Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Configuring a Relational Variable One-to-One Mapping (ELUG)"
m (New page: <div style="float:right;border:1px solid #000000;padding:5px">__TOC__ Related Topics</div> This secti...) |
m (→How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Java) |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float:right;border:1px solid #000000;padding:5px">__TOC__ | <div style="float:right;border:1px solid #000000;padding:5px">__TOC__ | ||
[[Special:Whatlinkshere/Configuring a Relational Variable One-to-One Mapping (ELUG)|Related Topics]]</div> | [[Special:Whatlinkshere/Configuring a Relational Variable One-to-One Mapping (ELUG)|Related Topics]]</div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
For information on how to create EclipseLink mappings, see [[Creating%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Creating a Mapping]]. | For information on how to create EclipseLink mappings, see [[Creating%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Creating a Mapping]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
This table lists the configurable options for a relational variable one-to-one mapping. | This table lists the configurable options for a relational variable one-to-one mapping. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 8: | ||
<span id="Table 37-1"></span> | <span id="Table 37-1"></span> | ||
| − | + | {| class="RuleFormalMax" dir="ltr" title="Configurable Options for Relational Variable One-to-One Mapping" summary="This table lists the configurable options common to Relational Variable One-to-One Mapping and categorizes them as Basic and Advanced and indicates if the option can be configured with the Workbench, Java, or both." width="100%" border="1" frame="border" rules="all" cellpadding="3" frame="border" rules="all" | |
| − | + | ||
| − | {| class="RuleFormalMax" dir="ltr" title="Configurable Options for Relational Variable One-to-One Mapping" summary="This table lists the configurable options common to Relational Variable One-to-One Mapping and categorizes them as Basic and Advanced and indicates if the option can be configured with the | + | |
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
! id="r1c1-t2" align="left" valign="bottom" | '''Option''' | ! id="r1c1-t2" align="left" valign="bottom" | '''Option''' | ||
| Line 27: | Line 15: | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| id="r2c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | | id="r2c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | ||
| − | [[Configuring%20a%20Relational%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Configuring Reference Descriptor]] | + | [[Configuring%20a%20Relational%20Mapping%20(ELUG)#Configuring Reference Descriptor|Configuring Reference Descriptor]] |
| headers="r2c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | | headers="r2c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | ||
[[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | [[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 22: | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| id="r3c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | | id="r3c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | ||
| − | [[Configuring%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Configuring a Type Conversion Converter]] | + | [[Configuring%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)#Configuring a Type Conversion Converter|Configuring a Type Conversion Converter]] |
| headers="r3c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | | headers="r3c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | ||
[[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | [[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 29: | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| id="r4c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | | id="r4c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | ||
| − | [[Configuring%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Configuring Read-Only Mappings]] | + | [[Configuring%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)#Configuring Read-Only Mappings|Configuring Read-Only Mappings]] |
| headers="r4c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | | headers="r4c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | ||
[[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | [[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 36: | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| id="r5c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | | id="r5c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | ||
| − | [[Configuring%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Configuring Mapping Comments]] | + | [[Configuring%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)#Configuring Mapping Comments|Configuring Mapping Comments]] |
| headers="r5c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | | headers="r5c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | ||
[[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | [[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | ||
| Line 69: | Line 57: | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| id="r8c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | | id="r8c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | ||
| − | [[#Configuring Query Key Association]] | + | [[#Configuring Query Key Association|Configuring Query Key Association]] |
| headers="r8c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | | headers="r8c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | ||
[[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | [[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | ||
| Line 76: | Line 64: | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| id="r9c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | | id="r9c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | ||
| − | [[#Configuring Class Indicator]] | + | [[#Configuring Class Indicator|Configuring Class Indicator]] |
| headers="r9c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | | headers="r9c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | ||
[[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | [[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | ||
| Line 83: | Line 71: | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| id="r10c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | | id="r10c1-t2" headers="r1c1-t2" align="left" | | ||
