjectQuery.executeCommitWithChangeSet(UpdateObjectQuery.java:84)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.queries.DatabaseQueryMechanism.executeWriteWithChangeSet(DatabaseQueryMechanism.java:290)
at org.eclipse.persistence.queries.WriteObjectQuery.executeDatabaseQuery(WriteObjectQuery.java:58)
at org.eclipse.persistence.queries.DatabaseQuery.execute(DatabaseQuery.java:740)
at org.eclipse.persistence.queries.DatabaseQuery.executeInUnitOfWork(DatabaseQuery.java:643)
at org.eclipse.persistence.queries.ObjectLevelModifyQuery.executeInUnitOfWorkObjectLevelModifyQuery(ObjectLevelModifyQuery.java:108)
at org.eclipse.persistence.queries.ObjectLevelModifyQuery.executeInUnitOfWork(ObjectLevelModifyQuery.java:85)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.UnitOfWorkImpl.internalExecuteQuery(UnitOfWorkImpl.java:2908)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.AbstractSession.executeQuery(AbstractSession.java:1291)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.AbstractSession.executeQuery(AbstractSession.java:1273)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.AbstractSession.executeQuery(AbstractSession.java:1233)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.CommitManager.commitChangedObjectsForClassWithChangeSet(CommitManager.java:265)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.CommitManager.commitAllObjectsWithChangeSet(CommitManager.java:128)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.AbstractSession.writeAllObjectsWithChangeSet(AbstractSession.java:3348)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.UnitOfWorkImpl.commitToDatabase(UnitOfWorkImpl.java:1422)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.commitToDatabase(RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.java:610)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.UnitOfWorkImpl.commitToDatabaseWithChangeSet(UnitOfWorkImpl.java:1527)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.UnitOfWorkImpl.issueSQLbeforeCompletion(UnitOfWorkImpl.java:3181)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.issueSQLbeforeCompletion(RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.java:332)
at org.eclipse.persistence.transaction.AbstractSynchronizationListener.beforeCompletion(AbstractSynchronizationListener.java:157)
at org.eclipse.persistence.transaction.JTASynchronizationListener.beforeCompletion(JTASynchronizationListener.java:68)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerSCInfo.doBeforeCompletion(ServerSCInfo.java:1239)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerSCInfo.callBeforeCompletions(ServerSCInfo.java:1214)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerSCInfo.startPrePrepareAndChain(ServerSCInfo.java:116)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.localPrePrepareAndChain(ServerTransactionImpl.java:1316)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.globalPrePrepare(ServerTransactionImpl.java:2132)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.internalCommit(ServerTransactionImpl.java:272)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.commit(ServerTransactionImpl.java:239)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.BaseRemoteObject.postInvoke1(BaseRemoteObject.java:625)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.StatelessRemoteObject.postInvoke1(StatelessRemoteObject.java:49)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.BaseRemoteObject.__WL_postInvokeTxRetry(BaseRemoteObject.java:444)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.SessionRemoteMethodInvoker.invoke(SessionRemoteMethodInvoker.java:53)
at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacade_of6sps_CollatzFacadeRemoteImpl.postUnitOfWork(Unknown Source)
at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacade_of6sps_CollatzFacadeRemoteImpl_WLSkel.invoke(Unknown Source)
at weblogic.rmi.internal.BasicServerRef.invoke(BasicServerRef.java:667)
at weblogic.rmi.cluster.ClusterableServerRef.invoke(ClusterableServerRef.java:230)
at weblogic.rmi.internal.BasicServerRef$1.run(BasicServerRef.java:522)
at weblogic.security.acl.internal.AuthenticatedSubject.doAs(AuthenticatedSubject.java:363)
at weblogic.security.service.SecurityManager.runAs(SecurityManager.java:146)
at weblogic.rmi.internal.BasicServerRef.handleRequest(BasicServerRef.java:518)
at weblogic.rmi.internal.wls.WLSExecuteRequest.run(WLSExecuteRequest.java:118)
at weblogic.work.ExecuteThread.execute(ExecuteThread.java:207)
at weblogic.work.ExecuteThread.run(ExecuteThread.java:176)
Caused by: java.sql.SQLDataException: The resulting value is outside the range for the data type BIGINT.
at org.apache.derby.client.am.SQLExceptionFactory40.getSQLException(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.am.SqlException.getSQLException(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.am.PreparedStatement.executeUpdate(Unknown Source)
at weblogic.jdbc.wrapper.PreparedStatement.executeUpdate(PreparedStatement.java:172)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.databaseaccess.DatabaseAccessor.executeDirectNoSelect(DatabaseAccessor.java:788)
... 53 more
Caused by: org.apache.derby.client.am.SqlException: The resulting value is outside the range for the data type BIGINT.
