Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "COSMOS Design 204959"
(New page: == '''Adding support for the CMDBf query service on top of the SML repository''' == === '''Change History''' === {|{{BMTableStyle}} !align="left"|Name: !align="left"|Date: !align="left"|...) |
m (→'''Change History''') |
||
| (70 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == ''' | + | == '''Provide reusable CMDBf APIs for adopters that intend to provide a CMDBf query/registration service''' == |
=== '''Change History''' === | === '''Change History''' === | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
!align="left"|Revised Sections: | !align="left"|Revised Sections: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Ali Mehregani |
| − | | | + | |10/04/2007 |
|<ul><li>Initial version</li></ul> | |<ul><li>Initial version</li></ul> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |David Whiteman | + | |David Whiteman |
| − | | | + | |10/05/2007 |
| − | |<ul><li>Added | + | |<ul><li>Added details regarding service transformations</li></ul> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Valentina Popescu |
| − | | | + | |10/23/2007 |
| − | |<ul> | + | |<ul><li>Updated SML Repository definition.</li></ul> |
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | </ul> | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 67: | Line 57: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== ''' Terminologies/Acronyms''' == | == ''' Terminologies/Acronyms''' == | ||
| Line 92: | Line 80: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|SML Repository | |SML Repository | ||
| − | | | + | |The SML Repository describes any SML model ( an SML model is a set of SML compliant resources ) together with a set of COSMOS API used to add new SML resources to the SML model and to query the SML model. |
|- | |- | ||
|Query service | |Query service | ||
|MDRs make data available to Clients via a Query service. Queries may select and return items, relationships, and/or graphs containing items and relationships. | |MDRs make data available to Clients via a Query service. Queries may select and return items, relationships, and/or graphs containing items and relationships. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Registration service | ||
| + | |This service is used to register a set of supported items and relationships with a federating CMDB. | ||
|} | |} | ||
== ''' Purpose ''' == | == ''' Purpose ''' == | ||
| − | + | This enhancement is associated with [https://bugs.eclipse.org/bugs/show_bug.cgi?id=204959 bugzilla 204959]. | |
| − | + | <p> | |
| − | + | The purpose of this enhancement is to refactor the CMDBf query code to make it more reusable. The SML repository already defines a set of APIs related to the CMDBf query. This set needs to be migrated to org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.query so that it can be reused by contributors who intend to provide a query service for a data provider. | |
| − | + | </p> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | </ | + | |
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | + | Another purpose of this enhancement is to implement the registration transformation code, and provide reusable APIs for the CMDBf registration service. | |
</p> | </p> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | + | This document will detail out the structure of the code and the minimum API set required to be implemented by contributors. The document will include code snippets to illustrate the simplicity in leveraging the available APIs. As part of the implementation of this enhancement the SML repository will be modified based on the refactored code. The set of classes provided in org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.query will be divided into the following sets: | |
| − | + | # CMDBfCommon.jar | |
| − | + | # CMDBfQueryTransformation.jar | |
| + | # CMDBfQueryService.jar | ||
| + | # CMDBfRegistrationTransformation.jar | ||
| + | # CMDBfRegistrationService.jar | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | The CMDBfCommon module will include any code that will be required by two or more of the other modules. The dependency of the modules is discussed in more details under the 'Implementation Detail' section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The set included under CMDBfQueryTransformation.jar will contain any necessary code for clients who intend to build a CMDBf query and consume a query response. It performs the following transformations: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * CMDBf XML query document > POJO representation of the query | ||