| − | [[#Configuring Unique Primary Key]] | + | [[#Configuring Unique Primary Key|Configuring Unique Primary Key]] |
| headers="r10c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | | headers="r10c1-t2 r1c2-t2" align="left" | | ||
[[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | [[Image:support.gif|Supported]] | ||
| Line 91: | Line 79: | ||
| + | This example shows how to create a variable one-to-one mapping and add it to a descriptor using Java code. | ||
| − | + | <span id="Example 39-1"></span> | |
| + | ''''' Variable One-to-One Mapping''''' | ||
| + | public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | ||
| + | VariableOneToOneMapping mapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // configure mapping | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | |||
| + | // add mapping to descriptor | ||
| + | descriptor.addMapping(mapping); | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | * [[Introduction%20to%20Relational%20Mappings%20(ELUG)|Variable One-to-One Mapping]] | + | For more information, see the following: |
| + | * [[Introduction%20to%20Relational%20Mappings%20(ELUG)#Variable One-to-One Mapping|Variable One-to-One Mapping]] | ||
* [[Configuring%20a%20Relational%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Configuring a Relational Mapping]] | * [[Configuring%20a%20Relational%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Configuring a Relational Mapping]] | ||
| + | * [[Configuring%20a%20Mapping%20(ELUG)|Configuring a Mapping]]. | ||
| Line 105: | Line 106: | ||
A source table has an indicator column that specifies the target table through the class indicator field. | A source table has an indicator column that specifies the target table through the class indicator field. | ||
| − | [[#Figure 37-1|Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field]] illustrates the <tt>EMPLOYEE</tt> table that has a <tt>TYPE</tt> column that indicates the target for the row (either <tt>PHONE</tt> or <tt>EMAIL</tt>). | + | The [[#Figure 37-1|Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field]] figure illustrates the <tt>EMPLOYEE</tt> table that has a <tt>TYPE</tt> column that indicates the target for the row (either <tt>PHONE</tt> or <tt>EMAIL</tt>). |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 114: | Line 115: | ||
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining a normal one-to-one relationship, except: | The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining a normal one-to-one relationship, except: | ||
| − | |||
* The reference class is a Java ''interface'', not a Java ''class''. However, the method to set the interface is identical. | * The reference class is a Java ''interface'', not a Java ''class''. However, the method to set the interface is identical. | ||
* You must specify a type indicator field. | * You must specify a type indicator field. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
* You must specify the foreign key names and the respective abstract query keys from the target interface descriptor. | * You must specify the foreign key names and the respective abstract query keys from the target interface descriptor. | ||
| − | Alternatively, you can use unique primary keys to specify the correct target. See [[#Configuring Unique Primary Key] for more information. | + | Alternatively, you can use unique primary keys to specify the correct target. See [[#Configuring Unique Primary Key|Configuring Unique Primary Key]] for more information. |
| − | + | ||
| Line 127: | Line 126: | ||
To specify the class indicators for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure: | To specify the class indicators for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure: | ||
| − | |||
# Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | # Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | ||
# Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br>'''''Figure 37-2 Class Indicator Info Tab''''<br>[[Image:clindfld.gif|Class Indicator Info Tab]] | # Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br>'''''Figure 37-2 Class Indicator Info Tab''''<br>[[Image:clindfld.gif|Class Indicator Info Tab]] | ||
| − | + | #Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select the field on the database table (associated with the mapping's descriptor) to use as the indicator for the variable mapping. | |
| − | Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select the field on the database table (associated with the mapping's descriptor) to use as the indicator for the variable mapping. | + | #Use the '''Indicator Type''' to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list. |
| − | + | #To specify the specific class indicator field values for each (nonabstract) child class, click '''Edit''' and enter the appropriate value for each child class. | |
| − | Use the '''Indicator Type''' to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | To specify the specific class indicator field values for each (nonabstract) child class, click '''Edit''' and enter the appropriate value for each child class. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| Line 147: | Line 141: | ||
''''' Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Class Indicator''''' | ''''' Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Class Indicator''''' | ||
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | ||
| − | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = | + | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping(); |
| − | + | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | ||
| Line 165: | Line 158: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | ||
| Line 174: | Line 164: | ||
==Configuring Unique Primary Key== | ==Configuring Unique Primary Key== | ||
| − | In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use a unique primary key in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in [[#Figure 37-4]]. This section includes information on implementing class indicators | + | In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use a unique primary key in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in the [[#Figure 37-4| Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key]] figure. This section includes information on implementing class indicators. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Alternatively, you can use a class indicator to specify the correct target. See [[#Configuring Class Indicator|Configuring Class Indicator]] for more information. | ||