at org.apache.derby.client.am.Statement.completeExecute(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.net.NetStatementReply.parseEXCSQLSTTreply(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.net.NetStatementReply.readExecute(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.net.StatementReply.readExecute(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.net.NetPreparedStatement.readExecute_(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.am.PreparedStatement.readExecute(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.am.PreparedStatement.flowExecute(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.am.PreparedStatement.executeUpdateX(Unknown Source)
... 56 more
; nested exception is:
Exception [EclipseLink-4002] (Eclipse Persistence Services - 2.1.2.v20101206-r8635): org.eclipse.persistence.exceptions.DatabaseException
- Server Logs
[EL Fine]: 2011-02-10 16:29:58.134--ClientSession(14259188)--Connection(9575331)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '7' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--UPDATE PARAMETERS SET MAXPATH = ?, MAXVALUE = ?, NEXTNUMBERTOSEARCH = ?, VERSION = ? WHERE ((ID = ?) AND (VERSION = ?)) bind => [958, 85563713241241454980420, 1980976057694913983, 2, 451, 1] [EL Fine]: 2011-02-10 16:29:58.149--ClientSession(14259188)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '7' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--VALUES(1) [EL Warning]: 2011-02-10 16:29:58.149--UnitOfWork(10050911)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '7' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--Local Exception Stack: Exception [EclipseLink-4002] (Eclipse Persistence Services - 2.1.2.v20101206-r8635): org.eclipse.persistence.exceptions.DatabaseException Internal Exception: java.sql.SQLDataException: The resulting value is outside the range for the data type BIGINT. Error Code: -1 Call: UPDATE PARAMETERS SET MAXPATH = ?, MAXVALUE = ?, NEXTNUMBERTOSEARCH = ?, VERSION = ? WHERE ((ID = ?) AND (VERSION = ?)) bind => [958, 85563713241241454980420, 1980976057694913983, 2, 451, 1] Query: UpdateObjectQuery(org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.Parameters@451( id: 451)) at org.eclipse.persistence.exceptions.DatabaseException.sqlException(DatabaseException.java:324) at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.databaseaccess.DatabaseAccessor.executeDirectNoSelect(DatabaseAccessor.java:797)
- Hibernate JPA logs
INFO: New max value: 1414236446719942480
INFO: Hibernate: update Parameters set bestIterationsPerSecond=?, globalDuration=?, globalStartTimestamp=?, maxPath=?, maxValue=?, nextNumberToSearch=?, partitionLength=?, version=? where id=? and version=?
WARNING: SQL Error: -1, SQLState: 22003
SEVERE: The resulting value is outside the range for the data type DECIMAL/NUMERIC(19,2).
SEVERE: Could not synchronize database state with session
org.hibernate.exception.DataException: could not update: [org.dataparallel.collatz.business.Parameters#32768]
at org.hibernate.exception.SQLStateConverter.convert(SQLStateConverter.java:77)
at org.hibernate.exception.JDBCExceptionHelper.convert(JDBCExceptionHelper.java:43)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.update(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2425)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.updateOrInsert(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2307)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.update(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2607)
at org.hibernate.action.EntityUpdateAction.execute(EntityUpdateAction.java:92)
at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.execute(ActionQueue.java:250)
at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:234)
at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:142)
at org.hibernate.event.def.AbstractFlushingEventListener.performExecutions(AbstractFlushingEventListener.java:298)
at org.hibernate.event.def.DefaultFlushEventListener.onFlush(DefaultFlushEventListener.java:27)
at org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl.flush(SessionImpl.java:1000)
at org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl.managedFlush(SessionImpl.java:338)
at org.hibernate.ejb.AbstractEntityManagerImpl$1.beforeCompletion(AbstractEntityManagerImpl.java:523)
at com.sun.enterprise.transaction.JavaEETransactionImpl.commit(JavaEETransactionImpl.java:412)
at com.sun.enterprise.transaction.JavaEETransactionManagerSimplified.commit(JavaEETransactionManagerSimplified.java:837)
at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.completeNewTx(BaseContainer.java:5040)
at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvokeTx(BaseContainer.java:4805)
at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvoke(BaseContainer.java:2004)
at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvoke(BaseContainer.java:1955)
at com.sun.ejb.containers.EJBObjectInvocationHandler.invoke(EJBObjectInvocationHandler.java:208)
at com.sun.ejb.containers.EJBObjectInvocationHandlerDelegate.invoke(EJBObjectInvocationHandlerDelegate.java:75)
at $Proxy199.postUnitOfWork(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.presentation.rmi.ReflectiveTie.dispatchToMethod(ReflectiveTie.java:146)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.presentation.rmi.ReflectiveTie._invoke(ReflectiveTie.java:176)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaServerRequestDispatcherImpl.dispatchToServant(CorbaServerRequestDispatcherImpl.java:682)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaServerRequestDispatcherImpl.dispatch(CorbaServerRequestDispatcherImpl.java:216)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.handleRequestRequest(CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.java:1841)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.handleRequest(CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.java:1695)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.handleInput(CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.java:1078)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.giopmsgheaders.RequestMessage_1_2.callback(RequestMessage_1_2.java:221)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.handleRequest(CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.java:797)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.dispatch(CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.java:561)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.protocol.CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.doWork(CorbaMessageMediatorImpl.java:2558)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.orbutil.threadpool.ThreadPoolImpl$WorkerThread.performWork(ThreadPoolImpl.java:492)
at com.sun.corba.ee.impl.orbutil.threadpool.ThreadPoolImpl$WorkerThread.run(ThreadPoolImpl.java:528)
Caused by: java.sql.SQLDataException: The resulting value is outside the range for the data type DECIMAL/NUMERIC(19,2).
at org.apache.derby.client.am.SQLExceptionFactory40.getSQLException(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.am.SqlException.getSQLException(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.derby.client.am.PreparedStatement.executeUpdate(Unknown Source)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.update(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2407)
... 37 more
Caused by: org.apache.derby.client.am.SqlException: The resulting value is outside the range for the data type DECIMAL/NUMERIC(19,2).
Analysis DI5:
- I suspect that it would be simplest to just convert the BigInteger to a string (VARCHAR2) and convert back when reading from the database. There may be a more efficient algorithm that involves partitioning or variable length scalar fields as well.
- The reality is that the DDL generation between EclipseLink and Hibernate are different. DDL generation in general should not be used for production. It would be better to fine tune the table creation myself.
- The DDL generation should pick up the column length annotation attribute though
@Entity public class Parameters implements Serializable { @Column(name="maxValue", length=512) private BigInteger maxValue;
- I will also be switching to a more production capable database like MySQL instead of Derby.