| + | * POJO representation of the query > CMDBf XML query document | ||
| + | * CMDBf XML query response > POJO representation of the query response | ||
| + | * POJO representation of the query response > CMDBf XML query response | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Adopters can choose to use CMDBfQueryTransformation.jar as is or have it tweaked based on their needs. What will be included in this jar file will be a concrete implementation of the transformations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly, CMDBfRegistrationTransformation.jar will include a concrete implementation of the transformation required from an XML registration request to a POJO representation (and vice-versa). | ||
| + | </p> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | + | CMDBfQueryService.jar will contain the necessary code for processing a query that conforms to CMDBf. This set will allow the user to provide implementation of selector handlers that are specific to a data provider. CMDBfQueryService.jar cannot be used as-is and will require a minimum API set to be implemented. | |
| + | |||
| + | Similarly, CMDBfRegistrationService.jar can be used by contributors to help in processing a registration request. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
== ''' Requirements ''' == | == ''' Requirements ''' == | ||
| + | The following is the list of requirements that this enhancement will address: | ||
| − | + | # Checking the conformance of a CMDBf query against its schema | |
| − | # | + | # Checking the conformance of a CMDBf registration request against its schema |
| − | # | + | # Transformation of CMDBf XML query from/to a POJO representation |
| + | # Transformation of CMDBf XML registration from/to a POJO representation | ||
| + | # A common method of processing a CMDBf query | ||
| + | # A common method of processing a registration request | ||
| − | == ''' | + | == ''' Implementation Detail ''' == |
| − | + | The plug-in org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.query will be refactored to org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services. The new plug-in will include a source folder for each of the modules mentioned earlier. The dependency of each module is depicted in the diagram below. The successive sections discuss the transformation and the processing APIs that will be included as part of this plug-in. | |
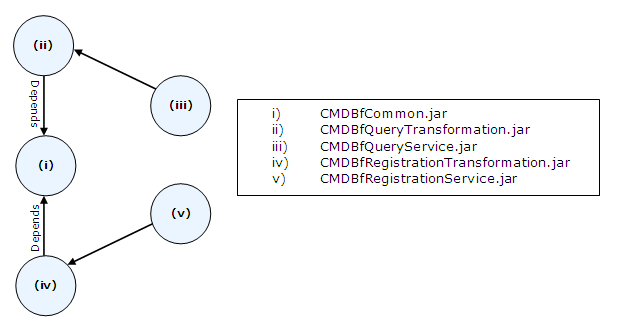
| − | + | [[Image:CMDBf-Dependency.png]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | ==== | + | == Transformations == |
| − | + | === Query === | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [http://cmdbf.org/CMDBf-v0.95.pdf CMDBf] specifies an XML-based syntax by which queries are submitted to the query service, which reports back a query result from the available MDRs, also using XML syntax. As part of our implementation of the query service, we internally accept POJOs to represent a graph of the query, and return the query result as a set of POJOs. The job of the transformers is to convert POJOs to and from the XML syntax detailed in the CMDBf specification. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | As part of [[COSMOS Design 200222]], a set of query transformations and an SML-repository-specific query service were designed and implemented. In an effort to make these components reusable, the query transformations will be refactored to share common components needed by other libraries in this design. The initial candidate classes to be moved to the common module are <tt>IXMLWritable</tt>, <tt>QueryServiceUtil</tt> (which will be renamed) and some of the fields in <tt>IQueryTransformerConstants</tt> (the ones pertaining to character constants and general SAX parsing). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | In addition, the previously implemented packages will be renamed to include the word "provisional", which in the [http://www.eclipse.org/tptp/home/documents/process/development/api_contract.html API contract specifications] we are reusing from the TPTP project, indicates that the APIs are experimental and will be evolved into stable public APIs. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Here is a simple example that illustrates the incoming query input transformation: | |