| Line 183: | Line 172: | ||
To specify the variable one-to-one mapping with a primary key, use this procedure: | To specify the variable one-to-one mapping with a primary key, use this procedure: | ||
| − | |||
# Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | # Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | ||
# Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br>'''''Figure 37-3 Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key'''''<br>[[Image:var11_map_conf_pk.gif|Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key]] | # Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br>'''''Figure 37-3 Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key'''''<br>[[Image:var11_map_conf_pk.gif|Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key]] | ||
| − | + | #*Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select none. | |
| − | Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select none. | + | #*Use the '''Indicator Type''' to select none. |
| − | + | #*Use the '''Indicator Value''' column to specify none. | |
| − | Use the '''Indicator Type''' to select none. | + | #After choosing the reference descriptor for the mapping, deselect the '''Include''' check boxes. |
| − | + | ||
| − | Use the '''Indicator Value''' column to specify none. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | After choosing the reference descriptor for the mapping, deselect the '''Include''' check boxes. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| Line 201: | Line 184: | ||
'''Note:''' You cannot deselect the value in the Class Indicator Field, unless the foreign key values in the source table are unique. | '''Note:''' You cannot deselect the value in the Class Indicator Field, unless the foreign key values in the source table are unique. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 216: | Line 194: | ||
''''' Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Unique Primary Key''''' | ''''' Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Unique Primary Key''''' | ||
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | ||
| − | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = | + | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping(); |
| − | + | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | ||
| Line 227: | Line 204: | ||
descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping); | descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | ||
| − | |||
===What You May Need to Know About Unique Primary Keys=== | ===What You May Need to Know About Unique Primary Keys=== | ||
| − | As [[#Figure 37-4|Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key]] illustrates, the value of the foreign key in the source table (<tt>C_ID</tt>) mapped to the primary key of the target table is unique. No primary key values among the target tables are the same, so primary key values are not unique just in the table, but also among the tables. | + | As the [[#Figure 37-4|Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key]] figure illustrates, the value of the foreign key in the source table (<tt>C_ID</tt>) mapped to the primary key of the target table is unique. No primary key values among the target tables are the same, so primary key values are not unique just in the table, but also among the tables. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 247: | Line 222: | ||
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining class indicator variable one-to-one relationships, except the following: | The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining class indicator variable one-to-one relationships, except the following: | ||
| − | |||
* A type indicator field is not specified. | * A type indicator field is not specified. | ||
* The class indicator values are not specified. | * The class indicator values are not specified. | ||
| Line 258: | Line 232: | ||
This section includes information on configuring query key assosications using development tools, as well as Java. | This section includes information on configuring query key assosications using development tools, as well as Java. | ||
| − | |||
===How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Workbench=== | ===How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Workbench=== | ||
| − | |||
To specify the query keys used for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure: | To specify the query keys used for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure: | ||
| − | |||
# Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | # Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | ||
# Click the '''Query Key Associations''' tab. The Query Key Associations tab appears<br><span id="Figure 37-5"></span>''''' Query Key Associations Tab'''''<br>[[Image:qkassoc.gif|Query Key Associations Tab]] | # Click the '''Query Key Associations''' tab. The Query Key Associations tab appears<br><span id="Figure 37-5"></span>''''' Query Key Associations Tab'''''<br>[[Image:qkassoc.gif|Query Key Associations Tab]] | ||
# Complete each field on the Query Key Associations tab. | # Complete each field on the Query Key Associations tab. | ||
| − | + | # Use the '''Indicator Type''' to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Use the '''Indicator Type''' to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
{| class="HRuleInformal" dir="ltr" title="This table defines each field on the tab." summary="This table defines each field on the tab." width="100%" border="1" frame="hsides" rules="rows" cellpadding="3" frame="hsides" rules="rows" | {| class="HRuleInformal" dir="ltr" title="This table defines each field on the tab." summary="This table defines each field on the tab." width="100%" border="1" frame="hsides" rules="rows" cellpadding="3" frame="hsides" rules="rows" | ||
|- align="left" valign="top" | |- align="left" valign="top" | ||
| Line 285: | Line 250: | ||
| id="r3c1-t4" headers="r1c1-t4" align="left" | '''Query Key Name''' | | id="r3c1-t4" headers="r1c1-t4" align="left" | '''Query Key Name''' | ||
| headers="r3c1-t4 r1c2-t4" align="left" | | | headers="r3c1-t4 r1c2-t4" align="left" | | ||