- See Derby documentation on BIGINT http://db.apache.org/derby/manuals/reference/sqlj126.html
- See http://download.oracle.com/javaee/5/api/javax/persistence/Column.html#precision%28%29
TypeConverter
- Use of a TypeConverter (not an ObjectTypeConverter) may be one option. We would map the BigInteger type to a String which could be stored in a column that is larger than the current 128 bit (16 byte) lenght of NUMERIC. This would eventually hit a maximum of 1-2K, where if we represented each bit as a 0 or 1 byte we could at least represent 1024 bits with this strategy.
@Entity @TypeConverters({@TypeConverter(name="BigIntegerToString",dataType=String.class,objectType=BigInteger.class)}) public class Parameters implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -1979843739878183696L; @Column(name="maxValue", nullable=false, length=512) @Convert("BigIntegerToString") private BigInteger maxValue;
DI 6: EAR Redeploy should not affect remote clients
- If the server application is temporarily down due to a redeploy - it should not affect clients.
- The fix is to catch the NoSuchObjectException and perform a series of timed re-posts to the session bean.
Analysis DI6:
- Error on the remote client is as follows when the server app is hot-redeployed (without clustering) at the same time as the client is pushing a data post to the server.
java.rmi.NoSuchObjectException: The object identified by: '312' could not be found. Either it was has not been exported or it has been collected by the distributed garbage collector. at weblogic.rjvm.ResponseImpl.unmarshalReturn(ResponseImpl.java:234) at weblogic.rmi.cluster.ClusterableRemoteRef.invoke(ClusterableRemoteRef.java:348) at weblogic.rmi.cluster.ClusterableRemoteRef.invoke(ClusterableRemoteRef.java:259) at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacade_of6sps_CollatzFacadeRemoteImpl_1034_WLStub.postUnitOfWork(Unknown Source) at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor5.invoke(Unknown Source) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597) at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.RemoteBusinessIntfProxy.invoke(RemoteBusinessIntfProxy.java:85) at $Proxy0.postUnitOfWork(Unknown Source) at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.presentation.SEClient.processUnitOfWork(SEClient.java:216)
- Solved by a finite number of repeated lookup operations - without a wait
- Action: A redeploy with an interval change from 10 to 11 bits
_collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/314])/314 _collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@8944( id: 8944) ID#8944 15125507-15126530 from: xps435 _collatz: Proc cores: 2 _collatz: Interval: 1023 _collatz: Range: 15125507 to: 15126530 While trying to lookup 'ejb.CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote' didn't find subcontext 'CollatzFacade#org'. Resolved 'ejb' _collatz: retry session bean lookup - possible redeploy in progress on central server: 0 While trying to lookup 'ejb.CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote' didn't find subcontext 'CollatzFacade#org'. Resolved 'ejb' _collatz: retry session bean lookup - possible redeploy in progress on central server: 1 While trying to lookup 'ejb.CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote' didn't find subcontext 'CollatzFacade#org'. Resolved 'ejb' .... _collatz: retry session bean lookup - possible redeploy in progress on central server: 32 While trying to lookup 'ejb.CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote' didn't find subcontext 'example'. Resolved 'ejb.CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence' _collatz: retry session bean lookup - possible redeploy in progress on central server: 33 _collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/322])/322 _collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@8953( id: 8953) ID#8953 15126531-15128578 from: xps435 _collatz: Proc cores: 2 _collatz: Interval: 2047 _collatz: Range: 15126531 to: 15128578 _collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/322])/322
- With a 1000ms wait
- Action: A redeploy with an interval change from 11 to 12 bits
_collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@10408( id: 10408) ID#10408 16117763-16119810 from: xps435 _collatz: Proc cores: 2 _collatz: Interval: 2047 _collatz: Range: 16117763 to: 16119810 While trying to lookup 'ejb.CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote' didn't find subcontext 'CollatzFacade#org'. Resolved 'ejb' _collatz: retry session bean lookup - possible redeploy in progress on central server: 0 _collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-2557087906773732497S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/331])/331 _collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@10453( id: 10453) ID#10453 16119811-16123906 from: xps435 _collatz: Proc cores: 2 _collatz: Interval: 4095
DI 7: Strategy for handling expected OptimisticLockException during high throughput concurrent traffic
- If I reduce the interval for each UnitOfWork from a comfortable 16 to 22 bits down to 8 bits (256 searches) this increases requests to the server to about 5 per second. If we run more than one client we almost immediately get an OptimisticLockException when one of the clients tries to overwrite shared memory (in the Parameters singleton entity). We expect this because of the concurrent nature of our distributed application. We will do a read, evaluate the change compared to our unsaved changes and retry if needed. We may need to do this a couple times - as the window between this manual 2-phase commit operation still has a small window of unmanaged concurrency between the read and write operations.
Client Log Exception
_collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(1326838513503838804S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [1326838513503838804S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/322])/322
javax.ejb.EJBException: BEA1-21603518C2783057A4BD: javax.persistence.OptimisticLockException: Exception [EclipseLink-5006] (Eclipse Persistence Services - 2.3.0.qualifier): org.eclipse.persistence.exceptions.OptimisticLockException
Exception Description: The object [org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.Parameters@2( id: 2)] cannot be updated because it has changed or been deleted since it was last read.
