Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EclipseLink/UserGuide/MOXy/Relationships/Privately Owned/One-to-One"
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{EclipseLink_MOXy | {{EclipseLink_MOXy | ||
Revision as of 10:47, 6 January 2011
EclipseLink MOXy
| EclipseLink | |
| Website | |
| Download | |
| Community | |
| Mailing List • Forums • IRC • mattermost | |
| Issues | |
| Open • Help Wanted • Bug Day | |
| Contribute | |
| Browse Source |
Mapping One-to-One Relationships
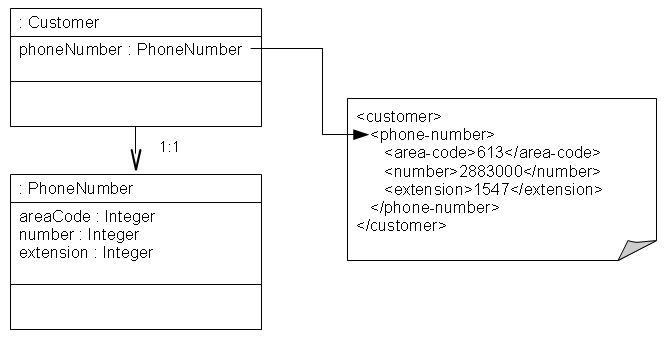
This section demonstrates several ways to map a one-to-one relationship between objects.
Mapping to a Complex Type
Given the XML schema in this example, the figure below illustrates a one-to-one relationship between two complex types.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:element name="address" type="address-type"/> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:complexType name="phone-type"> <xsd:element name="area-code" type="xsd:int"/> <xsd:element name="number" type="xsd:int"/> <xsd:element name="extension" type="xsd:int"/> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
The following example shows how to annotate your Java class to obtain this mapping with EclipseLink. All that is needed is the standard JAXB @XmlElement annotation.
@XmlRootElement @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) public class Customer { @XmlElement(name="phone-number") private PhoneNumber phoneNumber; ... } @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) public class PhoneNumber { @XmlElement(name="area-code") private Integer areaCode; private Integer number; private Integer extension; ... }
The example below shows how to to define your mapping information in EclipseLink's OXM metadata format.
... <java-type name="Customer"> <xml-root-element name="customer"/> <java-attributes> <xml-element java-attribute="phoneNumber" name="phone-number" type="PhoneNumber"/> </java-attributes> </java-type> <java-type name="PhoneNumber"> <java-attributes> <xml-value java-attribute="areaCode" name="area-code" type="java.lang.Integer"/> <xml-value java-attribute="number" type="java.lang.Integer"/> <xml-value java-attribute="extension" type="java.lang.Integer"/> </java-attributes> </java-type> ...
"Self" Mappings
EclipseLink allows you to configure your one-to-one mapping such that the data from the target object will appear inside the source object's XML element. Using the example above, this means that the "PhoneNumber" information would appear directly under the "customer" element, and not wrapped in a "phone-number" element. This is referred to as a "self" mapping, and is achieved by setting the target object's XPath to "." (dot). The following example demonstrates a self mapping declared in annotations.
@XmlRootElement @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) public class Customer { @XmlPath(".") private PhoneNumber phoneNumber; ... } public class PhoneNumber { ... }
The example below shows a self mapping defined on EclipseLink OXM metadata format.
... <java-type name="Customer"> <xml-root-element name="customer"/> <java-attributes> <xml-element java-attribute="phoneNumber" type="PhoneNumber" xml-path="."/> </java-attributes> </java-type> <java-type name="PhoneNumber"> ... </java-type> ...
Using a self mapping, the following XML will be produced:
<customer> <area-code>613</area-code> <number>2883000</number> <extension>1547</extension> </customer>