| − | The name of the query key (from the referenced descriptor) for this association. See [[Configuring%20a%20Descriptor%20(ELUG)|Configuring Query Keys]] for more information. | + | The name of the query key (from the referenced descriptor) for this association. See [[Configuring%20a%20Descriptor%20(ELUG)#Configuring Query Keys|Configuring Query Keys]] for more information. |
|} | |} | ||
===How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Java=== | ===How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Java=== | ||
| − | |||
The API to configure query key associations is <tt>org.eclipse.persistence.mappings.VariableOneToOneMapping</tt> method <tt>addForeingQueryKeyName(String, String)</tt>. | The API to configure query key associations is <tt>org.eclipse.persistence.mappings.VariableOneToOneMapping</tt> method <tt>addForeingQueryKeyName(String, String)</tt>. | ||
For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | ||
| − | |||
| Line 300: | Line 263: | ||
==Configuring Class Indicator== | ==Configuring Class Indicator== | ||
| − | In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use an indicator column in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in [[#Figure 37-1|Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field]]. This section includes information on implementing class indicators. | + | In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use an indicator column in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in the [[#Figure 37-1|Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field]] figure. This section includes information on implementing class indicators. |
A source table has an indicator column that specifies the target table through the class indicator field. | A source table has an indicator column that specifies the target table through the class indicator field. | ||
| − | [[#Figure 37-1|Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field]] illustrates the <tt>EMPLOYEE</tt> table that has a <tt>TYPE</tt> column that indicates the target for the row (either <tt>PHONE</tt> or <tt>EMAIL</tt>). | + | The [[#Figure 37-1|Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field]] figure illustrates the <tt>EMPLOYEE</tt> table that has a <tt>TYPE</tt> column that indicates the target for the row (either <tt>PHONE</tt> or <tt>EMAIL</tt>). |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 313: | Line 276: | ||
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining a normal one-to-one relationship, except: | The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining a normal one-to-one relationship, except: | ||
| − | |||
* The reference class is a Java ''interface'', not a Java ''class''. However, the method to set the interface is identical. | * The reference class is a Java ''interface'', not a Java ''class''. However, the method to set the interface is identical. | ||
* You must specify a type indicator field. | * You must specify a type indicator field. | ||
| Line 319: | Line 281: | ||
* You must specify the foreign key names and the respective abstract query keys from the target interface descriptor. | * You must specify the foreign key names and the respective abstract query keys from the target interface descriptor. | ||
| − | Alternatively, you can use unique primary keys to specify the correct target. See [[#Configuring Unique Primary Key] for more information. | + | Alternatively, you can use unique primary keys to specify the correct target. See [[#Configuring Unique Primary Key|Configuring Unique Primary Key]] for more information. |
| − | + | ||
| Line 326: | Line 287: | ||
To specify the class indicators for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure: | To specify the class indicators for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure: | ||
| − | |||
# Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | # Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | ||
| − | # Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br>''''' | + | # Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br><span id="Figure 37-2"></span>''''' Class Indicator Info Tab''''<br>[[Image:clindfld.gif|Class Indicator Info Tab]] |
| − | + | #Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select the field on the database table (associated with the mapping's descriptor) to use as the indicator for the variable mapping. | |
| − | Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select the field on the database table (associated with the mapping's descriptor) to use as the indicator for the variable mapping. | + | #Use the '''Indicator Type''' to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list. |
| − | + | #To specify the specific class indicator field values for each (nonabstract) child class, click '''Edit''' and enter the appropriate value for each child class. | |
| − | Use the '''Indicator Type''' to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | To specify the specific class indicator field values for each (nonabstract) child class, click '''Edit''' and enter the appropriate value for each child class. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 347: | Line 302: | ||
''''' Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Class Indicator''''' | ''''' Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Class Indicator''''' | ||
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | ||
| − | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = | + | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping(); |
| − | + | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | ||
| Line 365: | Line 319: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | ||
| Line 374: | Line 326: | ||
==Configuring Unique Primary Key== | ==Configuring Unique Primary Key== | ||
| − | In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use a unique primary key in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in [[#Figure 37-4]]. This section includes information on implementing class indicators | + | In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use a unique primary key in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in the [[#Figure 37-4|Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key]] figure. This section includes information on implementing class indicators. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Alternatively, you can use a class indicator to specify the correct target. See [[#Configuring Class Indicator|Configuring Class Indicator]] for more information. | ||
| Line 383: | Line 334: | ||