| − | + | <tt>InputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(example1().getBytes());<br> | |
| + | Query query = QueryInputTransformer.transform(inputStream);</tt> | ||
| − | + | Assume that <tt>example1()</tt> returns a String containing the XML syntax for a <query> as specified in the CMDBf spec. | |
| − | < | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | === Registration === | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | CMDBf specifies a registration service by which MDRs register items and relationships with the federating CMDB. The process for registration involves an XML-based transaction, similar to how the query service works. This enhancement will provide a transformer to convert a registration request from XML to a POJO graph structure, and will also provide the reverse of that transformation. In addition, it will provide another transformer that will convert a registration response output by the MDR from a POJO graph structure to the XML-based syntax expected by the CMDBf spec, and will again provide a reverse of that transformation. The reverse transformations are needed by some clients of the registration service, and also are useful in unit testing of the implementation. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The following new classes will provide these transformations: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | The | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.RegistrationInputTransformer | |
| − | + | org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.RegistrationOutputTransformer | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The following are the transformation APIs on the RegistrationInputTransformer class: | |
| − | The | + | |
| − | </ | + | static public RegisterRequest transform(InputStream) |
| + | static public InputStream transform(RegisterRequest) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following are the transformation APIs on the RegistrationOutputTransformer class: | ||
| + | |||
| + | static public RegisterResponse transform(InputStream) | ||
| + | static public InputStream transform(RegisterResponse) | ||
| + | |||
| + | RegisterRequest and RegisterResponse POJOs will consist of APIs and classes that match or closely mirror the corresponding element names in the CMDBf data model. RegisterRequest will reside in the <tt>org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.input.artifacts</tt> package and RegisterResponse will live in the <tt>org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.response.artifacts</tt> package. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here is a simple example that illustrates the incoming registration input transformation: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tt>InputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(example1().getBytes());<br> | ||
| + | RegisterRequest registerRequest = RegistrationInputTransformer.transform(inputStream);</tt> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Assume that <tt>example1()</tt> returns a String containing the XML syntax for a <registerRequest> as specified in the CMDBf spec. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Services == | ||
| + | === Query === | ||
| + | The class diagram below displays the interfaces and default implementations that will be included for the query service. All that a contributor is required to do is to register the classes that will be used as handlers for the selectors. The default implementation of the CMDBf query operation will look up the appropriate handlers and will invoke them accordingly. | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
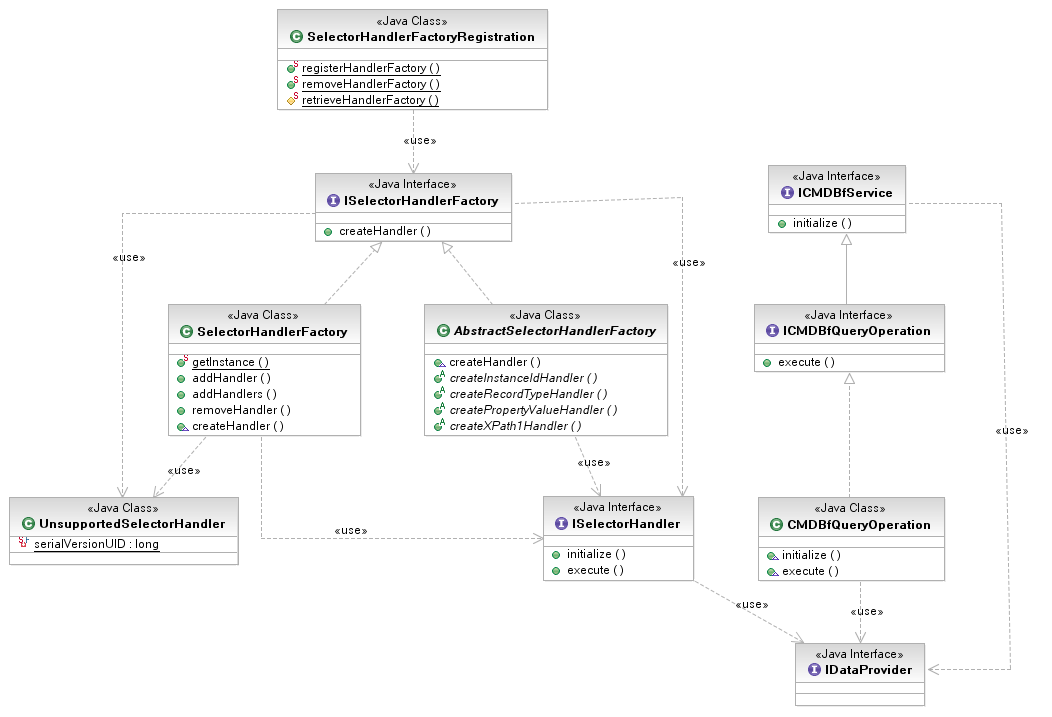
| − | + | [[Image:QueryService-v1.png]] | |
</p> | </p> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | + | The following is a snippet of code that illustrates how a contributor can register a set of selector handlers with the default implementation of <code>ISelectorHandlerFactory</code>.: | |
| − | </ | + | |
| − | < | + | <code> |
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | SelectorHandlerFactory.getInstance().addHandlers | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | new URI ("http://cosmos.org/mdrId"), | ||
| + | ISelectorHandlerFactory.ITEM_TEMPLATE, | ||
| + | new String[] | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.InstanceIdHandler", | ||
| + | "org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.RecordTypeHandler", | ||