Class> org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.Parameters Primary Key> 2
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.commitToDatabase(RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.java:623)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.UnitOfWorkImpl.commitToDatabaseWithChangeSet(UnitOfWorkImpl.java:1486)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.UnitOfWorkImpl.issueSQLbeforeCompletion(UnitOfWorkImpl.java:3109)
at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.sessions.RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.issueSQLbeforeCompletion(RepeatableWriteUnitOfWork.java:331)
at org.eclipse.persistence.transaction.AbstractSynchronizationListener.beforeCompletion(AbstractSynchronizationListener.java:157)
at org.eclipse.persistence.transaction.JTASynchronizationListener.beforeCompletion(JTASynchronizationListener.java:68)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerSCInfo.doBeforeCompletion(ServerSCInfo.java:1239)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerSCInfo.callBeforeCompletions(ServerSCInfo.java:1214)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerSCInfo.startPrePrepareAndChain(ServerSCInfo.java:116)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.localPrePrepareAndChain(ServerTransactionImpl.java:1316)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.globalPrePrepare(ServerTransactionImpl.java:2132)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.internalCommit(ServerTransactionImpl.java:272)
at weblogic.transaction.internal.ServerTransactionImpl.commit(ServerTransactionImpl.java:239)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.BaseRemoteObject.postInvoke1(BaseRemoteObject.java:625)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.StatelessRemoteObject.postInvoke1(StatelessRemoteObject.java:49)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.BaseRemoteObject.__WL_postInvokeTxRetry(BaseRemoteObject.java:444)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.SessionRemoteMethodInvoker.invoke(SessionRemoteMethodInvoker.java:53)
at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacade_of6sps_CollatzFacadeRemoteImpl.postUnitOfWork(Unknown Source)
at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacade_of6sps_CollatzFacadeRemoteImpl_WLSkel.invoke(Unknown Source)
at weblogic.rmi.internal.BasicServerRef.invoke(BasicServerRef.java:667)
at weblogic.rmi.cluster.ClusterableServerRef.invoke(ClusterableServerRef.java:230)
DI7: Analysis
- It would be better that we handle this on the server in the session bean. We can then leverage this single solution regardless of what client we use (RMI/EJB, WebService, JAX-RS).
- We will be using a @TypeConverter which is provided beyond the JPA specification using native EclipseLink ORM.
DI 8: Variable Partition between Different Client Capabilities
- We will attempt to use a homogeneos set of distributed processors, however we will need to accomidate processing nodes with a variance of capabilities.
- The collatz problem is well suited to parallization because of the relative independence of the calculations on individual sequences. However, if we wish to optimize the algorith so we can reduce the calculation times by an order of magnitude - then we will need to use the symmetry of previos calculations.
- Example: a large proportion of numbers greater than 27 will contain the 27:110:9232 record (27=start, 110=sequence path lenght, 9232=maximum value). One optimation would be do abort sequences that would not reach a max path or max value if their current path:max was merged with 27:110:9292 if they hit 27 at any time in their sequence.
- Therefore, we will need an evaluation step for new nodes so that we can distribute the appropriate # of UnitOfWork packets so that all the processors work the same amount of time.
- Q)Why manage calculation time?
- A)
DI9: Force binary compatibility with Model changes via the serialVersionUID
javax.ejb.EJBException: ; nested exception is:
java.rmi.UnmarshalException: Incoming message header or abbreviation processing failed ; nested exception is:
java.io.InvalidClassException: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.ActiveProcessor; local class incompatible:
stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 6472979075266547411, local class serialVersionUID = 1; nested exception is: java.rmi.UnmarshalException:
Incoming message header or abbreviation processing failed ; nested exception is:
java.io.InvalidClassException: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.ActiveProcessor; local class incompatible:
stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 6472979075266547411, local class serialVersionUID = 1
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.RemoteBusinessIntfProxy.unwrapRemoteException(RemoteBusinessIntfProxy.java:121)
at weblogic.ejb.container.internal.RemoteBusinessIntfProxy.invoke(RemoteBusinessIntfProxy.java:96)
at $Proxy0.requestUnitOfWork(Unknown Source)
at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.presentation.SEClient.processUnitOfWork(SEClient.java:214)
at org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.presentation.SEClient.main(SEClient.java:275)
Caused by: java.rmi.UnmarshalException: Incoming message header or abbreviation processing failed ; nested exception is:
java.io.InvalidClassException: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.ActiveProcessor; local class incompatible:
stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 6472979075266547411, local class serialVersionUID = 1
at weblogic.rjvm.MsgAbbrevJVMConnection.dispatch(MsgAbbrevJVMConnection.java:507)
at weblogic.rjvm.t3.MuxableSocketT3.dispatch(MuxableSocketT3.java:330)
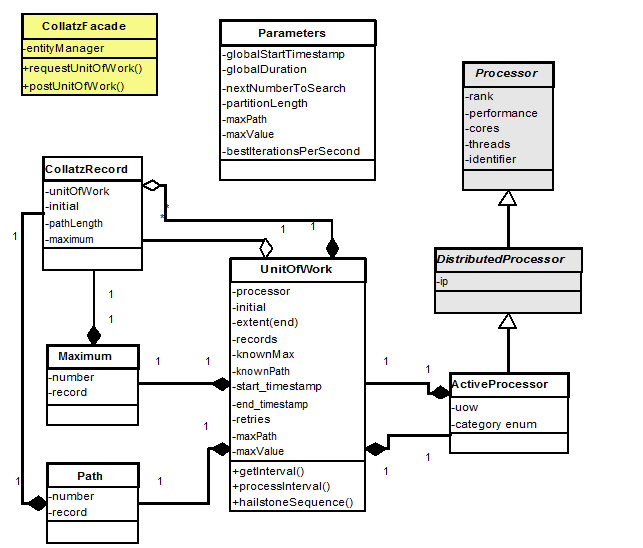
Data Model
- The following UML class diagram details the data model for the business objects. We will be using JPA entities and mappedsuperclass artifacts.