To specify the variable one-to-one mapping with a primary key, use this procedure: | To specify the variable one-to-one mapping with a primary key, use this procedure: | ||
| − | |||
# Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | # Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | ||
| − | # Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br>''''' | + | # Click the '''Class Indicator Info''' tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.<br><span id="Figure 37-3"></span>''''' Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key'''''<br>[[Image:var11_map_conf_pk.gif|Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key]] |
| − | + | #Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select none. | |
| − | Use the '''Class Indicator Field''' to select none. | + | #Use the '''Indicator Type''' to select none. |
| − | + | #Use the '''Indicator Value''' column to specify none. | |
| − | Use the '''Indicator Type''' to select none. | + | #After choosing the reference descriptor for the mapping, deselect the '''Include''' check boxes. |
| − | + | ||
| − | Use the '''Indicator Value''' column to specify none. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | After choosing the reference descriptor for the mapping, deselect the '''Include''' check boxes. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| Line 401: | Line 346: | ||
'''Note:''' You cannot deselect the value in the Class Indicator Field, unless the foreign key values in the source table are unique. | '''Note:''' You cannot deselect the value in the Class Indicator Field, unless the foreign key values in the source table are unique. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 417: | Line 357: | ||
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) { | ||
| − | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = | + | VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping(); |
| − | + | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact"); | ||
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class); | ||
| Line 428: | Line 367: | ||
descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping); | descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | For more information about the available methods for <tt>VariableOneToOneMapping</tt>, see the ''EclipseLink API Reference''. | ||
| − | |||
===What You May Need to Know About Unique Primary Keys=== | ===What You May Need to Know About Unique Primary Keys=== | ||
| − | As [[#Figure 37-4|Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key]] illustrates, the value of the foreign key in the source table (<tt>C_ID</tt>) mapped to the primary key of the target table is unique. No primary key values among the target tables are the same, so primary key values are not unique just in the table, but also among the tables. | + | As the [[#Figure 37-4|Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key]] figure illustrates, the value of the foreign key in the source table (<tt>C_ID</tt>) mapped to the primary key of the target table is unique. No primary key values among the target tables are the same, so primary key values are not unique just in the table, but also among the tables. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 448: | Line 385: | ||
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining class indicator variable one-to-one relationships, except the following: | The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining class indicator variable one-to-one relationships, except the following: | ||
| − | |||
* A type indicator field is not specified. | * A type indicator field is not specified. | ||
* The class indicator values are not specified. | * The class indicator values are not specified. | ||
| Line 459: | Line 395: | ||
This section includes information on configuring query key assosications using development tools, as well as Java. | This section includes information on configuring query key assosications using development tools, as well as Java. | ||
| − | |||
| Line 467: | Line 402: | ||
# Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | # Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the '''Navigator'''. Its attributes appear in the Editor. | ||
| − | # Click the '''Query Key Associations''' tab. The Query Key Associations tab appears<br>''''' | + | # Click the '''Query Key Associations''' tab. The Query Key Associations tab appears.<br><span id="Figure 37-5"></span>''''' Query Key Associations Tab'''''<br>[[Image:qkassoc.gif|Query Key Associations Tab]] |
# Complete each field on the Query Key Associations tab. | # Complete each field on the Query Key Associations tab. | ||
| + | # Use the '''Indicator Type''' to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list. | ||
Use the following information to enter data in each field on the tab: | Use the following information to enter data in each field on the tab: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="HRuleInformal" dir="ltr" title="This table defines each field on the tab." summary="This table defines each field on the tab." width="100%" border="1" frame="hsides" rules="rows" cellpadding="3" frame="hsides" rules="rows" | {| class="HRuleInformal" dir="ltr" title="This table defines each field on the tab." summary="This table defines each field on the tab." width="100%" border="1" frame="hsides" rules="rows" cellpadding="3" frame="hsides" rules="rows" | ||
| Line 486: | Line 418: | ||
| id="r3c1-t4" headers="r1c1-t4" align="left" | '''Query Key Name''' | | id="r3c1-t4" headers="r1c1-t4" align="left" | '''Query Key Name''' | ||
| headers="r3c1-t4 r1c2-t4" align="left" | | | headers="r3c1-t4 r1c2-t4" align="left" | | ||
| − | The name of the query key (from the referenced descriptor) for this association. See [[Configuring%20a%20Descriptor%20(ELUG)|Configuring Query Keys]] for more information. | + | The name of the query key (from the referenced descriptor) for this association. See [[Configuring%20a%20Descriptor%20(ELUG)#Configuring Query Keys|Configuring Query Keys]] for more information. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 508: | Line 435: | ||
[[Category: EclipseLink User's Guide]] | [[Category: EclipseLink User's Guide]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Release 1]] |
[[Category: Task]] | [[Category: Task]] | ||
| + | [[Category: ORM]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:39, 20 August 2008
Contents
For information on how to create EclipseLink mappings, see Creating a Mapping.
