Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EDT:EUnit Testing"
m (→JavaScript) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= EUnit Test Framework Overview<br> = | = EUnit Test Framework Overview<br> = | ||
| − | == What is EUnit? == | + | == What is EUnit? == |
EUnit stands for EGL Unit testing framework. It is a simple open source framework to write and run repeatable EGL tests. Its features include:<br> | EUnit stands for EGL Unit testing framework. It is a simple open source framework to write and run repeatable EGL tests. Its features include:<br> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
*Test case documentation <br> | *Test case documentation <br> | ||
| − | == How to write test cases using EUnit<br> | + | EUnit tests are written in EGL. You write the tests in a normal EGL project, then use the EUnit tooling to create a "test driver" for each target language you want to test in. The test driver is runnable code (a Java program or a JavaScript RUIHandler) that will execute the tests and create a report of their results.<br> |
| + | |||
| + | == How to write test cases using EUnit<br> == | ||
1. Create an EGL Project, for example: '''eunit.test'''<br> | 1. Create an EGL Project, for example: '''eunit.test'''<br> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
3. Open the library with the EGL Editor, and remove the automatically generated code.<br> | 3. Open the library with the EGL Editor, and remove the automatically generated code.<br> | ||
| − | 4. Type the variable declarations and functions (we treat each function as an EUnit test case) in the library | + | 4. Type the variable declarations and functions (we treat each function as an EUnit test case) in the library. Functions that perform a test should have the '''@Test''' annotation. For example:<br> |
<pre>package libs; | <pre>package libs; | ||
import org.eclipse.edt.eunit.runtime.LogResult; | import org.eclipse.edt.eunit.runtime.LogResult; | ||
| Line 56: | Line 58: | ||
end | end | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | 5. Each @Test function should perform only one test. Use functions of the library '''org.eclipse.edt.eunit.runtime.LogResult''' to record the results of the test. LogResult's functions include:<br> | |
| + | <pre>// Report a success. | ||
| + | function passed(str String in) | ||
| − | + | // Report a failure. | |
| + | function failed(str String in) | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Calls passed() if testCondition is true, and calls failed() if it's false. | ||
| + | function assertTrue(message String in, testCondition boolean in) | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Write a message to the EUnit report. This is useful for adding extra | ||
| + | // information about failures. | ||
| + | function logStdOut(logmsg String in) | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Report that a variation was not run. You might use this when you know | ||
| + | // test will fail but you don't want it to be treated as an error. Known | ||
| + | // bugs would report "skipped" while new bugs would report "failed". | ||
| + | function skipped(str String in) | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Compares the 'actual' string with the 'expected' string. Calls passed() | ||
| + | // if they're equal, and calls failed() if they're not equal. | ||
| + | function assertStringEqual(message String in, expected String in, actual String in) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | LogResult also has functions similar to assertStringEqual that check values of other types: assertBigintEqual, assertDateEqual, assertTimeEqual, etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Tips<br> ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Put closely related tests into the same library, and use packages to organize the libraries. | ||
| + | *If an exception is thrown from a @Test function, EUnit will report it as a failure.<br> | ||