| + | "org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.PropertyValueHandler", | ||
| + | "org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.XPath1Handler" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | </code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once the selectors are registered a client can make use of the CMDBf query service using the default implementation of <code>ICMDBfQueryOperation</code>. The argument passed into the <code>initialize</code> method represents a data provider that will be passed to each of the selector handlers. The selector handlers can cast the argument to a specific type that can process native queries that is understandable by a specific data provider. The following snippet of code illustrates how the query operation can be invoked: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code> | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | // Create a CMDBf query operation object and have it initialized | ||
| + | CMDBfQueryOperation cmdbfQueryOperation = new CMDBfQueryOperation(); | ||
| + | cmdbfQueryOperation.initialize(new SampleDataProvider()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Execute the query | ||
| + | Query query = retrieveQuery(); | ||
| + | cmdbfQueryOperation.execute(query); | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | </code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Assuming <code>retrieveQuery()</code> will return a POJO representation of a CMDBf query. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Registration === | ||
| + | The diagram below shows the relationship between the classes of the registration service. The APIs are very symmetric to the ones provided for the query service. An adopter will need to subscribe register handlers for specific MDR IDs. The subscribed register handlers will be invoked if the MDR ID of the registration request matches that of the ID associated with the handler. | ||
| + | |||
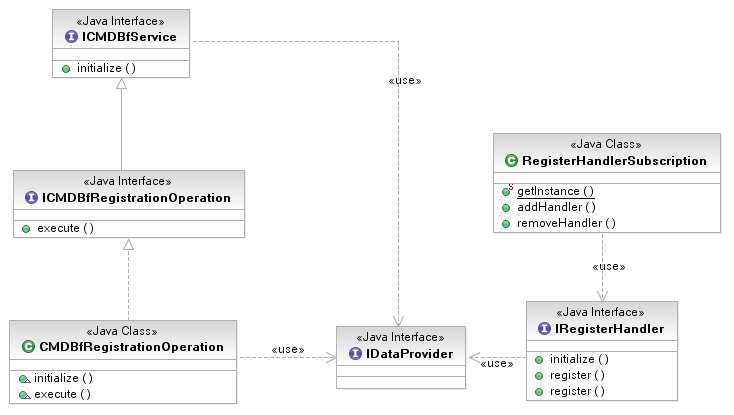
| + | [[Image:RegistrationService-v2.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The snippet of code below shows how a client can subscribe a registration handler. <code>CustomRegistrationHandler</code> is expected to be an implementation of <code>IRegisterHandler</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code> | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | RegisterHandlerSubscription.getInstance().addHandler | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | new URI("http://cosmos.org/mdrId"), | ||
| + | new CustomRegistrationHandler() | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | </code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The default implementation of <code>ICMDBfRegistrationOperation</code> can be used to process a registration request. The snippet below shows how a client can use the operation: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code> | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | // Perform the initialization | ||
| + | CMDBfRegistrationOperation registrationOperation = new CMDBfRegistrationOperation(); | ||
| + | registrationOperation.initialize(new SampleDataProvider()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Execute the operation | ||
| + | Registration registration = retrieveRegistration(); | ||
| + | registrationOperation.execute(registration); | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | </code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Assuming <code>retrieveRegistration()</code> will return a POJO representation of a CMDBf registration request. | ||
== ''' Test Coverage ''' == | == ''' Test Coverage ''' == | ||
| + | |||
Unit tests will need to perform the following tests: | Unit tests will need to perform the following tests: | ||
| − | * | + | * Transform a RegisterRequest POJO to XML and back to a POJO, and compare the start and end POJOs |
| − | + | * Transform a RegisterResponse POJO to XML and back to a POJO, and compare the start and end POJOs | |
| − | + | * Process an empty query | |
| − | * | + | * Processing a query with just one item |
| − | + | * Processing a query with a relationship and no items | |
| − | * | + | * Processing a query with matching items and an unmatched relationship |
| − | * | + | * Processing a query with matching items and a matched relationship |
| − | * | + | * Processing a query with a relationship that has cardinality |