Implementation
JPA Model
- This model is shared among the EJB container, the SE and WAR clients
UnitOfWork
- This entity follows the UnitOfWork design pattern, it encapsulates state and operations on the model
@Entity public class UnitOfWork implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; @OneToMany(mappedBy="unitOfWork", fetch=FetchType.EAGER) // record are an ordered list private List<CollatzRecord> records; @OneToOne private ActiveProcessor processor; private BigInteger initial; private BigInteger extent; @OneToOne private Maximum knownMax; @OneToOne private Path knownPath; private Long startTimestamp; private Long endTimestamp; private Integer retries; // we could get both of these by querying on the max amd path for 2 entries in the records field private BigInteger maxPath; private BigInteger maxValue; @Version private Long version;
ActiveProcessor
@Entity public class ActiveProcessor extends DistributedProcessor implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 6472979075266547411L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; @OneToOne private UnitOfWork activeUnitOfWork; private int category; @Version private Long version;
CollatzRecord
@Entity public class CollatzRecord implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 4023830926240714638L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; @ManyToOne(fetch=FetchType.EAGER) private UnitOfWork unitOfWork; private BigInteger initial; private BigInteger pathLength; private BigInteger maximum; @Version private Long version;
Maximum
- This entity represents the CollatzRecord entities that are maximum value instances.
- Example: 27 has a maximum value of 9232.
@Entity public class Maximum implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -1635723758025553884L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; @OneToOne // needs to be bidirectional private CollatzRecord record; private Long identifier; @Version private Long version;
Path
- This entity represents the CollatzRecord entities that are maximum path instances.
- Example: 27 has a maximum path of 110 iterations.
@Entity public class Path implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 268842373670007801L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; @OneToOne private CollatzRecord record; private Long identifier; @Version private Long version;
Parameters
- This entity represents the persistent shared memory state of the distributed application.
@Entity //@TypeConverters({@TypeConverter(name="BigIntegerToString",dataType=String.class,objectType=BigInteger.class)}) public class Parameters implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -1979843739878183696L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; private BigInteger nextNumberToSearch; private Long globalStartTimestamp; @Column(name="globalduration", length=512) private BigInteger globalDuration; @Column(name="bestIterationsPerSecond", length=512) private BigInteger bestIterationsPerSecond; @Column(name="partitionLength", length=512) private BigInteger partitionLength; @Column(name="maxPath", length=512) private BigInteger maxPath; @Column(name="maxValue", nullable=false, length=512) //@Convert("BigIntegerToString") private BigInteger maxValue; @Version private Long version;
EE Server
persistence.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"> <persistence-unit name="CollatzGF-ejbPU" transaction-type="JTA"> <provider>org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider</provider> <!--provider>org.hibernate.ejb.HibernatePersistence</provider--> <jta-data-source>jdbc/Collatz2</jta-data-source> <class>org.dataparallel.collatz.business.ActiveProcessor</class> <class>org.dataparallel.collatz.business.CollatzRecord</class> <class>org.dataparallel.collatz.business.Maximum</class> <class>org.dataparallel.collatz.business.Parameters</class> <class>org.dataparallel.collatz.business.Path</class> <class>org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork</class> <exclude-unlisted-classes>false</exclude-unlisted-classes> <properties> <!-- EclipseLink --> <property name="eclipselink.target-server" value="SunAS9"/> <property name="eclipselink.target-database" value="Derby"/> <!-- turn off DDL generation after the model is stable --> <property name="eclipselink.ddl-generation" value="drop-and-create-tables"/> <property name="eclipselink.ddl-generation.output-mode" value="database"/> <property name="eclipselink.logging.level" value="FINEST"/> <!-- enable SQL parameter binding visibility logging to override ER 329852 --> <property name="eclipselink.logging.parameters" value="true"/> <!-- http://netbeans.org/kb/docs/web/hibernate-jpa.html --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true"/> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create-drop"/> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
SE Client
- The SE client will need a reference to the EE libraries of the server, here are the locations of the relevant jars. In the case of GlassFish - the gf-client.jar' is a manifest only jar that references the other EE jars by relative paths (so do not move it). In the case of WebLogic - the wlfullclient.jar library must be generated at design-time.
- GlassFish 3.0.x
- C:\opt\nbglassfish301\glassfish\modules\gf-client.jar
- GlassFish 3.1
- C:\opt\nbgf31b41\glassfish\lib\gf-client.jar
- WebLogic 10.3.4.0
- c:\jdk1.6.0\bin\java -cp .;../resource/wlfullclient.jar org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.presentation.SEClient gx660a t3://192.168.0.199:7001
- GlassFish 3.0.x
JNDI name for Remote Session Bean
- For a bean named
@Stateless(name="CollatzFacade",mappedName="ejb/CollatzFacade") // mappedName for ejb3.0 only
- The client must resolve the following name in GlassFish.
private static final String SESSION_BEAN_REMOTE_NAME = "java:global/CollatzGF/CollatzGF-ejb/CollatzFacade!org.dataparallel.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote";
- The client must resolve the following name in WebLogic.
private static final String SESSION_BEAN_REMOTE_NAME = "ejb/CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote";
SE Client Classpath
JNDI InitialContext Setup for GlassFish
- The following line will setup the InitialContext properties properly for GlassFish when it is not run in the same JVM as GlassFish.
c:\jdk1.6.0-32b\bin\java -cp .;C:/opt/gf31b40/glassfish/lib/gf-client.jar;CollatzModel-jar.jar;CollatzGF-ejb.jar -Djava.naming.factory.initial=com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.CNCtxFactory -Dorg.omg.CORBA.ORBInitialHost=127.0.0.1 -Dorg.omg.CORBA.ORBInitialPort=3700 org.dataparallel.collatz.presentation.SEClient
JNDI InitialContext Setup for WebLogic
- The following line will setup the InitialContext properties properly for GlassFish when it is not run in the same JVM as GlassFish.
c:\jdk1.6.0\bin\java -cp .;../resource/wlfullclient.jar org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.presentation.SEClient
- We will fallback on the design-time code below if the JNDI parameters are not entered at runtime
public static String serverT3[] = {"t3://10.156.52.246:7001"}; private static final String CONTEXT_FACTORY_NAME = "weblogic.jndi.WLInitialContextFactory";
WebService Client
JMS Client
JAX-RS Client
Hardware
- There are 3 networks that I am simulating on (two at work, one at home) with a total of 23 cores available.
