Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
User:Rick.barkhouse.oracle.com/VTD
VTD-XML Investigation
VTD-XML (http://vtd-xml.sourceforge.net/) is a high-performance XML processing model that deals with XML in a binary form, instead of the traditional text form. VTD stands for Virtual Token Descriptor.
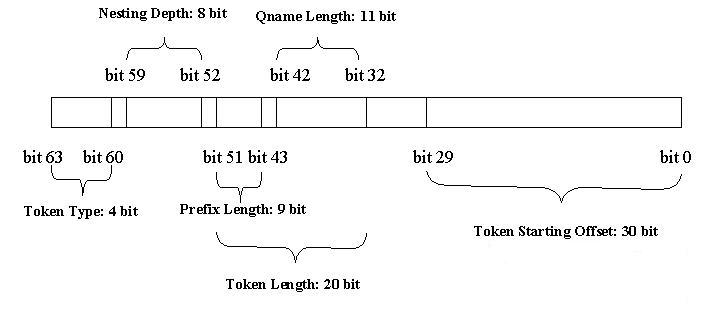
VTD-XML parses an XML document and builds an internal data structure representing the entire XML document in byte[] form. Each "token" of the XML document is represented as the following 64-bit integer:
- It is a binary format specification, not an API specification
- A VTD record is a primitive data type (integer multiple of 32 bits) that encodes the following parameters of a token in an XML file:
- Starting offset
- Length
- Nesting depth
- Token type
- VTD requires that XML document be maintained intact in memory.
- Our current VTD record layout further specifies the following:
- Use 64 bits as the primitive type (b63~b0)
- Big endian
- Starting offset: 30 bits (b29 ~ b0) maximum value is 2^30 -1 = 1G -1
- Length: 20 bits (b51 ~ b32) maximum value is 2^20-1 = 1M -1
- For some token type
- Prefix length: 9 bits (b51~ b43) max value 511
- Q-name length: 11 bits (b42 ~ b 32) max value 1023
- For some token type
- Depth: 8 bits (b59~b52) max value is 2^8-1 = 255
- Token type: 4 bits (b63~b60)
- Reserved bit: 2 bits (b31: b30)
VTD-XML Core Concepts
Unmarshalling a VTD-XML document
VTDGen vg = new VTDGen(); // from existing byte[] // true indicates namespace aware vg.setDoc(byte[]); vg.parse(true); // - or - // from file vg.parseFile("old.xml",false)