| − | * | + | * Processing a query with unregistered selector handlers |
| − | * | + | * Processing an empty registration request |
| − | * | + | * Processing a registration request with one item |
| − | * | + | * Processing a registration request with matched items and missing relationship |
| − | * | + | * Processing a registration request with matched items and a relationship |
| − | * | + | * Processing a registration request with a relationship and no items |
| − | * | + | * Processing a registration request with missing registration handlers |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== ''' Task Breakdown ''' == | == ''' Task Breakdown ''' == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
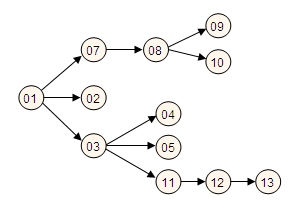
| − | + | The following section includes the tasks required to complete this enhancement <!--along with a PERT chart that displays the dependencies of each task-->. | |
| − | + | [[image:CMDBf-PertChart-v1.png]] | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # Refactor plugin, package and class names in cmdbf.query plugin to represent the 5 different jar configurations | ||
| + | # Refactor the JUnits for the query transformation | ||
| + | # Create graph representation of registration request and response | ||
| + | # Create the registration input transformer | ||
| + | # Create the registration output transformer | ||
| + | # Add in JUnits for the registration transformer | ||
| + | # Add in the APIs for processing a CMDBf query | ||
| + | # Implement a generic implementation of the CMDBf query processor | ||
| + | # Add in JUnits for the CMDBf query APIs | ||
| + | # Modify the SML repository to make use of the new API set | ||
| + | # Add in the APIs for processing a CMDBf registration request | ||
| + | # Implement a generic implementation of the CMDBf registration processor | ||
| + | # Add in JUnits for the registration APIs | ||
| + | |||
| + | == '''Open Issues/Questions '''== | ||
| − | + | All reviewer feedback should go in the [[Talk:COSMOS_Design_204959|Talk page for 204959]]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[Category:COSMOS_Bugzilla_Designs]] | [[Category:COSMOS_Bugzilla_Designs]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:22, 23 October 2007
Contents
Provide reusable CMDBf APIs for adopters that intend to provide a CMDBf query/registration service
Change History
| Name: | Date: | Revised Sections: |
|---|---|---|
| Ali Mehregani | 10/04/2007 |
|
| David Whiteman | 10/05/2007 |
|
| Valentina Popescu | 10/23/2007 |
|
Workload Estimation
| Process | Sizing | Names of people doing the work |
|---|---|---|
| Design | 1 | David/Ali |
| Code | 2 | David/Ali |
| Test | 1 | David/Ali |
| Documentation | 0.4 | |
| Build and infrastructure | 0.2 | |
| Code review, etc.* | 0.2 | |
| TOTAL | 4.8 |
Terminologies/Acronyms
The terminologies/acronyms below are commonly used throughout this document. The list below defines each term regarding how it is used in this document:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| MDR | management data repository |
| CMDBf | specification for a CMDB that federates between multiple MDRs[1] |
| federating CMDB | the CMDB that federates between MDRs, offering a common access point to clients and correlating identifying record data |
| CMDB | configuration management database |
| SML Repository | The SML Repository describes any SML model ( an SML model is a set of SML compliant resources ) together with a set of COSMOS API used to add new SML resources to the SML model and to query the SML model. |
| Query service | MDRs make data available to Clients via a Query service. Queries may select and return items, relationships, and/or graphs containing items and relationships. |
| Registration service | This service is used to register a set of supported items and relationships with a federating CMDB. |
Purpose
This enhancement is associated with bugzilla 204959.
The purpose of this enhancement is to refactor the CMDBf query code to make it more reusable. The SML repository already defines a set of APIs related to the CMDBf query. This set needs to be migrated to org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.query so that it can be reused by contributors who intend to provide a query service for a data provider.
Another purpose of this enhancement is to implement the registration transformation code, and provide reusable APIs for the CMDBf registration service.