- W1: Production NOC off-grid subnet (7 threads total)
- One 4-core Q6600 server (with up to 3 threads for local clients)
- Four 1-core P630 clients (with up to 8 threads - but in practice I run the CPU's at 50% with a single thread)
- W2: Development NOC (3 threads total)
- One 2-core E8400 server (with up to 1 thread for local clients)
- One 2-core SunFire (near Corei7-920 performance) client (with 2 threads)
- H1: Development NOC (13 threads total)
- One 4-core Corei7-920 server (with up to 6 threads for local clients)
- Four 1-core P630 clients (with up to 8 threads - but in practice I run the CPU's at 50% with a single thread)
- One 2-core T4400 client (1 thread)
- One 2-core E8400 client (1 thread)
- One 1-core P520 client (1 thread)
- W1: Production NOC off-grid subnet (7 threads total)
- Here is a screencap of the H1 NOC with 13 threads on 8 physical machines.
Preliminary Performance Numbers
- From a 4 hour test on the H1 NOC above
Performance
- We need to set a baseline and test various simulations in 2 or more variables so that we get the optimum configuration before we start a large run that could last for months.
Performance Criteria
- The following criteria will be used to optimize the distributed performance of the application.
Multicore Usage
- All the current CPU's available have 1,2,3 or 4 cores. Some of them are hyperthreaded.
- Q) Do we really get N times performance gain if we use up all the hardware cores?
- A) If we look at a dual-core (non-HT) system we get a 76% speedup with a 12% drop in performance per core if both are used.
Analysis: Multicore
- 2 threads on a dual-core E8400 (100% cpu)
_collatz: threads,Interval,start,end: 2,8388607,687865859,696254466 _collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(1986630296164710704S:10...:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [1986630296164710704S:10...:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/314])/314 _collatz: results sent to server after 77720 ms _collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@87( id: 87) ID#87 654311427-662700034 from: gx660a _collatz: threads,Interval,start,end: 2,8388607,696254467,704643074 _collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(1986630296164710704S:10...:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [1986630296164710704S:10...:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/314])/314 _collatz: results sent to server after 78142 ms _collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@92( id: 92) ID#92 696254467-704643074 from: gx660b
- 1 thread on a dual-core E8400 (50% cpu)
_collatz: threads,Interval,start,end: 2,8388607,771751939,780140546 _collatz: Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(1986630296164710704S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [1986630296164710704S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/314])/314 _collatz: results sent to server after 68781 ms _collatz: process UnitOfWork: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@104( id: 104) ID#104 796917763-805306370from: gx660b
- We see a 12% drop of performance on both hardware cores if both are active. Howeve that also means a 76% increase in performance when both hardware cores are used.
Multithread Usage
- For each core above we may have hyperthreading available - it was available on the Pentium IV and again on the Corei7-9xx. The question is what is the optimum number of threads? I would expect that we need to determine how many soft cores the machine has (hard + hyperthreaded) and not use more than this number. This would be 2 for a single core P4-630, 2 for a dual core E8400 or T4400, 4 for a quad core Q6600 and 8 for a Corei7-920.
- The other question is do we really get a performance gain when using the hyperthreaded cores. Or if I use 2 threads on a single core P-630 or 8 threads on a Corei7-920 what is the performance gain? From initial experimentation it looks like we can get up to a 50% performance increase by using the HT cores. Use of the HT cores will slow down the hard cores as both share cache and ram. Therefore if the algorithm was kept in register memory we would be able to use the superscalar execution queues.
Local vs remote threads
- If I use 4 threads on a 4 core chip like the 920 or 4 single threads on 4 separate P630 machines - what kind of gain do I see?
Network Bandwidth
- Not an issue.
- We are using Gigabit ethernet. So far because of the low data transmission of our application I rarely see the network go above 1%.
Preliminary Performance Numbers
- There are 3 networks that I am simulating on (two at work, one at home) with a total of 23 cores available. The standard work packet at this point is 2^23 numbers - or 8,388,608. Processing these 8 million numbers takes a range of 55 to 330 seconds depending on the processor for numbers below 12 billion.
- The processing time for 23 bits for P4-630 class vintage pentium IV processors running the latest SUN 32-bit 1.6.0_23 JVM ranges from 110 to 230 seconds.
- The best processing time for the 64-bit SUN JVM (which although it has 4-5 times better Long scalar processing - does not help with BigInteger) is around 70 seconds.
- For some reason I get varying numbers for different machines running the same JVM on the same Chip with a variance of up to 50% that shouldn't be due to RAM/HD differences.