This table lists the configurable options for a relational variable one-to-one mapping.
| Option | Workbench | Java |
|---|---|---|
This example shows how to create a variable one-to-one mapping and add it to a descriptor using Java code.
Variable One-to-One Mapping
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) {
VariableOneToOneMapping mapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping();
// configure mapping
...
// add mapping to descriptor
descriptor.addMapping(mapping);
}
For more information, see the following:
Configuring Class Indicator
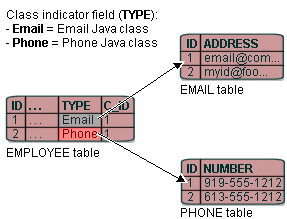
In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use an indicator column in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field. This section includes information on implementing class indicators.
A source table has an indicator column that specifies the target table through the class indicator field.
The Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field figure illustrates the EMPLOYEE table that has a TYPE column that indicates the target for the row (either PHONE or EMAIL).
Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining a normal one-to-one relationship, except:
- The reference class is a Java interface, not a Java class. However, the method to set the interface is identical.
- You must specify a type indicator field.
- You specify the class indicator values on the mapping so that mapping can determine the class of object to create.
- You must specify the foreign key names and the respective abstract query keys from the target interface descriptor.
Alternatively, you can use unique primary keys to specify the correct target. See Configuring Unique Primary Key for more information.
How to Configure a Class Indicator Using Workbench
To specify the class indicators for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure:
- Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the Navigator. Its attributes appear in the Editor.
- Click the Class Indicator Info tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.
Figure 37-2 Class Indicator Info Tab'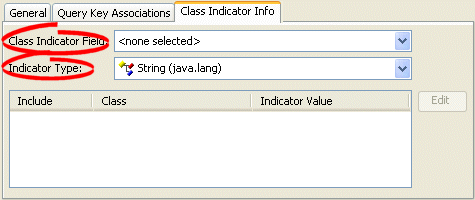
- Use the Class Indicator Field to select the field on the database table (associated with the mapping's descriptor) to use as the indicator for the variable mapping.
- Use the Indicator Type to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list.
- To specify the specific class indicator field values for each (nonabstract) child class, click Edit and enter the appropriate value for each child class.
How to Configure a Class Indicator Using Java
This example illustrates how to define a variable one-to-one mapping using a class (type) indicator in Java code.
Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Class Indicator
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) {
VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping();
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact");
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class);
variableOneToOneMapping.setForeignQueryKeyName ("C_ID", "id");
variableOneToOneMapping.setTypeFieldName("TYPE");
// configure class indicators
variableOneToOneMapping.addClassIndicator(Email.class, "Email");
variableOneToOneMapping.addClassIndicator(Phone.class, "Phone");
variableOneToOneMapping.dontUseIndirection();
variableOneToOneMapping.privateOwnedRelationship();
// add mapping to descriptor
descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping);
}
For more information about the available methods for VariableOneToOneMapping, see the EclipseLink API Reference.
Configuring Unique Primary Key
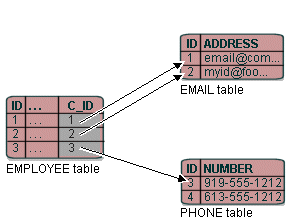
In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use a unique primary key in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in the Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key figure. This section includes information on implementing class indicators.
Alternatively, you can use a class indicator to specify the correct target. See Configuring Class Indicator for more information.
How to Configure a Unique Primary Key UsingWorkbench
To specify the variable one-to-one mapping with a primary key, use this procedure:
- Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the Navigator. Its attributes appear in the Editor.
- Click the Class Indicator Info tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.