| + | *If you want to disable some test cases for certain languages, you can use '''targetLang''' in the annotation. For example, below is a test case which won't be run in JavaScript.<br> | ||
<pre>function runAssignmentFunction01(){@Test {targetLang = [JAVA]}} | <pre>function runAssignmentFunction01(){@Test {targetLang = [JAVA]}} | ||
variation = "constant initialization"; | variation = "constant initialization"; | ||
| Line 64: | Line 93: | ||
end | end | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | == | + | == Creating the test driver<br> == |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
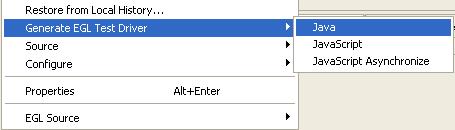
| − | + | Right click on your EUnit project and choose '''Generate EGL Test Driver > Java''' or '''Generate EGL Test Driver > JavaScript'''.<br> | |
[[Image:Eunit004.JPG]] | [[Image:Eunit004.JPG]] | ||
| − | + | The name of the test driver project will be the name of your EUnit project, plus '''eunit.java''' or '''eunit.javascript'''.<br> | |
| − | + | You must re-create your test driver if you add or remove @Test functions in the EUnit project. But you don't have to re-create the test driver if you modify an existing @Test function.<br> | |
| + | ==== Tips<br> ==== | ||
| − | + | *You can create a test driver from packages or egl files instead of an entire project. <br> | |
| − | + | == How to run tests using EUnit<br> == | |
| − | + | === Java === | |
| + | Go to project '''eunit.test.eunit.java''', folder '''generatedJava''', and run'''test.RunAllTests_pgm.egl '''as an EGL Java Main Application.<br> | ||
=== JavaScript === | === JavaScript === | ||
| + | There are two ways to execute the test: | ||
| − | + | *Go to project '''eunit.test.eunit.javascript''', folder '''EGLSource''', and run '''eunitgen.RunAllTests_rui.egl''' as an EGL Rich UI Applic. | |
| + | *Go to project '''eunit.test.eunit.javascript''', folder'''EGLSource''', and deploy '''eunit_test_eunit_javascript.egldd''' to a target project. Start the server and then run the HTML file in the browser.<br> | ||
| − | + | == Viewing the results == | |
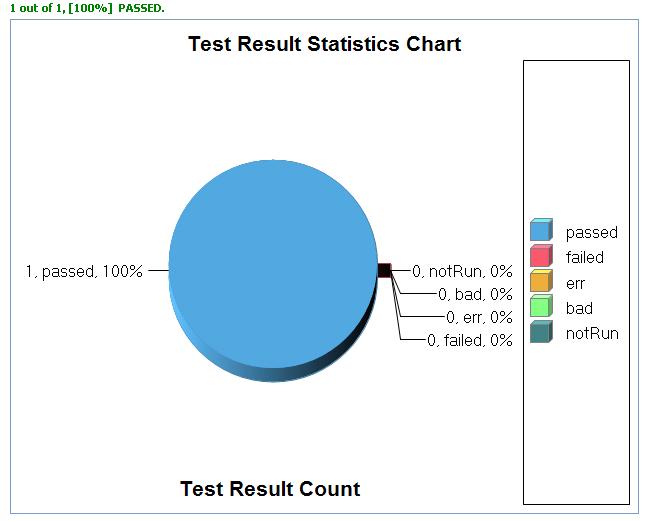
| − | + | Refresh your test driver project. You should see a new folder, '''ResultRoot'''. It will have a subfolder whose name is a timestamp of the form yyyymmdd_hhmmss. Expand the subfolder and open the file '''ResultSummary.trs'''. You'll see a summary of the results. If you have BIRT installed you'll also see the results in a pie chart. | |
| − | + | [[Image:Eunit005.JPG]] | |
| − | + | You can also go through every individual report by clicking the leaf node of the result tree and navigating to the corresponding source file. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | [[Category:EDT]] | |
| − | + | <br> | |
Revision as of 11:44, 19 December 2012
Contents
EUnit Test Framework Overview
What is EUnit?
EUnit stands for EGL Unit testing framework. It is a simple open source framework to write and run repeatable EGL tests. Its features include:
- Tooling to generate a test program and run the test cases – Provided by EDT Framework
- Manual and automated
- Can be run as often as needed (on demand, nightly build, etc.)
- GUI and command line interfaces
- Logging, reporting, analyzing
- Can be used in a multiple-language environment (Java, JavaScript, etc)
- Test cases
- Test case documentation
EUnit tests are written in EGL. You write the tests in a normal EGL project, then use the EUnit tooling to create a "test driver" for each target language you want to test in. The test driver is runnable code (a Java program or a JavaScript RUIHandler) that will execute the tests and create a report of their results.
How to write test cases using EUnit
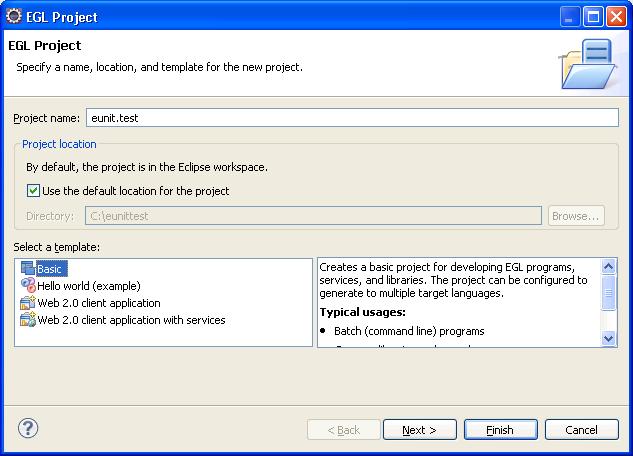
1. Create an EGL Project, for example: eunit.test
- Select Basic as the template.
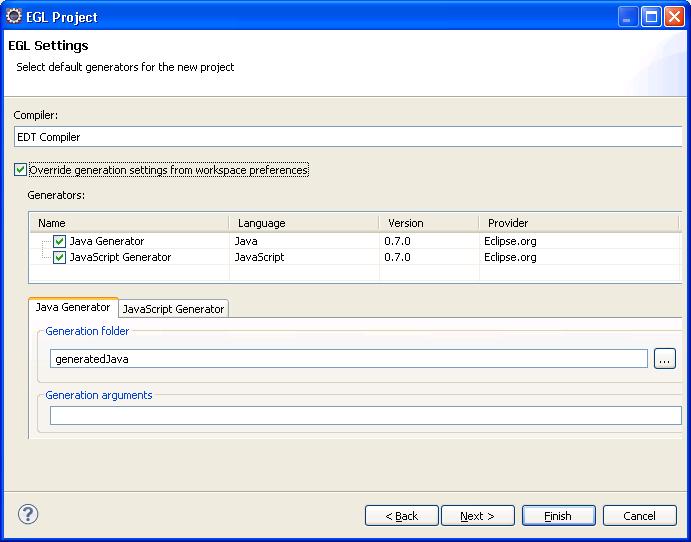
- Select the generators:
1) If you will run the testing on both Java and JavaScript platforms, leave the default settings (both Java and JavaScript generators selected).