Testing
WebLogic 10.3.4.0 Server Logs
####<10-Feb-2011 12:42:25 o'clock PM VET> <Info> <EJB> <mfobrien-pc2> <AdminServer> <[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '5' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)'> <<WLS Kernel>> <> <> <1297357945922> <BEA-014022> <******** org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote is bound with JNDI name:ejb/CollatzFacade#org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote ********> ####<10-Feb-2011 12:42:25 o'clock PM VET> <Info> <EJB> <mfobrien-pc2> <AdminServer> <[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '5' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)'> <<WLS Kernel>> <> <> <1297357945922> <BEA-010009> <EJB Deployed EJB with JNDI name org_eclipse_persistence_example_distributed_CollatzEARorg_eclipse_persistence_example_distributed_CollatzEJB_jarCollatzFacade_Home.> ... [EL Fine]: 2011-02-10 14:07:31.718--ServerSession(23787511)--Connection(23714705)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '16' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--SELECT ID, CATEGORY, RANK, THREADS, PERFORMANCE, IDENT, CORES, VERSION, ACTIVEUNITOFWORK_ID FROM ACTIVEPROCESSOR WHERE (IDENT = ?) bind => [xps435] _collatz: requestUnitOfWork(2442133504-2443182080) [EL Finest]: 2011-02-10 14:07:31.718--UnitOfWork(16753671)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '16' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--PERSIST operation called on: org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=null]. [EL Finest]: 2011-02-10 14:07:31.718--UnitOfWork(16753671)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '16' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--assign sequence to the object (848 -> org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=null]) [EL Fine]: 2011-02-10 14:07:31.718--ClientSession(21885694)--Connection(9190088)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '16' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--INSERT INTO UNITOFWORK (ID, STARTTIMESTAMP, VERSION, MAXPATH, EXTENT, INITIAL, RETRIES, ENDTIMESTAMP, MAXVALUE, KNOWNMAX_ID, PROCESSOR_ID, KNOWNPATH_ID) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) bind => [848, 1297363051718, 1, 993, 2443182080, 2442133505, 0, null, 7125885122794452160, 846, 1, 847] Processing UOW: org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=848]
GlassFish 3.1 Server Logs
- The EE server is the same for all test cases below
Server Logs
INFO: GlassFish Server Open Source Edition 3.1-b41 (41) startup time : Felix (7,984ms), startup services(750ms), total(8,734ms)
INFO: EclipseLink, version: Eclipse Persistence Services - 2.2.0.v20110202-r8913
CONFIG: Connected: jdbc:derby://localhost:1527/collatz2
INFO: file:/C:/_Netbeans691Projects/CollatzGF/dist/gfdeploy/CollatzGF/CollatzGF-ejb_jar/_CollatzGF-ejbPU login successful
INFO: Portable JNDI names for EJB CollatzFacade : [java:global/CollatzGF/CollatzGF-ejb/CollatzFacade, java:global/CollatzGF/CollatzGF-ejb/CollatzFacade!org.dataparallel.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote]
INFO: Glassfish-specific (Non-portable) JNDI names for EJB CollatzFacade : [ejb/CollatzFacade, ejb/CollatzFacade#org.dataparallel.collatz.business.CollatzFacadeRemote]
...
FINER: client acquired: 16292112
FINER: TX binding to tx mgr, status=STATUS_ACTIVE
FINER: acquire unit of work: 30797517
...
INFO: Creating new org.dataparallel.collatz.business.ActiveProcessor[id=1]
FINE: INSERT INTO ACTIVEPROCESSOR (ID, CATEGORY, CORES, IDENT, PERFORMANCE, RANK, THREADS, VERSION, ACTIVEUNITOFWORK_ID) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
bind => [1, 0, null, xps435, null, null, 2, 1, null]
INFO: _collatz: requestUnitOfWork(2147483648-2148532224)
FINE: INSERT INTO UNITOFWORK (ID, ENDTIMESTAMP, EXTENT, INITIAL, MAXPATH, MAXVALUE, RETRIES, STARTTIMESTAMP, VERSION, KNOWNMAX_ID, KNOWNPATH_ID, PROCESSOR_ID) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
bind => [5, null, 2148532224, 2147483649, 1, 1, 0, 1297284064640, 1, 3, 4, 1]
FINE: INSERT INTO PARAMETERS (ID, BESTITERATIONSPERSECOND, GLOBALDURATION, GLOBALSTARTTIMESTAMP, MAXPATH, MAXVALUE, NEXTNUMBERTOSEARCH, PARTITIONLENGTH, VERSION) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
bind => [2, null, null, 1297284064640, 1, 1, 2148532224, 1048576, 1]
INFO: Processing UOW: org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=5]
FINER: client acquired: 15148865
...
FINEST: Connection released to connection pool [read].
INFO: New max path : 967
INFO: New max value: 6694105047793216
TC1: Remote Session Bean Lookup on GlassFish 3.1 from SE Client on Same JVM
- As you can see above, we let a single remote client run for a couple seconds so that it reported a completed UnitOfWork entity packet back to the session bean that holds the dependency injected persistence context on the server.
SE Client Logs
run: 9-Feb-2011 4:11:01 PM com.sun.enterprise.v3.server.CommonClassLoaderServiceImpl findDerbyClient Context for xps435 : javax.naming.InitialContext@18fd984 INFO: Cannot find javadb client jar file, derby jdbc driver will not be available by default. Remote Object: org.dataparallel.collatz.business._CollatzFacadeRemote_Wrapper@498cb673 Narrowed Session Bean: org.dataparallel.collatz.business._CollatzFacadeRemote_Wrapper@498cb673 UnitOfWork from: xps435 = org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=5] 2147483649-2148532224 Range: 2147483649 to: 2148532224 M,1048575,0,2148041982,693 ,6694105047793216 ,8666 , P,1048575,0,2148398424,967 ,966616035460 ,14359 , UnitOfWork from: xps435 = org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=8] 2148532225-2149580800 Range: 2148532225 to: 2149580800 BUILD STOPPED (total time: 27 seconds)
TC2:Remote Session Bean Lookup on GlassFish 3.1 from SE Client on Different JVM - Local Machine
SE Client Logs
- This naming error is all over the internet - it means that the JNDI bean name below was not found (this exact code without the InitialContext parameters work when run inside NetBeans).