Figure 37-3 Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key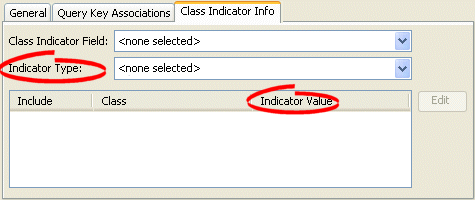
- Use the Class Indicator Field to select none.
- Use the Indicator Type to select none.
- Use the Indicator Value column to specify none.
- After choosing the reference descriptor for the mapping, deselect the Include check boxes.
|
Note: You cannot deselect the value in the Class Indicator Field, unless the foreign key values in the source table are unique. |
How to Configure a Unique Primary Key Using Java
This example illustrates how to define a variable one-to-one mapping using a unique primary key in Java code.
Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Unique Primary Key
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) {
VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping();
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact");
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class);
variableOneToOneMapping.setForeignQueryKeyName ("C_ID", "id");
variableOneToOneMapping.dontUseIndirection();
variableOneToOneMapping.privateOwnedRelationship();
// add mapping to descriptor
descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping);
}
For more information about the available methods for VariableOneToOneMapping, see the EclipseLink API Reference.
What You May Need to Know About Unique Primary Keys
As the Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key figure illustrates, the value of the foreign key in the source table (C_ID) mapped to the primary key of the target table is unique. No primary key values among the target tables are the same, so primary key values are not unique just in the table, but also among the tables.
Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key
If there is no indicator stored in the source table, EclipseLink cannot determine to which target table the foreign key value is mapped. Therefore, EclipseLink reads through all the target tables until it finds an entry in one of the target tables. This is an inefficient way of setting up a relation model. The class indicator is much more efficient as it reduces the number of reads performed on the tables to get the data. In the class indicator method, EclipseLink knows exactly which target table to look into for the data.
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining class indicator variable one-to-one relationships, except the following:
- A type indicator field is not specified.
- The class indicator values are not specified.
The type indicator field and its values are not needed, because EclipseLink goes through all the target tables until data is finally found.
Configuring Query Key Association
This section includes information on configuring query key assosications using development tools, as well as Java.
How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Workbench
To specify the query keys used for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure:
- Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the Navigator. Its attributes appear in the Editor.
- Click the Query Key Associations tab. The Query Key Associations tab appears
Query Key Associations Tab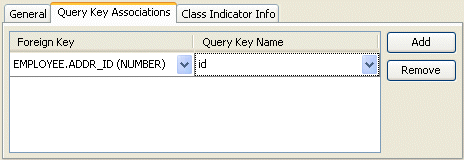
- Complete each field on the Query Key Associations tab.
- Use the Indicator Type to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Foreign Key | The field from the database table to use as the foreign key in this relationship. |
| Query Key Name |
The name of the query key (from the referenced descriptor) for this association. See Configuring Query Keys for more information. |
How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Java
The API to configure query key associations is org.eclipse.persistence.mappings.VariableOneToOneMapping method addForeingQueryKeyName(String, String).
For more information about the available methods for VariableOneToOneMapping, see the EclipseLink API Reference.
Configuring Class Indicator
In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use an indicator column in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in the Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field figure. This section includes information on implementing class indicators.
A source table has an indicator column that specifies the target table through the class indicator field.
The Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field figure illustrates the EMPLOYEE table that has a TYPE column that indicates the target for the row (either PHONE or EMAIL).
Variable One-to-One Mapping using Class indicator Field
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining a normal one-to-one relationship, except:
- The reference class is a Java interface, not a Java class. However, the method to set the interface is identical.
- You must specify a type indicator field.
- You specify the class indicator values on the mapping so that mapping can determine the class of object to create.
- You must specify the foreign key names and the respective abstract query keys from the target interface descriptor.
Alternatively, you can use unique primary keys to specify the correct target. See Configuring Unique Primary Key for more information.
How to Configure a Class Indicator Using Workbench
To specify the class indicators for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure:
- Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the Navigator. Its attributes appear in the Editor.
- Click the Class Indicator Info tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.
Class Indicator Info Tab'
- Use the Class Indicator Field to select the field on the database table (associated with the mapping's descriptor) to use as the indicator for the variable mapping.
- Use the Indicator Type to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list.
- To specify the specific class indicator field values for each (nonabstract) child class, click Edit and enter the appropriate value for each child class.