This document will detail out the structure of the code and the minimum API set required to be implemented by contributors. The document will include code snippets to illustrate the simplicity in leveraging the available APIs. As part of the implementation of this enhancement the SML repository will be modified based on the refactored code. The set of classes provided in org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.query will be divided into the following sets:
- CMDBfCommon.jar
- CMDBfQueryTransformation.jar
- CMDBfQueryService.jar
- CMDBfRegistrationTransformation.jar
- CMDBfRegistrationService.jar
The CMDBfCommon module will include any code that will be required by two or more of the other modules. The dependency of the modules is discussed in more details under the 'Implementation Detail' section. The set included under CMDBfQueryTransformation.jar will contain any necessary code for clients who intend to build a CMDBf query and consume a query response. It performs the following transformations:
- CMDBf XML query document > POJO representation of the query
- POJO representation of the query > CMDBf XML query document
- CMDBf XML query response > POJO representation of the query response
- POJO representation of the query response > CMDBf XML query response
Adopters can choose to use CMDBfQueryTransformation.jar as is or have it tweaked based on their needs. What will be included in this jar file will be a concrete implementation of the transformations. Similarly, CMDBfRegistrationTransformation.jar will include a concrete implementation of the transformation required from an XML registration request to a POJO representation (and vice-versa).
CMDBfQueryService.jar will contain the necessary code for processing a query that conforms to CMDBf. This set will allow the user to provide implementation of selector handlers that are specific to a data provider. CMDBfQueryService.jar cannot be used as-is and will require a minimum API set to be implemented. Similarly, CMDBfRegistrationService.jar can be used by contributors to help in processing a registration request.
Requirements
The following is the list of requirements that this enhancement will address:
- Checking the conformance of a CMDBf query against its schema
- Checking the conformance of a CMDBf registration request against its schema
- Transformation of CMDBf XML query from/to a POJO representation
- Transformation of CMDBf XML registration from/to a POJO representation
- A common method of processing a CMDBf query
- A common method of processing a registration request
Implementation Detail
The plug-in org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.query will be refactored to org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services. The new plug-in will include a source folder for each of the modules mentioned earlier. The dependency of each module is depicted in the diagram below. The successive sections discuss the transformation and the processing APIs that will be included as part of this plug-in.
Transformations
Query
CMDBf specifies an XML-based syntax by which queries are submitted to the query service, which reports back a query result from the available MDRs, also using XML syntax. As part of our implementation of the query service, we internally accept POJOs to represent a graph of the query, and return the query result as a set of POJOs. The job of the transformers is to convert POJOs to and from the XML syntax detailed in the CMDBf specification.
As part of COSMOS Design 200222, a set of query transformations and an SML-repository-specific query service were designed and implemented. In an effort to make these components reusable, the query transformations will be refactored to share common components needed by other libraries in this design. The initial candidate classes to be moved to the common module are IXMLWritable, QueryServiceUtil (which will be renamed) and some of the fields in IQueryTransformerConstants (the ones pertaining to character constants and general SAX parsing).
In addition, the previously implemented packages will be renamed to include the word "provisional", which in the API contract specifications we are reusing from the TPTP project, indicates that the APIs are experimental and will be evolved into stable public APIs.
Here is a simple example that illustrates the incoming query input transformation:
InputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(example1().getBytes());
Query query = QueryInputTransformer.transform(inputStream);
Assume that example1() returns a String containing the XML syntax for a <query> as specified in the CMDBf spec.
Registration
CMDBf specifies a registration service by which MDRs register items and relationships with the federating CMDB. The process for registration involves an XML-based transaction, similar to how the query service works. This enhancement will provide a transformer to convert a registration request from XML to a POJO graph structure, and will also provide the reverse of that transformation. In addition, it will provide another transformer that will convert a registration response output by the MDR from a POJO graph structure to the XML-based syntax expected by the CMDBf spec, and will again provide a reverse of that transformation. The reverse transformations are needed by some clients of the registration service, and also are useful in unit testing of the implementation.
The following new classes will provide these transformations:
org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.RegistrationInputTransformer org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.RegistrationOutputTransformer
The following are the transformation APIs on the RegistrationInputTransformer class:
static public RegisterRequest transform(InputStream) static public InputStream transform(RegisterRequest)
The following are the transformation APIs on the RegistrationOutputTransformer class:
static public RegisterResponse transform(InputStream) static public InputStream transform(RegisterResponse)
RegisterRequest and RegisterResponse POJOs will consist of APIs and classes that match or closely mirror the corresponding element names in the CMDBf data model. RegisterRequest will reside in the org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.input.artifacts package and RegisterResponse will live in the org.eclipse.cosmos.dc.cmdbf.services.provisional.registration.transform.response.artifacts package.