- @Stateless(name="CollatzFacade",mappedName="ejb/CollatzFacade")
C:\_experiment\Collatz>c:\jdk1.6.0\bin\java -cp .;C:/opt/nbgf31b41/glassfish/lib/gf-client.jar;CollatzModel-jar.jar;CollatzGF-ejb.jar -Djava
.naming.factory.initial=com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.CNCtxFactory -Dorg.omg.CORBA.ORBInitialHost=127.0.0.1 -Dorg.omg.CORBA.ORBInitialPort=3700 o
rg.dataparallel.collatz.presentation.SEClient
Context for xps435 : javax.naming.InitialContext@122cdb6
javax.naming.NameNotFoundException [Root exception is org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.NotFound: IDL:omg.org/CosNaming/NamingContext/N
otFound:1.0]
at com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.ExceptionMapper.mapException(ExceptionMapper.java:44)
at com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.CNCtx.callResolve(CNCtx.java:485)
at com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.CNCtx.lookup(CNCtx.java:524)
at com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.CNCtx.lookup(CNCtx.java:502)
at javax.naming.InitialContext.lookup(InitialContext.java:392)
TC3:Remote Session Bean Lookup on GlassFish 3.1 from SE Client on Different JVM - Remote Machine
SE Client Logs
TC13: Remote Session Bean Lookup on WebLogic 10.3.4.0 from SE Client on Different JVM - Remote Machine
SE Client Logs
C:\_experiment\org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.CollatzSE\bin>c:\jdk1.6.0\bin\java -cp .;wlfullclient.jar org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.presentation.SEClient Context for xps435 : javax.naming.InitialContext@1b1aa65 Remote Object: ClusterableRemoteRef(-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/363])/363 Narrowed Session Bean: ClusterableRemoteRef(-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer [-6871653033103817620S:10.156.52.246:[7001,7001,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]:base_domain:AdminServer/363])/363 UnitOfWork from: xps435 = org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=5] 2147483649-2148532224 Range: 2147483649 to: 2148532224 M,1048575,0,2148041982,693 ,6694105047793216 ,9374 , P,1048575,0,2148398424,967 ,966616035460 ,15390 , UnitOfWork from: xps435 = org.dataparallel.collatz.business.UnitOfWork[id=8] 2148532225-2149580800
Results
EclipseLink 2.2 on GlassFish 3.1 within the same JVM in NetBeans 6.9.1
EclipseLink 2.2 on WebLogic 10.3.4.0 from either @Local or @Remote clients
- Scenario: 2 remote clients on a SunFire server against a E8400 based server
[EL Fine]: 2011-02-14 13:58:45.562--ClientSession(4065049)--Connection(14012120)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '16' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--UPDATE PARAMETERS SET NEXTNUMBERTOSEARCH = ?, VERSION = ? WHERE ((ID = ?) AND (VERSION = ?)) bind => [2868903938, 343, 4, 342] [EL Fine]: 2011-02-14 13:58:45.562--ServerSession(8921344)--Connection(5230969)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '16' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--SELECT ID, CATEGORY, CORES, IDENT, PERFORMANCE, RANK, THREADS, VERSION, ACTIVEUNITOFWORK_ID FROM ACTIVEPROCESSOR WHERE (IDENT = ?) bind => [sunVM1] _collatz: requestUnitOfWork(2868903938-2877292546) for processor org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.ActiveProcessor@89( id: 89) bind => [470, null, 2877292546, 2868903939, 1049, 7125885122794452160, 0, 1297708125562, 1, null, null, 89] _collatz: Processing UOW: org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.UnitOfWork@469( id: 469) from processor: sunVM2 bind => [2877292546, 344, 4, 343] [EL Fine]: 2011-02-14 13:59:02.5--ServerSession(8921344)--Connection(8995870)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '19' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--SELECT ID, CATEGORY, CORES, IDENT, PERFORMANCE, RANK, THREADS, VERSION, ACTIVEUNITOFWORK_ID FROM ACTIVEPROCESSOR WHERE (IDENT = ?) bind => [sunVM2] _collatz: requestUnitOfWork(2877292546-2885681154) for processor org.eclipse.persistence.example.distributed.collatz.model.ActiveProcessor@112( id: 112) [EL Fine]: 2011-02-14 13:59:02.5--ClientSession(10474054)--Connection(31369678)--Thread(Thread[[ACTIVE] ExecuteThread: '19' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)',5,Pooled Threads])--INSERT INTO UNITOFWORK (ID, ENDTIMESTAMP, EXTENT, INITIAL, MAXPATH, MAXVALUE, RETRIES, STARTTIMESTAMP, VERSION, KNOWNMAX_ID, KNOWNPATH_ID, PROCESSOR_ID) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) bind => [471, null, 2885681154, 2877292547, 1049, 7125885122794452160, 0, 1297708142500, 1, null, null, 112]
Status
- Document start on 09 Feb 2011 - estimated completion 5-15 days
Statistics
JOPS per Watt
- Since we have not implemented the core scalar integer processing in native C, SSE C or even GPU C the current "Java Operations (JOPS) per watt will suffice until we are able to state MIPS but not FLOPS.
- The W1 NOC consisting of 5 machines (without monitor) consumes 6.9A of 120V power = 828W(RMS) or 828VA at 50% CPU.
- The operations performed between 13:15 and 15:46 (151 min = 9060 sec) was (5662310402 - 1577058306 = 4,085,252,096).
- This distributed result is 450,900 JOPS / 6.9A = 545 JOPS/Watt
TODO
- According to http://jazoon.com/Portals/0/Content/slides/tu_a6_1630-1650_champenois.pdf the OEPE plugin supports EJB 3.1 @Singleton beans - however I was under the impression that this EJB 3.1 part and EJB Lite were not yet in WebLogic 10.3.4.0 - need to verify this by example
- Get the JNDI name working for remote session bean lookup from an SE client in another JVM for GlassFish (this is working for WebLogic). Currently I can only get the case where the SE client is run in the same JVM as the server to work (where we use the no-arg constructor of InitialContext())