2) If you will run the testing on a specific platform, select Override generation settings from workspace preferences and choose a generator.
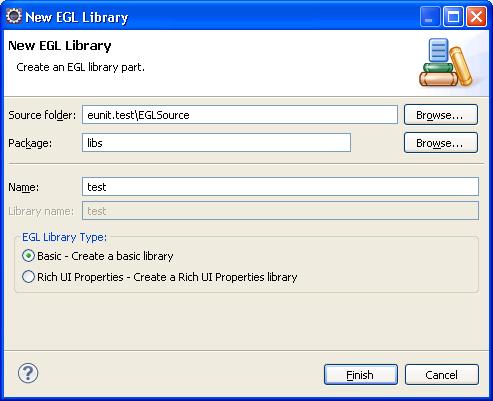
2. Create an EGL Library, for example: test, and provide a package name, such as libs.
3. Open the library with the EGL Editor, and remove the automatically generated code.
4. Type the variable declarations and functions (we treat each function as an EUnit test case) in the library. Functions that perform a test should have the @Test annotation. For example:
package libs;
import org.eclipse.edt.eunit.runtime.LogResult;
import org.eclipse.edt.eunit.runtime.Test;
// basic library
library test
const constFlexName string = "Fred Smith";
varFlexName string;
variation string;
function runAssignmentFunction01(){@Test {}}
variation = "constant initialization";
LogResult.assertStringEqual1("Fred Smith", constFlexName);
end
end
5. Each @Test function should perform only one test. Use functions of the library org.eclipse.edt.eunit.runtime.LogResult to record the results of the test. LogResult's functions include:
// Report a success. function passed(str String in) // Report a failure. function failed(str String in) // Calls passed() if testCondition is true, and calls failed() if it's false. function assertTrue(message String in, testCondition boolean in) // Write a message to the EUnit report. This is useful for adding extra // information about failures. function logStdOut(logmsg String in) // Report that a variation was not run. You might use this when you know // test will fail but you don't want it to be treated as an error. Known // bugs would report "skipped" while new bugs would report "failed". function skipped(str String in) // Compares the 'actual' string with the 'expected' string. Calls passed() // if they're equal, and calls failed() if they're not equal. function assertStringEqual(message String in, expected String in, actual String in)
LogResult also has functions similar to assertStringEqual that check values of other types: assertBigintEqual, assertDateEqual, assertTimeEqual, etc.
Tips
- Put closely related tests into the same library, and use packages to organize the libraries.
- If an exception is thrown from a @Test function, EUnit will report it as a failure.
- If you want to disable some test cases for certain languages, you can use targetLang in the annotation. For example, below is a test case which won't be run in JavaScript.
function runAssignmentFunction01(){@Test {targetLang = [JAVA]}}
variation = "constant initialization";
LogResult.assertStringEqual1("Fred Smith", constFlexName);
end
Creating the test driver
Right click on your EUnit project and choose Generate EGL Test Driver > Java or Generate EGL Test Driver > JavaScript.
The name of the test driver project will be the name of your EUnit project, plus eunit.java or eunit.javascript.
You must re-create your test driver if you add or remove @Test functions in the EUnit project. But you don't have to re-create the test driver if you modify an existing @Test function.
Tips
- You can create a test driver from packages or egl files instead of an entire project.
How to run tests using EUnit
Java
Go to project eunit.test.eunit.java, folder generatedJava, and runtest.RunAllTests_pgm.egl as an EGL Java Main Application.
JavaScript
There are two ways to execute the test:
- Go to project eunit.test.eunit.javascript, folder EGLSource, and run eunitgen.RunAllTests_rui.egl as an EGL Rich UI Applic.
- Go to project eunit.test.eunit.javascript, folderEGLSource, and deploy eunit_test_eunit_javascript.egldd to a target project. Start the server and then run the HTML file in the browser.
Viewing the results
Refresh your test driver project. You should see a new folder, ResultRoot. It will have a subfolder whose name is a timestamp of the form yyyymmdd_hhmmss. Expand the subfolder and open the file ResultSummary.trs. You'll see a summary of the results. If you have BIRT installed you'll also see the results in a pie chart.