How to Configure a Class Indicator Using Java
This example illustrates how to define a variable one-to-one mapping using a class (type) indicator in Java code.
Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Class Indicator
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) {
VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping();
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact");
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class);
variableOneToOneMapping.setForeignQueryKeyName ("C_ID", "id");
variableOneToOneMapping.setTypeFieldName("TYPE");
// configure class indicators
variableOneToOneMapping.addClassIndicator(Email.class, "Email");
variableOneToOneMapping.addClassIndicator(Phone.class, "Phone");
variableOneToOneMapping.dontUseIndirection();
variableOneToOneMapping.privateOwnedRelationship();
// add mapping to descriptor
descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping);
}
For more information about the available methods for VariableOneToOneMapping, see the EclipseLink API Reference.
Configuring Unique Primary Key
In variable one-to-one mappings, you can use a unique primary key in the source table to specify the correct target table, as illustrated in the Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key figure. This section includes information on implementing class indicators.
Alternatively, you can use a class indicator to specify the correct target. See Configuring Class Indicator for more information.
How to Configure a Unique Primary Key UsingWorkbench
To specify the variable one-to-one mapping with a primary key, use this procedure:
- Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the Navigator. Its attributes appear in the Editor.
- Click the Class Indicator Info tab. The Class Indicator Info tab appears.
Class Indicator Info Tab, Configuring Primary Key
- Use the Class Indicator Field to select none.
- Use the Indicator Type to select none.
- Use the Indicator Value column to specify none.
- After choosing the reference descriptor for the mapping, deselect the Include check boxes.
|
Note: You cannot deselect the value in the Class Indicator Field, unless the foreign key values in the source table are unique. |
How to Configure a Unique Primary Key Using Java
This example illustrates how to define a variable one-to-one mapping using a unique primary key in Java code.
Defining Variable One-to-One Mapping Using a Unique Primary Key
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) {
VariableOneToOneMapping variableOneToOneMapping = new VariableOneToOneMapping();
variableOneToOneMapping.setAttributeName("contact");
variableOneToOneMapping.setReferenceClass (Contact.class);
variableOneToOneMapping.setForeignQueryKeyName ("C_ID", "id");
variableOneToOneMapping.dontUseIndirection();
variableOneToOneMapping.privateOwnedRelationship();
// add mapping to descriptor
descriptor.addMapping(variableOneToOneMapping);
}
For more information about the available methods for VariableOneToOneMapping, see the EclipseLink API Reference.
What You May Need to Know About Unique Primary Keys
As the Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key figure illustrates, the value of the foreign key in the source table (C_ID) mapped to the primary key of the target table is unique. No primary key values among the target tables are the same, so primary key values are not unique just in the table, but also among the tables.
Variable One-to-One Relationship with Unique Primary Key
If there is no indicator stored in the source table, EclipseLink cannot determine to which target table the foreign key value is mapped. Therefore, EclipseLink reads through all the target tables until it finds an entry in one of the target tables. This is an inefficient way of setting up a relation model. The class indicator is much more efficient as it reduces the number of reads performed on the tables to get the data. In the class indicator method, EclipseLink knows exactly which target table to look into for the data.
The principles of defining such a variable class relationship are similar to defining class indicator variable one-to-one relationships, except the following:
- A type indicator field is not specified.
- The class indicator values are not specified.
The type indicator field and its values are not needed, because EclipseLink goes through all the target tables until data is finally found.
Configuring Query Key Association
This section includes information on configuring query key assosications using development tools, as well as Java.
How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Workbench
To specify the query keys used for a variable one-to-one mapping, use this procedure:
- Select the variable one-to-one mapping in the Navigator. Its attributes appear in the Editor.
- Click the Query Key Associations tab. The Query Key Associations tab appears.
Query Key Associations Tab
- Complete each field on the Query Key Associations tab.
- Use the Indicator Type to specify the data type of the class indicator field by selecting the data type from the list.
Use the following information to enter data in each field on the tab:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Foreign Key | The field from the database table to use as the foreign key in this relationship. |
| Query Key Name |
The name of the query key (from the referenced descriptor) for this association. See Configuring Query Keys for more information. |
How to Configure a Query Key Association Using Java
The API to configure query key associations is org.eclipse.persistence.mappings.VariableOneToOneMapping method addForeingQueryKeyName(String, String).
For more information about the available methods for VariableOneToOneMapping, see the EclipseLink API Reference.