Here is a simple example that illustrates the incoming registration input transformation:
InputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(example1().getBytes());
RegisterRequest registerRequest = RegistrationInputTransformer.transform(inputStream);
Assume that example1() returns a String containing the XML syntax for a <registerRequest> as specified in the CMDBf spec.
Services
Query
The class diagram below displays the interfaces and default implementations that will be included for the query service. All that a contributor is required to do is to register the classes that will be used as handlers for the selectors. The default implementation of the CMDBf query operation will look up the appropriate handlers and will invoke them accordingly.
The following is a snippet of code that illustrates how a contributor can register a set of selector handlers with the default implementation of ISelectorHandlerFactory.:
SelectorHandlerFactory.getInstance().addHandlers
(
new URI ("http://cosmos.org/mdrId"),
ISelectorHandlerFactory.ITEM_TEMPLATE,
new String[]
{
"org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.InstanceIdHandler",
"org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.RecordTypeHandler",
"org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.PropertyValueHandler",
"org.eclipse.cosmos.sample.handlers.XPath1Handler"
}
);
Once the selectors are registered a client can make use of the CMDBf query service using the default implementation of ICMDBfQueryOperation. The argument passed into the initialize method represents a data provider that will be passed to each of the selector handlers. The selector handlers can cast the argument to a specific type that can process native queries that is understandable by a specific data provider. The following snippet of code illustrates how the query operation can be invoked:
// Create a CMDBf query operation object and have it initialized CMDBfQueryOperation cmdbfQueryOperation = new CMDBfQueryOperation(); cmdbfQueryOperation.initialize(new SampleDataProvider()); // Execute the query Query query = retrieveQuery(); cmdbfQueryOperation.execute(query);
Assuming retrieveQuery() will return a POJO representation of a CMDBf query.
Registration
The diagram below shows the relationship between the classes of the registration service. The APIs are very symmetric to the ones provided for the query service. An adopter will need to subscribe register handlers for specific MDR IDs. The subscribed register handlers will be invoked if the MDR ID of the registration request matches that of the ID associated with the handler.
The snippet of code below shows how a client can subscribe a registration handler. CustomRegistrationHandler is expected to be an implementation of IRegisterHandler.
RegisterHandlerSubscription.getInstance().addHandler
(
new URI("http://cosmos.org/mdrId"),
new CustomRegistrationHandler()
);
The default implementation of ICMDBfRegistrationOperation can be used to process a registration request. The snippet below shows how a client can use the operation:
// Perform the initialization CMDBfRegistrationOperation registrationOperation = new CMDBfRegistrationOperation(); registrationOperation.initialize(new SampleDataProvider()); // Execute the operation Registration registration = retrieveRegistration(); registrationOperation.execute(registration);
Assuming retrieveRegistration() will return a POJO representation of a CMDBf registration request.
Test Coverage
Unit tests will need to perform the following tests:
- Transform a RegisterRequest POJO to XML and back to a POJO, and compare the start and end POJOs
- Transform a RegisterResponse POJO to XML and back to a POJO, and compare the start and end POJOs
- Process an empty query
- Processing a query with just one item
- Processing a query with a relationship and no items
- Processing a query with matching items and an unmatched relationship
- Processing a query with matching items and a matched relationship
- Processing a query with a relationship that has cardinality
- Processing a query with unregistered selector handlers
- Processing an empty registration request
- Processing a registration request with one item
- Processing a registration request with matched items and missing relationship
- Processing a registration request with matched items and a relationship
- Processing a registration request with a relationship and no items
- Processing a registration request with missing registration handlers
Task Breakdown
The following section includes the tasks required to complete this enhancement .
- Refactor plugin, package and class names in cmdbf.query plugin to represent the 5 different jar configurations
- Refactor the JUnits for the query transformation
- Create graph representation of registration request and response
- Create the registration input transformer
- Create the registration output transformer
- Add in JUnits for the registration transformer
- Add in the APIs for processing a CMDBf query
- Implement a generic implementation of the CMDBf query processor
- Add in JUnits for the CMDBf query APIs
- Modify the SML repository to make use of the new API set
- Add in the APIs for processing a CMDBf registration request
- Implement a generic implementation of the CMDBf registration processor
- Add in JUnits for the registration APIs
Open Issues/Questions
All reviewer feedback should go in the Talk page for 204959.